Pain in the ear when pressing on the tragus. Inflammatory diseases of the external auditory canal and methods of their treatment
External otitis - it is an inflammation of the outside auditory canal. This disease is not very serious and painful, like inflammation of the middle ear. In some cases, it goes away by itself, without any treatment, sometimes it is necessary to help a little with the recovery.
External otitis is of two types:
- Limited - in this case, inflammation occurs due to the formed abscess inside the ear canal. At the same time, a person experiences pain, which disappears after the opening of the abscess and the release of pus from it.
- Diffuse - in contrast to limited otitis, the inflammatory process captures the entire auditory canal, and not just a small surface with an infection site located on it.
Why does external otitis appear?
In the case of limited otitis, the cause is inflammation of the hair follicle, as a result of which the furuncle develops. This process is no different from the development of a boil on any other part of the body (for example, see).
The appearance of diffuse otitis guilty:
- staphylococcus;
- streptococci;
- allergic reaction;
- fungal infection.
There are also several factors contributing to the development inflammatory process in the external auditory canal, namely:
- Sores and scratches in the ear canal. They appear due to mechanical damage to the epithelium (when trying to clean the ear with some hard objects, such as a toothpick or a match) or eczema, causing peeling of the skin in the ear and the appearance of sores.
- Prolonged presence of water in the ear canal. This happens in swimmers or in people with sulfur plugs in ears that interfere with the normal outflow of fluid after bathing. The skin in the ear canal has a protective layer that prevents the development of infection. However, if water is constantly in the ear, this layer disappears, and beneficial conditions for the pathogenic microflora appear.
Manifestations of otitis externa
Restricted and diffuse otitis have their own symptoms, but should consider the general manifestations of the disease, which can be observed with any type of otitis:
- Eternal pain in the ear.
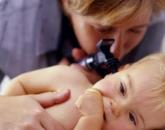
- Increased pain when trying to pull off auricle back or click on the cartilage near the ear canal (it is called the tragus).
- Increase lymph nodes near the ear.
- Swelling of the ear canal.
- Hearing impairment. Typically, this symptom occurs with otitis media, if the boil closes the ear canal and this reduces hearing.
- Itching in the auditory canal. As a rule, this phenomenon is most often observed with otitis of fungal origin. Itching can also be caused by eczema.
With limited otitis, there are specific signs:
- At the onset of the disease, the pain is pulsating. At this time, just the maturation of the abscess. The pain is especially strong when chewing, when trying to delay the auricle or to press on the tragus.
- Puffiness and reddening are observed only on one side of the external auditory canal, in the place of furuncle maturation.
With diffuse otitis, the pain is not as strong as with limited, and it is often replaced by itching. The auditory canal is inflamed and swollen all over, and not just on one side. Since the disease, in most cases, causes an infection, it can easily spread to eardrum. In this case, the person observed discharge from the ear canal and hearing loss.
Treatment of the disease
It used to be that with any earache best remedy - This is a cotton swab moistened with boric alcohol. People thought that by such warming they contribute to a speedy recovery. Recently, however, doctors forbid the use of boric alcohol for treatment of otitis, and this is not surprising. After causing the alcohol solution to the inflamed surface, a person causes a tissue burn, and it is a favorable factor for the appearance of severe irritation. Therefore, completely different methods of treatment of otitis are used now.
For different types external otitis, there are different methods of treatment. To accelerate the recovery of a patient with otitis media, you will need:
- To perform a surgical operation to open the boil. After opening, the pus comes out, and the patient immediately begins to experience a significant improvement in the condition and a reduction in earache.
- . This will contribute to the rapid healing of the wound left after the boil.
Sometimes the patient has several boils. Such a phenomenon is no longer talking about the usual inflammation of the hair follicle, but about the presence of pathogenic microflora in human blood. In this case, antibiotic treatment is prescribed, not only topically, but also in the form of injections or tablets.
