Runny nose in infants (1 month): treatment. Treatment of rhinitis in a month-old baby
Any age - this is a very common phenomenon. According to pediatricians, it is not necessary for each symptom of a cold to seek medical help and give drops to the child. Runny nose can be different, as well as treatment. Let's talk about the main causes and symptoms of a runny nose in infants at 1 month. What is the treatment of rhinitis in infants in 1 month? How does the famous doctor Komarovsky advise treating the runny nose in infants?
Anatomy of the nasopharynx in children
In babies, the nasopharynx and sinuses are different from adults. For several years after birth, the nasopharynx will still develop, grow in size and change its structure. When air enters the nasal sinuses, it goes through 3 stages:
- Cleansing;
- Heat;
- Moisturizing.
A small child has 2 nasal passages - upper and middle, and lower (which every adult person has) - is absent. The lower nasal passage in small children will be formed only in 4 years. It is the absence of the lower nasal passage and the physiological inability of the paranasal sinuses to cope with the cleansing, heating and humidification of the air lead to permanent (runny nose) in babies.
Before you begin to treat a child’s runny nose (and you need to treat it), you need to understand the reason for it.
Causes of rhinitis
Virus
Viruses are the first and most common cause of the common cold in children, both at 1 month and 5 years. In this case, your child is diagnosed with an acute respiratory viral infection by a pediatrician and prescribes further treatment.
Bacteria
Bacteria, streptococcus and others can penetrate the mucous membrane of the nasal passages. It is she (the bacterium) that provokes the development of a viral-bacterial infection.
Cold
If the child is overcooled, the risk of a cold is very high. Due to hypothermia in the child, the temperature regulation of the vessels in the nasopharynx is disturbed. That is, in simple words, blood circulation is initially disturbed, and this process is followed by a runny nose.
Allergy
A child at 1 month of age may develop an allergic reaction to external adverse factors that surround it. In particular, it is a dusty room, inadequate food (infant formula), household chemicals of aggressive impact.
Injury
Mechanical damage to the nasopharynx - a blow to the nose, a cut, a scratch in the nose provokes a runny nose. Also, as instillation into the nose of unsuitable drops (for example, containing alcohol).
Symptoms
A child has a runny nose with swelling of the mucous membrane of the nasal passages and the release of large amounts of mucus / sputum. With a cold, a child sniffles, cannot breathe, often opens his mouth and breathes through his mouth.
In infants in 1 month runny nose can lead to a deterioration of the general condition of the body. Because the kids at that age still do not know how to breathe through their mouths and, as a result, because of the "clogged" nose they lack oxygen. Also, parents should understand that a child at that age does not know how to blow out mucus from the nose, therefore, he (the baby) needs help in every way. To do this, you can use the most common aspirator Otrivin Baby or a syringe (in the absence of other devices).
The air that the sick child breathes must be clean, humid, cool. Regardless of what the cause of a cold baby, his nasal sinuses will be inflamed.
Treatment of rhinitis in Komarovsky
A child has viral rhinitis if: the mucus in the nose is clear, it is difficult to breathe through the nose, the body temperature is elevated; bacterial rhinitis, if: snot is green or yellow, nose is stuffed up, temperature is high; allergic rhinitis, if the body temperature is not elevated, the general state of health is not worsened, breathing is frequent, and the nose is plentiful.
The main thing that needs to be done at the first stage of the treatment of rhinitis is to prevent the mucus in the nose from drying out.
To do this, we clean the air, often ventilate, do wet cleaning. A child needs to be watered a lot and constantly. Drinking should be excessive in order for the body to be able to recover. You can drink with ordinary warm water, compote, herbal tea, raspberry tea.
Important! In no case do not allow dehydration in a child with a cold.
Signs of dehydration will be: severe thirst, dry skin, dry mucous membrane, infrequent urination in a child (look at diapers), urine has a yellow color. With these symptoms, you should give the child water as often as possible.
Sinus cleansing
Komarovsky says the importance of cleansing the nasal passages in infants during a cold. The mucus can be removed in several ways: remove the needle from the syringe and with this tool gently draw the mucus. A more civilized way is to clean the mucous membrane with the help of aspirators - they are sold in the form of a pear, or pay attention to the simple aspirators of Otrivin Baby.
