Otitis disease. Video: Otitis symptoms in a child. External otitis - symptoms
You have java script disabled in your browser, you need to enable it, or you will not be able to get all the information on the article "Otitis and symptoms of manifestation."
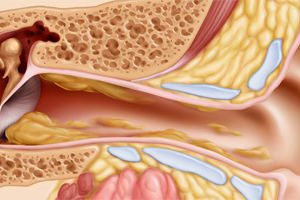
External (diffuse) otitis. Mostly this form of otitis begins to develop as complications against the background of purulent chronic otitis. They are caused by the constant formation of purulent secretions in the affected eardrum, as well as infection of tissues in the area auditory canal. Manifestations of this form of otitis are redness of the ear canal and the appearance of pain in this area. In some cases, diffuse otitis (diffuse otitis) is triggered by skin irritation that occurs in the auditory canal area under the influence of chemicals or under the influence of mechanical injury, followed by the addition of infection.
Complications are treated mainly pharmacologically, less often by surgery. In the case of external otitis media, that is, the middle ear cavity, in the case of otitis media. Untreated properly and on time otitis media can lead to serious complications for both children and adults.
You can access the article at any time, on any device, from your website or from a mobile application. Recommendations from the doctor. . Middle ear infection is a common childhood illness. There are studies that show that at the age of 3 years, four out of five children have at least one episode of otitis.
Most often, the middle ear is affected by inflammation, which is defined as tubootitis (or eustachitis). You can find more information about this disease in the section “Otolaryngology” on our website in the article, but now we’ll briefly discuss the main principles of symptoms.
Tubo-otitis as a disease is inflammation of the auditory tube, and it is this tube that first of all reacts to the process of infection penetration, which manifests itself in the form of redness and edema. As a rule, this is accompanied by the closure of the lumen against the background of the effects of edema, as a result of which the pressure in the middle ear decreases. In turn, directly for the patient, a number of these processes will manifest themselves in hearing loss along with congestion. In addition, this state is accompanied by a sensation in the area of the large ear of his own voice.
Untreated, otitis media can even lead to serious complications. Constant pain in the ears. The fluid spreads in the ear. Otitis can occur in both a child and an adult. Children have factors such as adenoid vegetation, colds caused by certain viruses that have not been treated properly.
Adults have predisposing factors as well as local services. For example, if a person has one, one, or he is prone to otitis. Properly untreated, otitis media can cause leakage and perforation of the eardrum, leading to a decrease or even loss of hearing.
As a rule, chewing and swallowing saliva slightly reduce these manifestations, which is explained by the short-term opening of the lumen of the auditory tube in these moments.
Without an appropriate impact from the immune system or doctor, inflammation of the middle ear cavity occurs in the complex. This, in turn, leads to the appearance of pains in the ear, which have a shooting character and extend to the region of the lower jaw, neck and temple. Seriously the temperature rises, the hearing that occurs as a result of the formation of exudate in the cavity of the middle ear, falls, then it becomes purulent.
Another complication of otitis media is the spread of infection from the middle ear to the mastoid. After this point, there is a very high risk that the infection will spread to the brain. And this is also a serious complication of otitis which was not treated on time.
Pain is relieved by analgesics, and sometimes concomitant otitis media is stopped with anti-anesthetic, also as directed by the doctor. One of best ways prevention of otitis media in adults - dry your ear with a cotton towel only. Adults are recommended to surgically correct the septum, treat rhinitis and treat allergies that may suffer.
By 3-4 days of the disease, the next stage begins to develop in the inflammatory process, in which, as a result of pus exposure, an opening appears in the eardrum (which is defined as perforation) and the exudate passes through the opening to the external auditory canal. In other words, at this stage, the patient will notice that fluid is expelled from the affected side through his auditory canal. As a rule, perforation is accompanied by a certain improvement in the general condition, the pain gradually decreases, the temperature drops.
In children, prevention of otitis media is carried out using anti-pneumococcal vaccination, especially if children are in kindergartens or schools. At the same time, children should receive education from their parents in order to properly blow their noses when they are cold.
