Serous lymphadenitis of the submandibular. Traditional methods of treatment of pathology. Lymphadenitis under the jaw - causes
Submandibular lymphadenitis can occur in an acute and chronic form. In the first case, only one or several nodes can undergo inflammation at a time. Although the acute course can be observed without the presence of pus, but most often it is caused by an abscess. At the same time pus can be localized in the node and fluctuate, which indicates that it moves along the node. This can trigger its breakthrough and more extensive inflammation. In addition, an acute infection can affect not only the knot, but also the surrounding tissue. They also swell and hurt.
In acute form pain sensations may affect the neck and jaw. The pain is caused by opening and closing the mouth.
Submandibular lymphadenitis in chronic form
Lymphadenitis submandibular (causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention described in the article) can occur in a chronic form. It can be triggered by improper treatment. acute illness. In acute lymph nodes, the lymph node swells, the skin around it becomes red, and in chronic form, the nodes harden.
In the chronic process, as well as in the acute, inflammation can affect the tissues adjacent to the node. The patient has the same signs as in the acute course: fever, redness of the skin, asthenia and fever.
If the disease is chronic, then doctors may resort to the surgical method, during which the affected node will be removed. The acute form is stopped by removing pus from the affected site with the further use of antibiotics.

The appearance of submandibular lymphadenitis in children
The disease in childhood occurs quite often. Infection can spread from various foci of inflammation. This could be an infection of the teeth, gums, throat, etc.
In infants such a disease can not develop, since the formation of lymph nodes occurs during the first three years of a child’s life.
If time does not stop the process in a child, then surgery may be necessary to remove the node. Therefore, it is important to start therapy in a timely manner. Many parents do not even suspect that the lymph nodes are located in the back of the head. Although submandibular lymphadenitis in children is diagnosed with ease.
The child complains of pain in the neck or lower jaw. Parent can grope nodes. They will be soft and mobile.
Diagnosis of the disease
There are a number of methods to help diagnose this disease. A doctor can make a diagnosis only by signs, without performing any examinations, as the symptoms of the disease are quite bright.
In addition to the visual method, as well as palpation, there are other diagnostic methods. For example, a doctor may prescribe a blood test to a patient. As already mentioned, the disease provokes an increase in the level of leukocytes.
Resort and to ultrasound. Ultrasound detects the presence of pus in the node. In addition, the doctor may carry out a puncture (collecting fluid for bacteriological analysis). Such a manipulation will help determine which bacteria provoked inflammation and which antibiotic should be prescribed in this case.
The basic principles of treatment
How does the submandibular lymphadenitis proceed? Symptoms and treatment folk remedies, as well as methods of traditional medicine indicate that the disease is inflammatory in nature, causing suppuration. Therapy is based on eliminating the infection that caused the inflammation.
As a rule, they resort to such drugs as:
- aluminum 8%). It has astringent and anti-inflammatory effects. Used as rinses and cold lotions. Before use, the product is diluted 10-20 times.
- Salt based solution. Used for rinsing.
- The use of antibiotics. They are prescribed in the form of tablets, as well as in the form of intramuscular injections. Among them, the most widely used drugs such as Cefalexin, Clindamycin, Amoxiclav, Lincomycin, Cefuroxime. Take antibiotics should only be prescribed by a doctor.

If submandibular lymphadenitis (symptoms and treatment are described) was diagnosed on early stagethen usually the use of rinses and antibiotics for edema is enough.
If pus is collected during inflammation, it is usually resorted to a simple operation that involves making a small incision and removing the pus through drainage.
In most patients, several nodes are affected at once. In this case, surgery is required. The doctor does under lower jaw small section. A drainage tube is inserted into it and pus is discharged. At the completion of the manipulation wound tightened clamps. After surgery, the patient should drink a course of antibiotics.
The use of folk remedies in the treatment of lymphadenitis
How is submandibular lymphadenitis stopped? Symptoms and treatment of folk remedies, as well as methods of traditional medicine are presented in this article. In most cases, the use of folk methods for lymphadenitis is a waste of time. The patient believes that he relieves his condition, and in fact the disease progresses and, as practice shows, leads to a hospital bed.