Rinse the nasal sinuses can be normal saline sodium chloride (sold in a pharmacy, is inexpensive). Bring several drops of saline into each nasal passage every 15–20 minutes. The mucus will be moistened and easier to move away from the nose. An alternative to saline can be:
- Aquamaris;
- Dolphin;
- Rizosin;
- Fluimarin;
- Hoomer spray.
Oil drops
Oil drops are needed to moisturize the mucous membrane of the nasal sinuses, preventing them from drying out. But, as Komarovsky says, it is better to avoid this stage of treatment and get along with the usual saline solution and the observance of optimal air temperatures in the room. It is not necessary to apply expensive nasal drops, you can do with an oil solution of vitamin E and A, olive oil, liquid paraffin. It is necessary to use such drops 4 times a day. Pharmacy oil drops: Menthol, Pinovit, Pinosol, Sinusan, Chlorphyllipt, Eucasept,
Applying a more serious treatment in the form of vasoconstrictor drops for infants at 1 month is not recommended, as they affect the heart and blood vessels (which is undesirable for a child). But, nevertheless, doctors often prescribe Nafazolin, Naphthyzinum, Sanorin, Nasol Bebi, Nasol Kids, Tizin, Bourdnil, Otrivin, Rinonorm, Rinostop, Galazolin, Xylen, Tizin Xylo, Sanorinchik, Fazin.
Conclusion: treatment of rhinitis in infants depends on the cause - the virus, bacteria, hypothermia, an allergic reaction. Once the cause is established, you can begin treatment. The main recommendations of treatment are: compliance with the temperature regime (cool air in the room, humidity 75%), abundant drinking, moisturizing and cleansing the nasal passages with saline, moisturizing with oil droplets.
For each age is characterized by certain difficulties and diseases. The peculiarity of the chest period is the high risk of complications and difficulties in diagnosing diseases. Due to the fact that the child cannot talk, we are not always able to understand what is bothering him. In this regard, only a pediatrician through a full examination can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. A runny nose in a month-old baby is not always a sign of the disease.
The fact is that in an infant in the first month of life, the mucous membrane of the nasal cavities continues to develop, like other structures of the body. Due to physiological restructuring, the mucosa adapts to new living conditions, as it is subjected to constant attack by microbes and irritating environmental factors (dust, smog).
As a result, increased mucus production can be observed, which parents perceive as a manifestation of rhinitis. In fact, this condition is called physiological rhinitis.
What triggers the appearance of snot?
A runny nose in infants often has a physiological origin, but the development of a runny nose is possible due to factors such as:
- infectious pathogens. Despite the protective immunoglobulins circulating in the baby’s blood, there is still the possibility of infecting the baby through injured nasal mucosa or against the background of immunodeficiency;
- allergens. Among the frequent allergic factors is to provide pollen, animal hair and hygiene products;
- environmental factors such as dry, dusty air. By irritating the mucous membrane of the nasal cavities, the dust provokes an increase in the production of mucus. In addition, overdrying the mucous makes it more susceptible to infection. Most often, dry air is in children's rooms, which parents warm up intensively for fear of hypothermia children;
- low temperature. Prolonged inhalation of cold air or general freezing is fraught with a cold. Against its background, one nasal passage may be laid first, then the second.
The presence of narrow nasal passages in infants leads to a rapid cessation of breathing, even with a slight swelling of the mucous membrane.
Symptoms of rhinitis
When a child suffers from a cold, the main task of parents is to timely detect the first signs of the disease. For rhinorrhea in the first days of the disease is characterized by transparency and watery consistency. In this form, snot persist for 3-4 days.
After this, the discharge becomes thicker, with a yellowish tinge, which indicates the beginning of the last stage of the common cold. If a sufficient level of immunity is present, the disease ends with recovery after 10 days from the appearance of the first signs.
There is one difference between allergic rhinitis - watery rhinorrhea throughout the course of the disease.
The snot in a month-old baby is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- difficulty breathing through the nose, which causes the newborn to breathe through the mouth, and shortness of breath appears. In doing so, breathing can become wheezing;
- dry mouth;
- capriciousness, anxiety;
- poor sleep;
- breast failure;
- digestive disorders. The appearance of diarrhea may be due to the ingestion of a large amount of air during feeding.