In the diffuse form, no operations are required. Here there is its own treatment regimen, namely:
- General antibiotic treatment. What kind of drugs to take, the doctor must determine, since it depends on the causative agent of the disease.
- Antiallergic medicines. They are necessary to relieve edema of the external auditory canal.
- Antifungal drugs, if otitis is caused by a fungus. Again, the specialist must identify the origin of the disease. It is not recommended to draw any conclusions.
- Non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, which not only quickly relieve the inflammatory process, but also reduce the pain in the ear. Usually prescribed Nurofen or Diclofenac.
- Strengthening immunity with the help of multivitamins.
- Ear instillation with antibiotic preparations. This will speed recovery. Sometimes doctors prescribe and antibacterial ointment. They are used with cotton swabs placed in the ear canal. Instead of antibacterial often use hormonal ointment.
With this treatment, otitis media is much faster than if no action is taken. You also need to know that the lack of treatment can cause the spread of infection to the middle ear, and this is a more serious disease that has severe course and causing serious complications.
Otitis (from the Greek. Ous, otos - ear) - is an inflammation of the ear. There is otitis externa (inflammation of the external auditory canal and the auricle), (inflammation auditory tube and the tympanic cavity) and internal otitis, or labyrinthitis (see).
External otitis. Two forms are observed - limited (external auditory canal) and diffuse. Limited external otitis develops as a result of the penetration of infection into the hair sacs and sebaceous glands of the skin of the fibro-cartilaginous part of the external auditory canal. Sometimes the process extends to the parotid tissue. The development of a boil is facilitated by minor injuries (for example, during manipulations in the external auditory canal), especially in persons suffering from purulent inflammation . Symptoms: severe pain in the ear, extending to the head, teeth, neck. The pain is exacerbated by chewing, pressing on the trestle, stifling the auricle. If the lumen of the external auditory canal is closed with a boil or pus, it decreases. On examination (sometimes directly at the entrance to the external auditory meatus) a furuncle is visible (see). Treatment: tampons moistened with boer liquid or boric alcohol are injected into the external auditory canal; warming compresses on the auricle, lamp Sollux,. Sometimes produce. When expressed by the general phenomena prescribed antibiotics. In prolonged cases, autohemotherapy is used (see).
Pain in the ear when you press the trestle can occur for various reasons. More often painful sensations are the result of exposure to infectious agents. This symptom should not be ignored, since the consequences can be quite serious.
The tragus is called a jut on outer area auricle, consisting mainly of cartilage tissue. Near the ear lobe there is an anticerokum, which is a paired organ of the tragus.
The tragus is the most important element of the auditory system, since it depends on it the normal perception of sounds coming from the source that is behind the person. Thanks to this body, a person has the ability to determine the direction of sound waves.
The cause of pain in the area of the tragus
The tragus is on to the outside ear and person can easily touch it. Sometimes such manipulations cause discomfort or pain. Why does the ear trestle hurt when pressed? The cause of this pathological phenomenon most often appears. Such a violation is characterized by the development of inflammation in the outer ear.
There are limited and. The development of limited inflammation occurs as a result of a pustule inside the ear canal.
The course of the disease is accompanied by severe pain. The pain subsides after the integrity of the abscess and violation of its contents outside.
Diffuse otitis media develops when exposed to pathogenic elements: staphylococci, streptococci, fungi. Also, the violation may be due to a hypersensitivity reaction of the body. In diffuse inflammation, the entire ear cavity and, consequently, the tragus are involved in the pathological process.
If the ear trestle is swollen and sore, the cause may be mechanical damage to the auricle. Quite often, cleaning the ear canal with unsuitable objects leads to a violation of the integrity of the epithelium. It is also possible the development of eczema, which is characterized by the formation of ulcers.
If your ear hurts when you press the trestle, it may be the water in the ear canal. This phenomenon is often observed in swimmers. Water washes away a layer of epithelium, which acts as a barrier against pathogenic microflora. As a result, pathogens have the ability to actively reproduce.