Otitis in infants can be dangerous because it has serious consequences and remains unworked, can lead to scarring of the eardrum, hearing loss, meningitis, mastoiditis, paralysis facial nerve or speech impairment. The space behind the eardrum, the middle ear, covers the auditory system and is empty inside, and the natural secrets formed here are eliminated by an internal path called the Eustachio tube.
In the absence of the required treatment, the liquid acquires a certain thickness of consistency with the simultaneous formation of fibrin threads in it, and adhesions to the scars begin to form. Because of the scarring in this case, there is a difficulty in the normal functioning inherent in the auditory ossicles, this, in turn, can lead to persistent hearing impairment.
In children, this does not always work well, probably because it is not fully mature and therefore does not have the necessary resistance, and the discharge is not completely eliminated. Anatomical features Children's otorhinolaring structures can cause an infection that affects one of the structures, which easily spreads to another.
This formation regresses after puberty. Thus, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and throat during viral or bacterial infection often accompanied by inflammation of the lymphoid structures of the throat: palatine tonsil Lushi and tonsil tonsil, from which a blood clot of Evstakhio can spread to the ear.
Internal otitis (labyrinthitis) . The disease in this form is accompanied by complaints of dizziness, accompanied by severe tinnitus and persistent hearing loss. Actually dizziness can manifest itself in a wide variety of diseases, but when it suddenly appears, following a cold from the patient who had previously suffered from the patient, combined with nausea and vomiting, there is every reason to consult a specialist for advice on the relevance of ear disease.
This pharyngeal tonsil, a place of frequent inflammation, may be hypertrophic due to chronic or recurrent infection, and then we say that there are adenoids. Tinnitus hypertrophy usually prevents breathing and depletion of nasal secretions, which leads to the well-known symptoms: nasal obstruction, rhinorrhea, mostly oral breathing, night snoring, nasal voice, etc.
Fever is a sign of inflammation and infection, but its appearance depends on the child’s immune system; a child with an inadequate immune system may be afebrile, even with serious infections. In this situation, there may be a confusion in the misuse of the word "polyps": all children have Lonsch's amygdala, but not all of them are hypertrophied to determine the clinical manifestations.
Diagnosing
Diagnosis of otitis is made on the basis of complaints from the patient, however, a significant obstacle in its conduct for young children is the limitations in oral contact due to the age of the children with the doctor. Detection of the disease is performed using methods such as:
- x-ray of the skull;
- otoscopy;
- hearing test (audiometry, tuning forks).
Otitis treatment
Otitis treatment can be either medicinal or surgical, which in particular is determined by the characteristics of its course, form, symptoms, and diseases associated with it. In any case, the effectiveness of treatment depends on how early the treatment began.
What babies say about otitis in babies. A midwife with bilateral otitis media received aerosol therapy, Nasomer and dexamethasone, as well as oral nurofen, azithromycin and arius. In most cases, mothers experience otitis persistence and mild symptom relief, and recommend that more doctors be advised.
What are middle ear infections? The middle ear is a small part of the ear in the immediate vicinity of the eardrum. It can be infected when microbes in the nose or throat reach near the ear. Middle ear infections usually occur in infections of the upper respiratory tractsuch as the common cold. At this time, the surface of the Eustash tube may ignite and block. The fluid collects in the middle ear, creating a land suitable for the development of bacteria and viruses, respectively creating an ear infection.
Otitis treatment follows certain rules that focus on the following:
- decrease pain sensations;
- decrease puffiness;
- measures to improve outflow from the middle ear pus;
- measures to reduce the swelling of the mucous membrane of the auditory tube;
- the use of antibiotics as a measure of the overwhelming nature, aimed at combating infection localized in the middle ear;
- local treatment using compresses and certain hygiene measures;
- surgical intervention (method of shunting the tympanic cavity, in the absence of efficiency - the eardrum is cut, which is defined as paracentesis).
In addition to these measures, physiotherapy procedures are used:
While the body is trying to fight the infection, pus is created in the ear. There is even more fluid to press eardrumcausing pain and sometimes hearing loss. A fever usually lasts from one to two days; pain and crying last 3-4 hours. Subsequently, some children experience intermittent pain for 4 days, although young people may have such pain for up to 9 days. According to studies of 240 children aged 6 months to 2 years, treatment of children with antibiotics can delay these symptoms by about one day.