In allergic rhinitis, tearing, swelling of the lips, eyelids, itching of the nose, eyes, conjunctival hyperemia, sneezing and cough may be observed. If the baby does not help in time, the risk of complications increases. Highlight the most frequent:
- sinusitis. Without treatment, mucus can accumulate in the paranasal sinuses, which leads to its infection and inflammation of the mucous cavities;
- otitis. In children, the auditory tube has a smaller diameter than in older age. As a result, even a small swelling of the mucous membranes can disrupt the air conduction and sanitization of cavities, which predisposes microbial reproduction. Otitis shows a decrease in auditory function and ear pain. The kid tries to lie down on the inflamed ear to relieve pain;
- pharyngitis. Often with rhinitis redness of the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall is detected, which indicates the development of pharyngitis;
- hypotrophy (weight loss) - observed on the background of malnutrition;
- convulsions - may be the result of high hyperthermia and dehydration;
- bronchospasm - develops due to prolonged exposure to allergic factors.
When inflammation spreads to the lower respiratory tract, the risk of laryngitis and bronchitis increases. A serious complication is stenosing laryngitis, which develops due to severe swelling of the laryngeal mucosa and vocal cords. Symptomatically, the pathology is manifested by hoarseness, barking cough and severe shortness of breath.
How to help the child?
In 1 month the use of folk remedies is not recommended. The mucous membrane of the nasal cavities is so thin and sensitive that the aggressive action of vegetable juices or aloe can lead to increased rhinorrhea. The treatment is carried out after consulting a pediatrician. Only a specialist can objectively assess the severity of the condition and prescribe the necessary medications permitted to infants.
If you suspect a complicated course of rhinitis, the doctor may suggest hospitalization. The child should be under medical supervision so as not to aggravate the course of the disease. If home therapy is allowed, a regular examination by a physician is required to analyze the dynamics of treatment and the correction of medical prescriptions.
To cure rhinitis, it is not enough to use drugs. A prerequisite is compliance with the regime:

As for drug therapy, it is not recommended for newborns. Purification of the mucous can be done with saline and saline solutions, for example, Aqua Maris. After instillation of the nose with these preparations, it is necessary to remove mucus using a special aspirator or a small syringe.
Remember, the introduction of the solution into the nasal cavity under pressure is prohibited.
In rare cases, the doctor may prescribe antiviral, antihistamine or vasoconstrictor drugs. Independent use of the listed drugs is not recommended, as they have side effects. Do not neglect preventive measures, and then your child will be healthy.
Good afternoon, dear readers!
I am always glad to welcome you on the pages of my blog!
An infant is a miracle that pleases its parents with every movement and every sound. However, such babies are haunted. In this article you can read why a snot appears in a month-old baby and how to act in such a situation.
A runny nose in an adult is not considered to be a disease. However, for a small baby, the appearance of snot is a big problem that parents do not easily cope with on their own. When a runny nose appears in a baby, it is necessary to consult a doctor!
Snot is the release of fluid from the nose of a baby of various texture and color.
- viruses
- bacteria
- physiological secretions (according to some pediatricians, a child under 2.5 months “tests” the environment with a spout)
- overheating
- hypothermia
- foreign bodies
- when feeding, it can choke with mom’s milk or mixture. They pass through the nasopharynx into the nose and can be excreted in the form of a thick, whitish or yellowish liquid.
Consider each cause of rhinitis in infants in more detail.
From the point of view of pediatricians, a runny nose in a baby occurs most often due to a weakened immunity. The body of a small baby does not yet have strong resources to resist the pathogenic bacteria, which very quickly penetrate the mucous membrane of the children's nose.
Given the fact that newborns have very short and narrow nasal passages, then a small number of viral pathogens is enough for the onset of a runny nose and the development of inflammation of the nasal mucosa. Many mothers notice that the snot in crumbs appeared after visiting relatives or friends. Very often, older children bring viruses and bacteria from kindergarten.
A runny nose in infants can occur as a result of overheating, in which there is heavy sweating, and the immature body of the crumb loses a large amount of moisture, the protective function of the immune system weakens.