Both forms of inflammation of the outer ear have similar symptoms and are manifested by the following symptoms: 
- pain in any contact with the organ of hearing;
- intense itching in the ear (most often observed with fungal infections and eczema);
- hearing loss (this symptom is more characteristic of a limited form of inflammation, in which the abscess overlaps the Eustachian tube);
- hyperemia of the skin in the ear;
- increase in size of nearby lymph nodes.
With limited otitis, the pain is pulsating and increases as the follicle matures. When chewing, pressing on the trestle painful sensations become more intense. Observed unilateral edema and reddening of the skin - from the localization of the abscess.
Diffuse inflammation is characterized by less intense pain. In this form of pathology, itching and full swelling of the Eustachian tube are more often noted.
Since in most cases the cause of the disease is an infection, there is a risk that the inflammatory process spreads to the eardrum. In such a situation, the hearing is noticeably disturbed and exudate is released from the ear cavity.
Not so long ago, boric alcohol was considered to be one of the most effective medicines for treating a sick ear. In this tool, a cotton wool was moistened and inserted into the ear canal. Proponents of this method of treatment argued that warming promotes healing.
Modern medicine offers more effective and safe methods treatment.
What to do if ear aches when pressing on the tragus? Therapeutic measures are assigned based on the type and stage of development of the pathological process. With a limited otitis, an abscess is opened (the procedure is carried out exclusively by a specialist in a hospital), then antibacterial drops are used. During surgery, the auricle is cleansed of purulent masses, as a result, the painful sensations disappear and the general condition of the patient improves. The antibiotic, in turn, will contribute to the speedy healing of the wound and will prevent the development of a secondary infection.
There are cases when several boils develop in the ear cavity. This indicates the presence of pathogens in the blood. In such situations, not only local, but also systemic antibacterial agents are used.
If the ear trestle hurts due to a diffuse inflammatory process, treatment is carried out with the help of the following drugs:
- antibiotics systemic. Before using these medications, it is imperative to determine the causative agent and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
- antifungal drugs. Means of this group are prescribed for the fungal nature of the disease. The drug is prescribed based on the type of fungi.
- antihistamines. These drugs allow you to remove the eustachian tube edema.
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Such drugs allow you to quickly remove the pain and stop the further development of the pathological process.
- multivitamin complexes to strengthen the body's defenses.
- ear drops with antibacterial effect. Local application antibiotic allows you to quickly eliminate the symptoms of the violation. Alternatively, drops can be applied ointment with a similar effect, which are introduced into the ear cavity with cotton wool.
With timely treatment, otitis of the outer ear is well treated and does not lead to complications.
To speed up the healing process, treatment of the disease should be comprehensive. Many experts recommend a massage of the sore ear as an addition to the main treatment:
- pull the ear up, down, sideways, make circular motions;
- press your palms to your ear and sharply remove them;
- massage the trestle itself;
- cover the ear with a palm and knock the fingers of the other hand on the back of the head;
- rub his ear with energetic movements.
Regular execution of such a massage will not only allow you to quickly cope with the ear disease, but also has a beneficial effect on the state of the whole organism.
Under limited inflammation external auditory meatus imply boils localized in the cartilaginous part, where the skin is rich in hair and sebaceous glands. Boils of the ear canal are found with general furunculosis, and also as a result of skin irritation during manipulations in the ear with hairpins, matches and other objects that are especially harmful during suppuration from the ear.
Disease begins severe pain in the ear, sometimes extending to the eyes, teeth, head, neck and especially aggravated by chewing due to the transfer of pressure of the articular head lower jaw on the walls of the external auditory canal. Gradually, the skin in this place turns red and swells to such an extent that the auditory canal is greatly narrowed (if several boils appear at the same time). Sometimes the soft tissues of the mastoid process swell, so that the disease has to be differentiated from mastoiditis and subperiosteal abscess. At the same time the parotid and cervical lymph nodes swell.