In any case, in 80% of cases, the immune system can fight infection and can heal the ear without the need for these medications. In more severe cases, more fluid can increase the pressure on the eardrum until it breaks, allowing the fluid to drain. In this case, the fever and pain usually disappear, and the infection heals. A healer usually heals himself in just a few weeks. Sometimes there are complications, such as chronic purulent otitis; This can occur after repeated ear infections.
- UHF for the nose area;
- laser therapy for the mouth of the auditory tube;
- pneumomassage oriented to the eardrum region.
In order to diagnose otitis, it is necessary to contact the attending pediatrician (therapist), subsequently consultation and treatment from an otolaryngologist (LOR) is required.
If you think you have Otitis and symptoms characteristic of this disease, an otolaryngologist may help you.
The accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. Hearing problems can occur due to the fact that fluid affects the functioning of the middle ear. This is called otitis media with effusion. Otitis with effusion can even occur if a child does not have an ear infection or an upper respiratory tract infection. In rare cases, complications can arise from a middle ear infection to fluid accumulation.
Examples include hearing loss or rupture of the eardrum. What are the causes of middle ear infection? A small tube connects the ear to the neck. This tube can swell up greatly due to a cold that can block the fluid inside the ear. This creates an ideal place for microbial growth and infection can occur. Ear infections are found in most cases in young children, because their tubes are very small and are blocked more quickly.
We also suggest using our online disease diagnostics service, which selects possible diseases based on the entered symptoms.
- This is an inflammation of the ear. The disease may be chronic or acute, purulent, or catarrhal. The severity of the pathological process depends entirely on the virulence of the microorganisms, and the state of the person’s immune defense plays a big role.Statistics say that 30% of all otolaryngological diseases are acute otitis media. Preschool children get sick much more often than adults. By the age of three, 80% of children tolerate otitis media.
The main symptom of the infection is pain - mild or strong. Infants and very young children may be very worried. It is very possible to pull out the ears and cry. They may have trouble sleeping or have a fever. You will see a thick yellowish liquid dripping from your ear. This occurs when the infection broke the eardrum and the fluid was removed. This is not a serious problem and usually eliminates pain. When the fluid builds up, but the infection does not occur, the children say that their ears are clogged.
They may have hearing problems during infection, but they usually return to normal when the fluid is removed. The fluid can flow in a few weeks. How is middle ear diagnosis diagnosed? The doctor will talk to you about the symptoms of your child. He examines the ear with a special, light to the end instrument, with which he can see the eardrum and can find out if he has fluid accumulations. The exam is not very disturbing, it depends on the sensitivity of each child.
To damage the organ of hearing, causing otitis, can:
Hemophilic sticks and other microorganisms.
Any inflammation of the ear is extremely dangerous, and you should consult a doctor immediately after the detection of the symptoms of the disease described below.
Otitis symptoms
Symptoms of otitisby which you can recognize the average acute otitisare the following signs: severe pain in the ear (according to patients it is described as shooting), fever, and after 1-3 days purulent discharge from the auditory canal. After the appearance of pus, the patient's condition usually improves, the temperature decreases, the pain becomes less pronounced or disappears altogether.
Middle ear infections are usually diagnosed with regard to disease, a general physical examination, and one ear. When an infection occurs, pneumatic otoscopy shows that the tympanum has a red or yellow and inflamed. If fluid develops without infection, the eardrum looks as if it were being pulled in. In both cases, the eardrum will not be elastic when you push air into your ear.
Timanometry, which checks the movement of the eardrum. Use a device that is located exactly inside the ear. It changes the air pressure in the ear, then measures how the eardrum reacts. ¢ Tests on hearing. A hearing test is recommended for children who have had fluid in one or both ears. Hearing tests can be done on Monday if hearing problems are suspected. ¢ tympanocentesis. When fluid remains behind the eardrum or if the infection continues even after using antibiotics, time may drain the fluid from the ear.
Pus is released from the breakthrough through the eardrum. Such an outcome of the disease is considered positive, with proper treatment, the hole in the eardrum is slowly overgrown, without affecting hearing.
With the unfavorable development of the disease, the pus cannot find a way out, and this is fraught with the fact that the infection may begin to spread inside the skull. Such otitis is able to go into, as well as in the brain. In order to avoid such terrible consequences, at the first symptoms of otitis, contact an otolaryngologist for advice and proper treatment.