The process of hypothermia also affects the baby’s immunity and can trigger the development of viral infections.
If children's rhinitis is a manifestation of an allergic reaction of the body to some foreign protein, then, as a rule, it is accompanied by itching and redness of the skin and sclera, tearing, swelling of the face. In such situations, the baby constantly scratches his eyes and nose with his hands and sneezes. With allergies, as a rule, the nose is blocked or clear snot is released.
In some children, there may be such cases when a runny nose is caused by a small foreign body in the nose. Little children are very curious and can put a small bead in their nose while playing. A child of one month of age alone can not shove anything into his nose, his fine motor skills of his fingers are not yet developed.

Such a “good deed” can be done by elder brothers or sister, so parents should not be left unattended with a month-old child. A foreign body in a small nose can disrupt the nasal breathing, cause severe discomfort in the crumbs, irritate the nasal mucosa, but most importantly, it can descend into the lower respiratory tract and cause bronchoabstruktsiyu or bronchospasm.
How is the runny nose in infants
Symptoms:
- the baby begins to breathe through the mouth, breathing, usually "sniffling"
- the baby has an unpleasant burning sensation in the nose, due to the constant drying out of the delicate nasal mucosa, so it becomes restless
- usually after 3 or 4 hours after the swelling of the nose, a clear liquid appears in the baby from the nasal passages
- mucous discharge from the nose, the child becomes moody and restless, refuses breast
What happens if the baby has a cold?
Complications of rhinitis:
- sinusitis
- infectious lesion of the larynx and bronchi
- adenoid inflammation
- respiratory failure leads to the development of oxygen starvation in a young child
What to do if a child has a stuffy nose and a runny nose?
Parent Tactics:
Treatment of folk remedies of rhinitis in a month-old baby without examination and recommendations of the pediatrician is prohibited.
If any nasal discharge or congestion occurs, you should immediately contact your local pediatrician, who will find out the cause and give recommendations on how to cure a cold. If within a few days or a week the snot has become more dense and green, then in this case the ENT doctor should treat the child.
- more often air the room where the baby is
- humidify the air in the nursery
- restrict visiting relatives and friends
- if the eldest child in the family has a viral illness, then it is best to isolate it from the baby (for example, let her stay with her grandmother for some time)
- if the runny nose is accompanied by even a slight increase in the baby’s body temperature, then it is recommended to give the baby more and more frequent drinking of ordinary boiled water from a bottle
- do not feed the baby forcibly
- more often take the baby
- talk gently and gently with the baby
- the child can not cope with the cold, so you need to buy a good suction pump.
- it is impossible to prevent the drying of the crusts in the baby's nose, so it is recommended to instill 1 drop of 0.9% saline sodium or gently lubricate the crumbs of sea buckthorn oil with each nostril
- try to give him a breast or a few drops of expressed breast milk (we must not forget that breast milk contains useful antibodies and immunoglobulins that will help the child cope with the infection).
Drug medications should be prescribed only by a pediatrician, it is not recommended to use them yourself on the advice of a friend or grandmother.
You can not bury a child of a month of age in the nose juice of aloe, beets or carrots, otherwise you can burn the delicate nasal mucosa of the baby.
You should not use the information of various forums on Internet sites, only the doctor must determine how to treat the runny nose in your baby.
Medications
Pediatricians, depending on the cause, which caused a runny nose in a month-old baby, prescribe the following groups of medications:
- vasoconstrictor
- antibacterial
- antiviral
- antiallergic
- sprays and washing solutions
To grow a healthy child, you must always read a lot of information about children or use training video courses, for example, a free webinar “ A child from birth to one year»
I hope this information is useful to you! I will be glad if you share this article on social networks and tell your relatives and friends about it! Subscribe to our blog updates! See you again!
A runny nose, accompanied by nasal congestion or, conversely, an excess of mucus is a very unpleasant phenomenon for an adult, and even more for a helpless baby. The situation is aggravated by the fact that the baby is constantly in a horizontal position and mucus from the nasal passages can flow into the nasopharynx causing a reflex cough.