Usually folk ways effective only at the initial stage of the disease. In any case, without the advice of a doctor, you cannot resort to using home methods.
Among the most popular folk methods treatment should be noted:
- Drinking ginger tea.
- Applying a compress with echinacea tincture on alcohol. One article l The drug is diluted with warm water in a ratio of 1: 2. The resulting mixture is impregnated with a bandage.
- Drinking Echinacea tincture. To this end, 30-35 drops of funds are diluted in half a glass of water. The medicine is taken three times a day.
- Drinking a blueberry drink. A handful of fresh berries should be pounded, pour gruel with water, soak for about an hour and drink. The procedure is repeated before each meal.
- Apply dandelion powder. To prepare such a medicine is possible only in summer. Dandelion roots are dried, then crushed. The resulting powder is eaten by 1 tsp. 30 minutes before meals.
- Drinking beet juice. Fresh fruit is squeezed out of juice and placed for 6 hours in the refrigerator (the foam should be removed). Drink medicine in the morning before breakfast. The taste of beet juice is not very pleasant, so it can be diluted by a quarter with carrot juice.
- Drinking garlic infusion. Two heads of garlic should be chopped and pour warm boiled water. They insist for 3 days. Twice a day, the medicine is stirred. Drink infusion of 2 tsp. between meals.
- Vitamin C consumption. The starting dose is 0.5 g three times a day. If the improvement is not observed, it is recommended to increase the vine to 2 g.
Preventive measures
How the submandibular lymphadenitis proceeds (symptoms and treatment), the photos in this article provide insight. The disease brings excruciating pain and requires the use of antibiotics. Often for the relief of disease requires surgery.

In order not to face such a problem as lymphadenitis, one should avoid infecting the body and treat all, even if not very serious diseases in a timely manner. Scratches and skin wounds should be avoided. When they appear, immediately treat with antiseptic agents. Do not underestimate the timely treatment of gums and caries, as they are the first to be able to provoke the development of such an unpleasant disease.
Submandibular lymphadenitis may occur after hypothermia or for a number of other reasons. His treatment is conservative or surgical and is prescribed only by a doctor.
Lymphadenitis under the jaw - causes
Submandibular lymph nodes are responsible for the processing of lymph, which moves away from the head, including from oral cavity. Under lymphadenitis understand the inflammatory process in the lymph node. Under the jaw, this pathology extremely rarely occurs primarily - most often it is secondary, that is, it becomes a consequence of the underlying disease. Initially, an inflammatory process occurs in the adjacent organ, and then the infection spreads to the regional lymph node. Disease code by ICD-10 - L.04.0. Lymphadenitis of the face, head, neck.

By the type of lymphadenitis is:
- sharp - develops with bright symptoms, no more than 1-3 weeks;
- chronic - accompanied by periodic remissions, exacerbations.
The disease can be serous, not accompanied by purulent processes, and purulent, in which the patient needs surgery. It appears with equal frequency in children and adults. The reasons may be as follows:

In adults, specific infections can cause lymphadenitis - tuberculosis, syphilis. In childhood trauma to the tonsils and throat also contribute to the development of pathology.
Clinical picture of lymphadenitis
In children under 3 years old, the symptoms of the disease cannot appear, because the lymph nodes finally develop only by this age. In the rest of the patients at the initial stage, the pathology does not show any signs, but after a couple of days the lymph nodes are enlarged, become hard, hard to touch, their palpation is very unpleasant. If at this stage the disease is not treated, it becomes acute. The lymph node becomes sharply painful, inflamed, gives "lumbago" - periodic severe pain, giving in the ear.
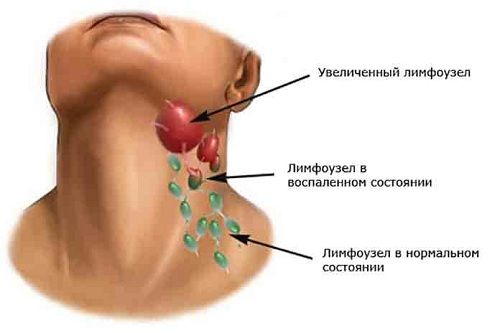
Redness, swelling (swelling) of the skin is observed in the affected neck. Sometimes the skin becomes burgundy, and swelling extends to the entire side of the neck. Joining pain when swallowing, weakness, body temperature rises. It is difficult for a person to fall asleep due to severe pain in the neck, he loses his appetite. If treatment is not started yet, lymphadenitis becomes purulent:
- blueness of the skin;
- trembling of the skin due to accumulation of pus;
- visible pus transfusions in the node;
- temperature up to 40 degrees;
- hyperthermia;
- strong pain when moving the jaw.
Chronic lymphadenitis is a consequence of the untreated acute form of the pathology, with it the lymph node is constantly hard, enlarged, slightly painful.
Diagnosis of the disease
Despite vivid clinical signs, it is not always possible to make a diagnosis without detailed examination. Lymphadenitis must be differentiated from oncological diseases, as well as its serous form with purulent - the order of treatment depends on it. It is necessary to ask for the help to the therapist, the ENT, the stomatologist, the maxillofacial surgeon. The main diagnostic methods, their results are presented below.
In chronic lymphadenitis, the main diagnostic method is ultrasound, according to the results of which the doctor will make conclusions about the presence of a sluggish inflammatory process.