The doctor uses a needle to push the tympanum and pull it out. The sample is usually opened and sent for analysis. These tests will show which bacteria cause the infection, and this the best treatment. Blood tests that are performed if immune problems occur.
Most ear infections disappear on their own. You can treat your child at home with antibiotics such as acetaminophen, a warm towel over your ear, etc. Do not administer aspirin to children up to 20 months. The doctor can give you ear dropsto ease the pain of your child.
It may happen that after infection the child does not hear well for a while. Call your doctor if she is over 3 or 4 months old. Children need to hear to learn to speak well. The doctor may prescribe antibiotics for ear infections, but it is better to treat with them. You should discuss this topic with your doctor. Their administration depends on the age of your child and the severity of the infection.
Otitis, depending on the location of inflammation, may be:
Outdoor;
Inland.
Swimmers often suffer from external otitis, which is why the disease is popularly called the "swimmer's ear." Inflammation starts because mechanical injury auricle or external auditory canal. Damage to the protective cover leads to the ingress and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, then it forms on this place.
Minor surgeries, such as inserting tubes in your ear, can help if your child has hearing problems or repeated infections. Can ear infections be prevented? There are many ways to prevent ear infections: do not smoke. Ear infections usually occur in children who are surrounded by cigarette smoke. Even smoke from clothes or hair can affect it. Washing hands and any other method of immunization can help a child.
In addition, make sure the baby does not fall asleep, suck the bottle and try to reduce the number of caregivers. You can prevent infections of your child’s ear by following these instructions: Do not smoke. Ear infections are most common in children who remain in cigarette smoke at home. Even cigarette smoke in your hair and clothes can affect it. Breast of your baby on the chest. Breastfeeding is known to reduce the risk of ear infections, especially if they are inherited from the family. If you feed the baby with a bottle, do not let him suck when he stretches.
If you do not immediately carry out the appropriate treatment, external otitis media becomes severe form and extends to the parotid cartilage and bone. With this type of patient's disease, the aching, throbbing pain, swelling of the ear, and a moderate fever are concerned.
With otitis media, the inflammatory process extends to the air-cavity of the middle ear, located just behind the eardrum: the tympanic cavity, the auditory tube and the mastoid process.
The form of otitis media often flows from catarrhal to purulent.
Acute catarrhal otitis middle ear occurs as a complication of acute respiratory infections or SARS, after the penetration of the pathogen into the tympanic cavity. At the initial stage, the level of hearing may decrease, tinnitus may appear, but the temperature remains normal or slightly increased.
If these symptoms are ignored, then further catarrhal otitis appears sharp and shooting pain in the ear, spreading to the eyes, neck, or throat. To cure such otitis can only get rid of the infection, for which an urgent need to consult a doctor.
Acute purulent otitis of the middle ear is a neglected catarrhal form. The disease manifests itself as a breakthrough of the eardrum and pus leakage, followed by a decrease in body temperature. Treatment, in addition to fighting infection, should include the permanent removal of pus from the ear, which only the health worker can do.
In addition, pus can not always come out by itself. If the eardrum is very strong, an operation is needed to puncture the eardrum. This procedure is called “paracentesis” and is performed using a local anesthetic drug: a puncture is made with a special tool at the most favorable point, and the pus is completely expelled.
After the pus is removed, the eardrum cicatrizes, and the quality of the hearing does not decline further.
If acute otitis media is not treated, the pus spreads inside the skull. As a result, internal otitis media develops, affecting the vestibular apparatus, causing and leading to at least partial or complete hearing loss. Therefore, at the first signs of otitis, do not try to drip something into your ears, or lay a tampon with alcohol or another antiseptic, but you need to go to the doctor urgently!
Each ENT disease is accompanied by increased mucus formation. With the increase of its quantity in case of an unsuccessful set of circumstances, mucus enters the Eustachian tube, disrupting the ventilation of the tympanic cavity. Cells of the tympanic cavity secrete inflammatory fluid. In addition to blocking the lumen of the Eustachian tube, pathogenic microorganisms normally included in the local microflora also contribute to the aggravation of inflammation.