In addition, children of the first months of life feed exclusively on milk, and the absence of nasal breathing makes this process much more difficult. A child may become moody, irritable, and completely refuse breastfeeding, which does not contribute to recovery, as babies receive immune cells with mother's milk for up to half a year, allowing them to transfer the disease faster and without complications.
However, a runny nose - a runny nose, and often young parents mistaken for rhinitis completely natural processes of nasal mucus from babies. That is why, before starting treatment, you should contact a pediatrician who determines the nature of the common cold, its cause, and only then makes appointments.
The secretion of mucus from the nose is a completely normal process, allowing you to get rid of dust, small particles and infections that enter through the nasopharynx during breathing. The secret secreted by the nasal mucosa contains mucin - a special protein capable of resisting viruses and bacteria. But the protein quickly loses its properties and with an excess of infection there is a need to constantly update it. That is why in respiratory diseases mucus from the nose is excreted in excessive amounts, which is called a rhinitis.
Before birth, the child is surrounded by amniotic fluid, and there is no need for nasal mucus, just like the mucosa itself. And only after birth, in the first month of life, the nasal mucosa begins to form, and with it the first discharge of a transparent character appears. Naturally, the process of secretion is not yet regulated by the body and in the first month a newborn gets a physiological rhinitis, which does not carry the danger of viral or bacterial diseases and does not require treatment. However, this does not mean that you need to let everything go of course and wait for the baby to cope on his own, since excess secrets can create difficulties of nasal breathing. Parents should clean the nasal passages with a cotton wool moistened with boiled water twice a day and, if necessary, do it more often.
In the event that a newborn, in addition to heavy discharge from the nose, is worried about coughing, fever, lack of appetite, the baby should be shown to the doctor.

Pathological
Also read:
The immune system of the newborn is not yet formed, the baby received a part of the protective cells at birth from the mother, and also constantly receives from breast milk, but even such immunity does not protect infants from viral and bacterial diseases, especially in the first month when the child is especially weak. The first manifestations of viral diseases in most cases are expressed in the form of rhinitis. The snot in a newborn with a cold appears in the form of heavy discharge of a transparent color, but unlike the physiological rhinitis, the general condition of the child indicates the disease. If not treated, or do it wrong, it can in a few days go into a bacterial cold, because the dried crust on the mucous membrane is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria.
The symptoms of bacteria being added to viruses are discoloration and consistency of discharge - snot becomes thick and becomes yellow or green.
Another reason for the common cold from which the baby is not insured, even if he is only one month old is allergic. Allergic rhinitis in a newborn is accompanied by sneezing, swelling of the face, eyelids, lacrimation, and the baby can often sneeze. In case of allergic rhinitis, sometimes it is enough to remove the cause of its occurrence - an allergen, as an illness passes without the use of drugs.
The cause of rhinitis can be determined by symptoms and a good pediatrician will make a diagnosis based on the results of the examination, however, in case of a long runny nose, mucus analysis should be performed. The analysis is quite simple and its results are based on the fact that the composition of the mucin varies depending on which infection or allergen threatens the body. So, in case of allergy in the nasal mucus, a large number of eosinophils is determined, if the cause of the common cold virus is leukocyte prevails, and in case of bacterial infection, neutrophils are detected. In this way, the results of the analysis will show the cause of rhinitis, which will allow the doctor to correctly prescribe treatment.
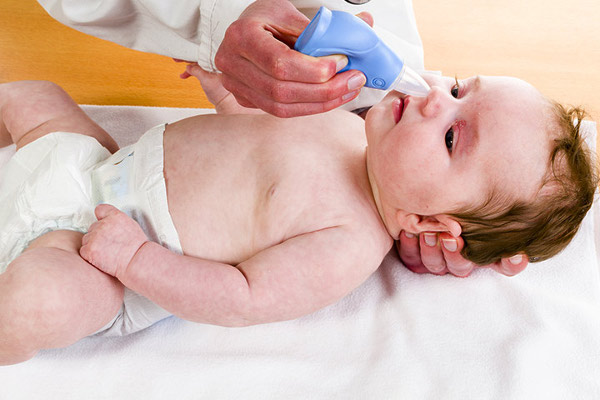
How to treat snot in an infant
In 80% of cases is of viral origin. Treat such a runny nose to children, no matter how old they are - 1 month or year, you need to be timely and very carefully. The doctor may prescribe treatment, which includes cleaning the nasal passages, irrigation of the mucous membranes, maintaining the indoor climate.