Lymphadenitis treatment
At home, it is possible to heal if the disease is not transferred to purulent stage. Apply physiotherapy techniques - electrophoresis of anesthetics, absorbable, anti-inflammatory drugs, UHF. The main method of therapy is taking antibiotics. The most common causative agents of the disease are staphylococci and streptococci, therefore antibiotics are recommended for treatment. wide spectrum from the group of macrolides, penicillins.

7-10 days to cope with the disease Amoxiclav, Flemoklav, for 5-7 days - Clarithromycin, Azithromycin. In some cases, doctors recommend combinations of antibiotics from different groups. In parallel, antiseptic rinsing of the oral cavity is used (if the reason lies in inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx), put lotions on the area of the lymph node with Burov's fluid. In the chronic form of the pathology, immunomodulators are additionally prescribed (Amixin, Polyoxidonium). When pus accumulates in the lymph node, an operation is performed. Under general or local anesthesia dissect the node, remove pus through drainage, washed cavity with antibiotics.
When several adjacent nodes are inflamed, an operation is performed under general anesthesia with the opening of the zone, the introduction of drainage into the subcutaneous tissue and the removal of melted tissue.
Folk remedies for submandibular lymphadenitis
At the very first stage of the disease, when there is no pus in the lymph node yet, you can try along with conservative means folk treatment according to these recipes:

Prevention of lymphadenitis under the jaw
Since in most cases the cause of the pathology are infections of upper respiratory tract and chronic pathologies, their treatment should be carried out in time. With chronic tonsillitis it is important to undergo therapy twice a year “ Tonsilor"Removing purulent plugs. Adenoids in children, leading to regular inflammatory processes, to be removed. Carious teeth, pulpitis, gum disease and periodontal disease should be cured, then visiting the dentist 2 times / year for preventive purposes.
- A disease, both adults and children. The reason is the inflammatory-infectious process of one of the organs in the body, which has resulted in a complication of the lymph nodes. There are about 100 lymph nodes in our body - this is what the defense of the immune system against bacteria and viruses expresses. Most often, the inflammation extends to the lymph nodes located on the neck. Acute lymphadenitis of the face is provoked by streptococci and staphylococcus bacteria.
The reasons
So, the main cause of lymphadenitis is penetration of streptococci and staphylococcus bacteria into epithelial tissue. How can these bacteria enter the lymph node and how can they be removed from there? Trauma, scratch, that is, any damage to the skin is a prerequisite for infection from the environment. The second way - the defeat of the lymph nodes through the flow of lymph. For example, if you have inflammatory process on the gums, bleeding, or there is already a diagnosis of "periodontitis" and "gingivitis", the infection penetrates into any part of the body through the lymph current. The third way is infection of the nasopharynx, tonsils, maxillary sinuses. Not enough rhinitis - get submandibular lymphadenitis. It is for all the reasons described here that lymphadenitis is a secondary disease. You will first need to cure the primary state of inflammation, and then carry out lymphadenitis therapy.
The submandibular lymphadenitis, as a disease, must be treated with caution. Because another reason for its occurrence may be Koch's wand (the one that causes tuberculosis) and the bacteria that provoke.
Symptoms
The main symptom is severe pain in the area of the lymph node, reddening of the skin at the site of inflammation and pain when touching this place. To the touch the skin can be hot - which means the progression of the inflammatory process.
The lymph node increases in size - due to tissue swelling and subsequent accumulation of pus. If at this moment to take a blood test, then there is an excess of the level of leukocytes - leukocytosis.
In the absence of antibiotic therapy in the treatment of lymphodenitis for several days there is a sharp deterioration in health, fever up to 39-40 degrees, weakness, chills, lethargy.
Submandibular lymphadenitis occurs in acute and chronic forms - consider them.
With a diagnosis of acute submandibular lymphadenitis, only one or several lymph nodes are inflamed at once. The node is constantly increasing in size, swelling, the skin around the site of inflammation turns red. In the tissues pus accumulates, which through time breaks through and infects the surrounding tissues. The patient has a sore neck, jaw, shoulder. Pain occurs during eating and communicating with someone.
If you do not cure completely acute submandibular lymphadenitis, then this translates this condition into a chronic form. In this case, the lymph node hardens, and the inflammatory process begins to spread to the surrounding tissue. Further, symptoms as in the acute form of the disease. Surgical treatment - the lymph node needs to be removed, while with acute submandibular lymphadenitis is treated with antibiotics.
Diagnostics
We list the methods for the diagnosis of lymphadenitis:
- Establishing a diagnosis of the symptoms and complaints of the patient;
- General blood analysis;
- Ultrasound (method determines the presence of pus inside the node);
- Puncture fluid from the lymph node for bacteriological analysis (the method will help determine which bacteria provoked the inflammatory process).
What doctor should I contact with my neck? To the maxillofacial surgeon and to the dentist.
Treatment
If you start the inflammatory process, the treatment is only surgical. But it is of two kinds. The first option - a doctor under anesthesia cuts the inflamed area, releases pus. A plus method is that it helps to avoid infection of surrounding tissues. If this is not done, there is a risk of sepsis (blood poisoning).
The second treatment option (non-traumatic) is the use of penicillin group antibiotics. List of medications (course duration 7 days):
- Cephalexin;
- Clindamycin;
- Amoxiclav;
- Lincomycin;
- Cefuroxime.
Treatment of purulent lymph nodes with folk remedies is impossible. With self-medication or without treatment, sepsis begins, followed by (with refusal of medical care) - fatal.
Prevention
Prevention submandibular lymphadenitis consists in maintaining oral hygiene and in the timely treatment of any inflammatory and infectious processes in the body (even if the patient does not feel pain and unpleasant symptoms - need to be treated). As mentioned above, with the flow of lymph, the bacteria spread throughout the body and can "strike" in the lymph nodes in the neck, groin, etc.
Disease prognosis
Lack of treatment provokes the onset of the chronic form of the disease. That involves only the operation, not drug therapy. There is a risk that the pus will burst out, resulting in infection of tissues, blood () and even - to death. Doctors argue that the consequences of not treating and late treatment for medical care with lymphadenitis - absolutely unpredictable. Do not forget who the neck and submandibular lymph nodes are a few centimeters from the dura mater. Pus from inflamed tissues at any time can spread to vital organs. What to do? Be more attentive to your health and do not forget to complain to your doctor in time and receive treatment recommendations from him.
It is a type of inflammation. lymph nodes, is the most common form of the disease. The main causes of submandibular lymphadenitis may be different inflammatory processes oral cavity with damaged teeth, chronic tonsillitis, and other diseases of the soft tissues of the gums. Submandibular lymphadenitis can be a sign of such common diseases as tonsillitis - chronic inflammation of the tonsils, gingivitis - inflammation of the gums, as well as obvious problems with the teeth.
Symptoms of submandibular lymphadenitis
The first sign of the disease is the occurrence of tight, painful nodes under the lower jaw, then they can be accompanied by ebbing pain, redness of the skin over the inflamed areas, an increase in body temperature, and sleep disorders. The disease, as a rule, develops gradually, with the alternate manifestation of its main features. At first, the inflamed lymph nodes are barely palpable, when you press them, the patient experiences a slight pain. At the initial stage of the disease, they are very mobile and have sharp outlines.