The causes of otitis are:
Penetration of infection from other ENT-organs - as a complication of a concomitant infectious viral disease;
Various diseases of the nose, sinuses and nasopharynx. This includes all types of rhinitis, the curvature of the nasal septum, and in children - (adenoid vegetation);
Injuries of the auricle;
Hypothermia and weakened immunity.
Complications and consequences of otitis
Although only ears ache in otitis, complications with inadequate treatment or lack of it can affect many organs. Incomplete treatment of otitis media leads to very terrible consequences - suppuration goes on to lower jaw, touching the salivary gland and often leading to disability.
But even more dangerous otitis does what this disease is not always easy to identify. For example, in some cases, the disease is not accompanied acute pain in the ears. Often due to otitis, the work is disrupted gastrointestinal tract. This is because our abdominal area and ear are connected by one nerve. Therefore, during otitis, especially in a child, the intestines may swell, vomiting and constipation may appear. That is, you can suspect appendicitis, in this case, you will be directed to a surgeon. But the diagnosis inflammatory diseases in young children it is necessary to carry out with the participation of the ENT specialist.
If a mother thinks that her child has just a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, and takes up self-treatment, in the meantime, otitis media can turn into a more serious disease - ooanthritis. This is a situation in which pus passes into ear region and another inflammation joins, causing the ears to bulge out, swelling appears and the temperature rises again. A complication can occur in the coming days or in a month, that is, it cannot be predicted. If these otitis symptoms are not noticed, then meningitis will develop in a couple of months, so be careful with otitis.
Other common complications of otitis include the transition to the chronic stage, the defeat of the vestibular apparatus and hearing loss.
In addition, complications of otitis include:
Meningitis and other intracranial complications (brain abscess, hydrocephalus) - the next stage after the anthrax, if measures are not taken on time;
Tearing of the eardrum and filling the ear cavity with pus;
Cholesteatoma - overlap of the auditory canal with a tumor-like cyst-like formation in the form of a capsule with dead skin and keratin;
Mastoiditis - inflammation mastoidcausing destruction auditory ossicles in the middle ear;
Gastrointestinal dysfunction -,;
Persistent hearing loss, hearing loss (up to complete deafness).
Chronic otitis media is extremely difficult to treat and greatly reduces the quality of life - hearing is impaired, there is a constant inflammatory process in the ears and suppuration occurs. Often, to get rid of chronic otitis in adults, conservative treatment is not enough, and you have to resort to surgery.
A competent doctor diagnoses acute otitis without special adaptations and innovative technologies. A regular examination of the auricle and the auditory canal with a head-mounted reflector (a mirror with a hole in the center) or an otoscope is enough to diagnose otitis.
How is external otitis diagnosed?
With external otitis, the doctor draws attention to the skin in the ear, the size of the ear canal and discharge from it. If the auditory lumen is severely narrowed, especially if the eardrum is not even visible, the skin turns red and there is a noticeable fluid discharge inside the ear, this allows the doctor to make a diagnosis of otitis externa.
How is otitis media diagnosed?
Acute otitis media is also diagnosed to a greater extent by external examination. The doctor is guided by some characteristic signs of this disease: a reddened eardrum, a restriction of its mobility and the presence of perforation.
All these symptoms are easy to check - it is enough for the patient to inflate his cheeks without opening his mouth. “Blowing out the ears” is a technique called the Valsalva maneuver that is constantly used by divers and divers in order to equalize the pressure in the ear during deep-sea descent. As air enters the tympanum, the membrane visibly bulges, and if the cavity is filled with liquid, there will be no flexion.
Perforation in the eardrum in otitis is noticeable to the naked eye after the overflow of the ear cavity with pus and its leakage upon breakthrough.
Update diagnosis of otitis media: audiometry
The study of hearing on a special device - audiometry, as well as the measurement of pressure inside the ear - tympanometry - is used to clarify the diagnosis for suspected chronic otitis.
If the severity of hearing with a flowing otitis media drops sharply, and bouts of dizziness begin, there is a reasonable suspicion of internal otitis (inflammation of the ear maze). In this case, they use audiometry, resort to the help of an otolaryngologist and a neurological examination.