To remove the accumulated mucus, since the baby does not have the skills of blowing your nose, a baby aspirator is used - a rubber bulb with a thick plastic tip to collect mucus. It is necessary to apply it extremely carefully, not leaning against the walls of the mucous membrane, otherwise the vacuum created by squeezing the aspirator can damage the system of small vessels of the baby’s mucous and the rhinitis will become chronic.
After the nose is clean, the mucous membrane is moistened, irrigating with special preparations intended for newborns, for example, Otrivin, Salin, Aqualor, Nosol, or with a simple saline solution. Moisturizing of the mucous is necessary so that the crusts do not form, and the mucosa itself does not crack.
To treat a baby from a cold is to help him, to cope with the natural process of the body's fight against the virus. To do this, create a climate in the room where the baby is. The air should be fresh, humid, and the temperature should not exceed 21 degrees. Also, the baby should be given a warm drink.
Under such conditions, the mucous will not dry up, mucin, counteracting microbes and viruses constantly updated, and a runny nose in a few days.
If an edema of the mucous membrane occurs, which is accompanied by difficulty in breathing the newborn, the doctor prescribes treatment with vasoconstrictor drops. Medications such as Nazivin, Farmazolin, Nazol, relieve a symptom, but do not eliminate the cause, and they also have many side effects. If you treat the baby with such drugs for more than 5 days, you can provoke the insensitivity of the blood vessels, and the edema will be aggravated. In case of mucosal swelling due to allergy, it is better to treat with a drug such as Vibrucol, which, in addition to vasoconstriction, is an antihistamine drug.
In newborns, it is necessary to use all the same prescriptions and to add nasal drops with an antiseptic effect. Protargol (with liquid discharge from the nose) or Albucidum is prescribed most often. Pinosol acts more gently, but it is strongly not recommended to treat it to the newborn in the first month, like other oil-based drugs because of the risk of oil entering the bronchi. For the same reason, you should not use drugs in the form of a spray or aerosol, for children under one year only a drop.
The action of a narrow-spectrum antibiotic is more precisely directed to a certain type of bacteria. However, both antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed only by a doctor after an accurate diagnosis - a bacterial rhinitis, it is not only useless to use them in case of viral or allergic rhinitis, but also dangerous. Self-treatment of a runny nose in a baby with potent drugs, such as antibiotics, antiseptics, glucocorticosteroids, vasoconstrictor and immunostimulants, is strictly prohibited.
Quite often, young mothers are perplexed: crumb on breastfeeding, but still he has sopelki, and even a cough. Doesn't mother's milk help to develop immunity?
In fact, an indicator of good immunity is not the absence of diseases, but the ability of the body to respond to them correctly. In the urban environment, the baby is faced with a huge number of viruses, even if only dad goes to work and the grandmother sometimes comes to visit. And what about the crumbs, if his older brother attends a kindergarten or school? And if the baby with his mother go to transport? It is quite normal in such a situation, no, no, yes, and to be inundated. If a runny nose runs easily, without fever, without complications - this is an indicator, and this is not bad - so modern pediatricians believe.
There are several types of rhinitis.
Infectiouscaused by viral or bacterial infection.
Allergic, Respectively, allergens, in babies mainly food. In this case, both nose and eyes “flow” - you need to consult a children's allergist.
Vasomotor runny nose associated with vascular problems in children is rare. To diagnose and treat it should a pediatrician or pediatric ENT doctor.
Runny nose caused by other causes - a foreign body in the nose, etc.
Of course, the most common infection is a runny nose, and this is how you should behave if your baby has soops.
Strategy for nose
In general, the secretion of mucus from the nose is a normal protective reaction of the body. If a baby has transparent light nozzles that do not obstruct breathing (a child can safely take a breast or suck a finger, do not try to breathe through his mouth) - do not worry and try to eliminate them. You just need to keep an eye on the baby and help the body fight: more often apply the baby to the breast, wipe the nose, gently if it is abundant.