Further, the nodes increase in size and do not allow painlessly lower and raise the jaw. After a certain period of time, which is usually not more than three days, the lymph nodes increase to a very noticeable size, the swelling that occurs spreads to the entire submandibular surface and continues to move down towards the collarbone, the skin surface becomes inflamed red, appears stretched. At the same time, the mucous membrane of the mouth also becomes inflamed and becomes red, any attempts to open the mouth are accompanied by constantly increasing pain.
Body temperature at this stage of the disease can rise up to 38 degrees, the patient often has a loss of appetite, an indifferent attitude to everything happening around, the appearance of insomnia and feelings of constant fatigue. If at this stage of the disease it is possible to correctly determine the source of the infection, then a speedy cure of lymphadenitis is still possible. Most often, patients engage in self-treatment, which does not bring positive results, and seek qualified help too late when the symptoms of lymphadenitis become more pronounced: the pain becomes shooting, the body temperature rises below 40 degrees, and the skin above the inflamed nodes becomes blood red and then and burgundy hue.
Blue skin indicates the presence in the lymph nodes of pus, which acquires a gradual release to the skin. Pus is actually not large but very dangerous.
Diagnosis of submandibular lymphadenitis may be difficult due to the similarity of its main symptoms with inflammation of the submandibular bed, sublingual region or salivary glands, perimaxillary infiltrate or abscess. Sometimes the doctor can hardly determine the exact localization of the inflammatory process.
Treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis
Treatment of inflamed submandibular lymph nodes is primarily aimed at eliminating the infection that caused the disease. It requires compliance with strict hygienic measures, which include rinsing the mouth with a special solution called “Burov's liquid”, as well as cold lotions using this product. If the inflammation becomes purulent, treatment should be carried out with the use of antibiotic drugs, warm lotions and heating with Slux (infrared radiation).
With purulent inflammation a single lymph node may be used for the treatment of a disease. A small surgical intervention is used in which a small skin incision is made above the inflamed area, the capsule of the node itself is cut, a special drainage catheter is inserted into the incision and the site is cleaned of pus accumulated in it.
As medical practice shows, several lymph nodes are often inflamed at once. In such a case, a more serious surgical intervention is used. It lies in the section of the submandibular region, the introduction of a tube for drainage into the open cavity with the subsequent closure of the wound using special clamps. In this case, the use of antibiotics.
Often it is the second method that is used. Treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis with antibiotics alone may be ineffective in some cases. It allows you to eliminate the main symptoms of the disease and alleviate the situation of the patient, but not cure the inflammation completely. Often, after such treatment, the disease returns and proceeds in a stronger form. Therefore, surgery is the main method for today to treat inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes.
The most common type of lesion of the submandibular lymph nodes is submandibular lymphadenitis. Lymph nodes are a barrier to infections that cause disease. Most often the disease develops due to diseases of the teeth and gums, as well as due to chronic tonsillitis.
Causes of submandibular lymphadenitis
This disease is not an independent pathology and develops only in the presence of infection in places along the lymph flow. The following inflammatory processes can lead to the disease:
- characterized by the presence of infection in the circulatory tissue;
- tonsillitis, in which the processes of inflammation of the tonsils are observed;
- caries of teeth, which has an old form;
- gingivitis is a gum disease.
Many are concerned that the occurrence of submandibular lymphadenitis may indicate development cancer disease. However, as statistics show, this ailment in 99% of cases has nothing to do with cancer tumors.
In some cases, inflammation may occur separately from other diseases. This is possible if the cause of infection was the injury.
Symptoms of submandibular lymphadenitis
The main sign of a developing ailment is pain in the area of the lymph nodes. At first, the pain is felt only during palpation, but then it becomes pulsating and constant. This causes discomfort to the patient, forcing him to take a forced position during sleep. In addition to the pain of the patient also bother
- hyperemia and edema of the affected area;
- enlarged lymph nodes in size;
- skin temperature rise over swollen lymph nodes;
- increase in body temperature;
- heat alternating with chill.
In chronic submandibular lymphadenitis, signs of intoxication are not so clearly expressed, because the patient’s general condition suffers little. When the disease becomes chronic, a radical treatment may be required, including the removal of the lymph node.
Traditional treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis
The fight against the disease is aimed at eliminating the cause of the infection. Treatment includes:
- rinsing with special solutions;
- overlay lotions;
- antibiotics;
- heating by infrared radiation;
- taking vitamins.
When the disease enters the purulent stage, surgery is performed. If there is an affected node, a cut is made above it, the introduction of a capsule of drainage and washing of the wound.
To ensure the effectiveness of therapy against submandibular lymphadenitis can include treatment with antibiotics. Receiving these drugs should be carried out even in the initial stages of the disease to slow its development. The most effective means are:
- Ampicillin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Ceftazidime;
- Amoxiclav
The course of treatment should last at least ten days, after which there is a decrease in the size of the lymph nodes.
Submandibular lymphadenitis - treatment of folk remedies
To speed up the healing process, you can use the old recipes.
Infusion of herbs:

To adhere to such treatment is necessary for a month.
To combat the disease you can apply compresses:
- Compress of soaked in gauze impose overnight and tied with a scarf.
- Also for compresses, you can use walnut tincture. To do this, the leaves of the plant (two spoons) are poured with vodka (100 g) and left to infuse for three days.
Popular
- What is useful mineral water
- What is the name of the Scottish skirt
- What women like a man archer
- Dosage and use of doxycycline when tick bite
- Sinupret - complete instructions
- Number of antennae in arachnid and insect crustaceans
- Help for enterobiasis for the pool, how much is valid
- Ceftriaxone suspension. What is ceftriaxone?
- Third degree breast cancer: prognosis and treatment
- Salt Scrub for the scalp