X-ray and computed tomography
Radiography in acute otitis is used to confirm its complications — severe intracranial infections or mastoiditis. These are quite rare cases, but if these are suspected dangerous complications, CT scan of the brain and temporal bones of the skull is necessary.
Determination of bacterial flora in otitis
Bacterial seeding for otitis, at first glance, it seems meaningless research. Indeed, for the cultivation of bacteria takes time, and the result of the analysis will be visible only for 6-7 days, and if timely treatment of otitis media is carried out, the disease should have passed by that time. But not all cases of otitis help the usual antibiotics, and if the doctor knows from the results of the smear, which microorganisms caused the otitis, then he will prescribe a obviously suitable drug.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and a few more words, press Ctrl + EnterAs soon as there are discomfort in the ears, whether it is a periodical congestion or aching pain, you should immediately consult a doctor for proper treatment. Otherwise, acute otitis media will most likely become chronic, leaving behind scars, thinning, retraction, or breakage on the eardrum, after which the patient will experience frequent inflammation and hearing loss.
If you go to the doctor on the same day when the pain appeared, it is impossible, then the only thing that can be done is to use inside antihistamines (by reducing the pressure in the ear, the pain subsides), and for severe pain - painkillers.
Attention: camphor oilinfusion boric alcohol, juice and phytocandi - any of these "healing" drugs for the treatment of otitis can lead to deafness for life. The same applies to warming with sand, salt or heating pad. Inflammatory process in the ear will increase several times because these folk remedies give bacteria food and accelerate their reproduction, causing accumulation of pus and severe swelling. Alcohol-based antiseptics are especially dangerous for children with delicate, sensitive mucous membranes.
But the worst thing is hitting the pus in the brain, leading to irreversible consequences - a person can remain permanently disabled!
How to treat otitis media?
Regardless of the form of otitis, the patient requires pain medication, so as to endure ear pain unbearable.
With otitis, the drug Otinum has proven itself well, which can significantly reduce pain in a few minutes. In addition to the anti-inflammatory effect, it has antimicrobial and antifungal effects, having a direct effect on the root cause of the disease.
What is the treatment of external otitis media?
If external otitis media is found in adults, the main treatment will be with ear drops. In a healthy person with normal immunity, external otitis media will pass with the use of only drops, antibiotics in injections or tablets will not be needed. Drops can consist only of an antibacterial drug, and can combine an antibiotic and an anti-inflammatory agent. External otitis drops are treated on average throughout the week.
Basically, for the treatment of external otitis prescribed:
Antibiotics - norfloxacin (Normaks), ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (Ciprolet), rifamycin (Otof);
Antibiotics with corticosteroids - Candibiotic (beclomethasone, lidocaine, clotrimazole, chloramphenicol), Sofradex (dexamethasone, framcetin, gramicidin);
Antiseptics (Miramistin);
Antifungal ointments - clotrimazole (Candide), natamycin (Pimafucin, Pimafukort) - are prescribed if external otitis media is of fungal origin.
What is the treatment of acute otitis media and ear labyrinth in adults?
Antibiotics
Otitis media is usually treated antibacterial drugs. But the treatment of otitis in adults is slightly different from the treatment of childhood disease - the frequency of self-recovery from otitis media in an adult is more than 90 percent, which practically reduces to no the need to use antibiotics. But the remaining 10 percent comes with very serious consequences, so if after the first two days of the disease there is no improvement, then antibiotics are prescribed.
An antibiotic should be prescribed by a qualified doctor, since this class of drugs is extremely dangerous because side effects. However, the death rate from complications of otitis reaches 28,000 people per year, therefore, as a rule, the treatment is justified. Usually antibiotics are prescribed in pill form, but if the patient cannot take a pill, injections are used.
To treat otitis media in adults, use:
Amoxicillin (Flemoxin Solutab, Ekobol, Ospamox or Amosin);
The combination of amoxicillin with clavunalic acid (Flemoklav, Augmentin, Ecoclav);
Cefuroxime (Cefurus, Aksetin, Zinnat, Zinatsef).
Other drugs may be prescribed, but it is important to comply with the main requirement of antibiotic therapy: complete a course of treatment that lasts at least a week. If microorganisms have not become extinct due to the interruption of antibiotic intake, bacteria develop resistance to this group of drugs, and antibiotics stop working.