In any disease state, it is necessary to facilitate the diet of the crumbs. If he gets complementary foods, do not force him to eat, - let him stay for some time only on breast milk. Artificial children also need to be fed with a “lighter” food.
Often on the second or third day, the mucus in the nose becomes thick, yellowish or greenish. If its volume decreases and there are no problems with breathing, we continue the same tactics. But if the nose is obviously stuffy, the runny nose is tightened and strengthened, which means that there is an active growth of the bacterial flora, the baby does not cope, and he needs help.
It is not necessary for children under 6 months to use vasoconstrictor drops - this is harmful for the delicate mucous membrane of the baby’s nose.
Much more correctly - use salted water for disinfection and cleaning of the nose (1 teaspoon per glass of water). Salt thins mucus and washes it off. There are ready-made preparations based on salt water - Aquamaris (drops and spray), Fiziomir Beybi (spray), Fiziomir Marimer, Aqualor. By all these means you need to help your child ease breathing.
For the children of the first half of life, it is preferable to use sprays, rather than drops. The fact is that the anatomically structure of the nasopharynx of the baby differs from that of an adult. In crumbs, if explained “on the fingers”, the nose and ears are quite close, but the nasal sinuses are not developed. Accordingly, washing the babies is not only meaningless (there is no mucus in the closed sinuses), but it is also dangerous - it is possible to provoke an infection of the ears.
If the runny nose is inhibited, the discharge is bulky, thick, green, the infection causes discharge from the eyes - self-treatment should be stopped and the doctor should be consulted, as the situation has become complicated. There are sparing antibacterial sprays, as well as homeopathic medicines, but they should be prescribed by a doctor as a baby.
What are the risks of such prolonged rhinitis? First of all, . An ENT specialist or pediatrician who owns an otoscope (a flashlight with a funnel for examining the ears) will first of all check the ears of the crumbs. Mom may suspect that something is wrong, if the baby, which has cleared the nose, still throws his chest, barely starting to suck - perhaps it is hampered by pain in the ear. People's way to "click on the trestle of the ear," to see if there is inflammation, can not be compared in diagnostic accuracy with the otoscope. With severe purulent otitis, the baby really hurts if you put pressure on the tragus - and in this case, you should literally run to the doctor. However, if the inflammation is only at the beginning of the auditory tube, the child will not react to pressure, although it is time to heal - and certainly with the help of a doctor.
Baby problems
Babies may have several "special" types of rhinitis, which are not found in older children.
At 2-3 months, the kids have wheezing, sort of "grunting" somewhere between the nose and throat, which scares the mother. Give the baby a chest and check the reaction. If the "grunts" disappeared - do not worry. The fact is that when regurgitation occurs, part of the gastric contents gets into the posterior nasal passages and continues to be digested there. As a result, such a grunting curd is formed in the baby's nasopharynx, usually a small amount of it is contained in the discharge from the nose. It is not dangerous for the health of the crumbs.
A special type of rhinitis - the so-called "tooth snot." When a baby's teeth erupt, especially the upper ones, this is often accompanied by nasal discharge. However, if the baby's temperature rises and the general condition worsens - consult a doctor.
At 1.5-2 months, mothers sometimes worry about a false rhinitis. At this age, the salivary glands are very active in the baby, the baby “blisters” - and even from the nose, it can even cough up, because periodically choking them. If in general the baby is cheerful and happy, then there is no need to worry about nasal discharge.
Urgent medical consultation is required if:
- runny nose, discharge from the nose prevent breathing and sucking;
- the baby becomes restless, throws the chest;
- wheezing goes down "below the throat," the cough does not look like "choked on saliva."
In other situations, you can cope with a runny nose with improvised means.
Babina Anna
Consultant: Olga Ivanovna Tkach,
head of pediatric department
"Center for Traditional Obstetrics"
Popular
- How to treat streptococcal infection
- How to bury drops in the ears: the algorithm and technique of instillation in a child and an adult
- Causes of sore throat if the tonsils are removed
- Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, or what is sinusitis
- Consequences of angina in the form of cough
- Sharp severe sore throat
- Why itches and itches inside the nose
- Funds from the arsenal of traditional medicine
- Stomach discomfort: causes, symptoms, treatment
- Otitis - folk remedies and prescriptions for treatment of otitis media at home