Very painful there is pressure on the trestle pa, the lower wall of the external auditory canal and the sink. If the boil is on the front wall, especially in the area of the Santorini crevices, the infectious principle can penetrate them into the parotid gland and cause its inflammation - parotitis. The temperature of the boil is increased depending on the response of the tissues. It is possible to distinguish limited inflammation of the outer ear from mastoiditis by the characteristic pain when pressed on the trestle, by the painlessness of the ear itself. mastoid with pressure and preservation of hearing. If the hearing is somewhat reduced (when the boil completely covers the external auditory canal), then this may sometimes depend not only on the narrowing of the external auditory canal, but also on simultaneous collateral hyperemia in the tympanic cavity.
Set availability not difficult. At otoscopy, limited swelling is observed, usually at the entrance to the external auditory canal, causing its constriction.
Sometimes it is impossible to even enter the ear funnel due to the narrowing and soreness of the ear canal.
Often after emptying boil the pain stops on its own and the process is eliminated if there is no relapse, which is often observed, especially with general furunculosis. In such cases, the disease can last for weeks, whereas in the absence of relapse, it usually ends in 3-5 days. The rare cases with the accompanying phenomena of mastoiditis and labyrinthitis are described (EG Bankovsky, 1932; MD D. Emelyanov, 1951).
Treatment. Until now, tampons or cotton rollers dipped into the remaining lumen of the external auditory canal are wetted in Burov’s liquid. Outside, a warming compress is placed from the same liquid or from alcohol (the Drilling fluid macerates the skin, which contributes to its thinning and quick break of the boil). At the same time prescribed painkillers inside: aspirin, pyramidone, pantopon, morphine. Sometimes you have to make a cut and put a tampon in the rayon.
Along with this wide apply thermal procedures, heating pads, sollux lamp (V. A. Aleksandrovskaya, 1939), blue light, UHF, ultraviolet rays, etc. Special success is attributed to the action of UHF currents, the mechanism of action of which lies in the uniform and deep heating, selective action on individual tissues and cells, to enhance metabolism, which contributes to the improvement of the course of immunological reactions, with prolonged active hyperemia, which causes inhibition of sympathetic nervous system (V. F. Krivorotova, 1941).
Fixed assetscurrently used in the treatment of furunculosis are penicillin and streptomycin. For persistent infections, 400,000 IU of penicillin should be administered intramuscularly every 12 hours together with streptomycin (0.5 g), since the cause can be either gram-positive or gram-negative pathogens.
On abortive the effect of autohemotherapy was indicated by I.P. Kutenov, who noted that after 2-3 injections of blood in the amount of 7-10 ml with an interval of 48 hours, external otitis passes. A. I. Reznikov also notes the success of autohemotherapy, but since, in his opinion, it does not prevent recurrences of boils, Mercury ointments and Creed ointment should be applied simultaneously. Some recommend treatment with Crede ointment alone (A. A. Sladkova, 1931; A. Bogomolny, 1935).
Great literature is dedicated to vaccine therapy. Vaccination therapy is carried out in the form of injections or place using tampons soaked in vaccine filtrate. A vaccine can be homogeneous, heterogeneous, or an autovaccine prepared ex tempore according to Bezredka (I. A. Dayhes, 1925; V. P. Chernyak, 1926; R. D. Bogomilsky, 1945).
According to the data this treatment method has an advantage over other methods in terms of speed of effect. On the basis of the study of the nervous trophism in the pathogenesis of diseases, novocaine infiltration of the surrounding tissue (blockade) was carried out.
Popular
- How many live with lung cancer
- Influenza in children: how to treat, what can and cannot be done to parents, what medicines will help?
- "They are people too ..." - you say
- What helps "Prednisolone"
- How are menstruation for endometriosis?
- The fourth stage of cancer, how many live with it
- Prednisolone ampoules instructions for use
- Effective treatments for inflammation of the appendages
- Sinupret - an effective herbal alternative to antibiotics in the treatment of sinusitis
- When do menstruation begin for the first time