Ear drops for otitis
Comprehensive treatment of otitis media often includes the use of drops. It is extremely important to know that not all ear drops are the same, and if your ear hurts, then not all drops will fit. The difference is that before damage to the eardrum and after its perforation active substance for the treatment of otitis media is completely different.
If the eardrum is intact, then use painkillers drops - Otipaks, Otinum or Otizol - with lidocaine, benzocaine or choline salicylate. In the catarral form of otitis media in adults, drops with an antibiotic will not help at all, since the substance does not fall into the source of inflammation - behind the eardrum.
When the pus has burst out, and the tympanic cavity is open, on the contrary, drops with anesthetic effect are contraindicated, as they can lead to undesirable consequences. Especially since with the discharge of pus the pain subsides.
To prevent re-suppuration or ingestion of pus in inner ear, antibiotics are prescribed to the open drum cavity - these are “Normaks”, “Tsiprofarm”, “Miramistin” and others; only a doctor should prescribe them. The use of ototoxic antibiotics, drugs on alcohol, with phenazone or choline salicylate is strictly prohibited.
Paracentesis of the eardrum - extreme measure
When therapeutic treatment Otitis media with medication has no effect, a large amount of pus accumulates behind the eardrum. This leads to a very severe pain and increased absorption of waste products of bacteria into the blood. There is a general intoxication of the body. As soon as these symptoms appeared, the doctors immediately appoint a paracentesis, an operation that prevents severe complications otitis
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. In the process of paracentesis, the eardrum is incised with a special needle in the thinnest place in order to minimally injure the tissues, and pus flows out through the opening. Moreover, a neatly incised wound grows much faster than a hole with natural perforation, and after the paracentesis a minimal one is formed.
The next day, there is a sharp improvement in health and accelerates the patient's recovery. This is especially true of paracentesis in the treatment of otitis in children.
Emergency paracentesis is indicated for:
Inflammation of the inner ear;
Damage to the dura mater, manifested in the form and nausea;
Lesion of the facial nerve;
If during three days after the start of antibacterial therapy, the pain does not subside and the suppuration does not subside.
Unlike external or average otitis of varying severity, the inflammation of the auditory labyrinth is treated comprehensively, and only in the conditions of a medical institution under the constant supervision of a neurologist and an otolaryngologist. For the treatment of the maze, not only antibiotics are required, but also neuroprotectors and drugs to improve the microcirculation of the blood in the inner ear.
The main goal of otitis prophylaxis in adults is that the Eustachian tube is not blocked by thick mucus. This is not such an easy task. As a rule, acute accompanied by liquid secretions, but in the process of treatment mucus often becomes much thicker, stagnating in the nasopharynx.
In order to prevent otitis caused by stagnant purulent processes from developing, it is necessary to promptly treat the corresponding ENT diseases - banal, or remove adenoids from the pharynx.
What to do to prevent complications of ENT diseases in the form of otitis media:
Use vasoconstrictor drugs in the nose to reduce mucosal edema;
Maintain fluid balance in the body, drink more water;
Timely take antipyretic drugs at very high temperature, not allowing it to hold;
Maintain the air temperature in the dwelling in the range of 18 to 20 degrees Celsius;
Maintain humidity in the room, air and regularly do wet cleaning;
Observe the measure in blowing your nose - do not overdo it, as it causes blocking auditory tubes and stagnation of infected mucus, and blowing out each nostril, clamping them separately.
But the most important prevention for the very first symptoms will be a timely visit to a doctor. He will examine the eardrum and determine in which part of the ear is otitis, whether the purulent exudate is collected in the tympanic cavity. You may need a blood test, or other examination, the results of which the doctor will select proper treatment and will save the patient from the terrible complications of otitis.
Popular
- What is useful mineral water
- What is the name of the Scottish skirt
- What women like a man archer
- Dosage and use of doxycycline when tick bite
- Sinupret - complete instructions
- Number of antennae in arachnid and insect crustaceans
- Help for enterobiasis for the pool, how much is valid
- Ceftriaxone suspension. What is ceftriaxone?
- Third degree breast cancer: prognosis and treatment
- Salt Scrub for the scalp