Disease dental cancer of the oral cavity. Oral Cancer: Symptoms and Treatment
Among the malignant tumors of the head and neck oral cancer in frequency ranks second after laryngeal cancer. Malignant tumors diagnosed in the oral cavity - this is mainly different kinds squamous cell carcinoma. According to the International Classification, malignant tumors originating from stratified epithelium are divided into:
- Intraepithelial carcinoma (carcinoma in situ).
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Types of squamous cell carcinoma:
- verrucous carcinoma;
- spindle cell carcinoma;
- lymphoepithelioma.
When describing cancer of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, there are three anatomical forms of the most common tumor growth: exophytic, or papillary; infiltrative and ulcerative-infiltrative.
Regardless of the anatomical form of the tumor and its localization, there are three periods of development of cancer of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity: the initial, the advanced and the neglect period.
Initial period. During this period, patients most often complain about the feeling of having foreign body, discomfort in the mouth. A number of patients complain of a burning sensation, moderate pain when eating. On examination of the oral cavity, erosion, small ulcers without severe infiltration, seals located on the mucous membrane of the cavity or in the submucosal layer, hyperkeratosis presented in the form of whitish spots, outgrowths of the mucous membrane with a whitish surface can be detected. Despite the diversity of the clinical picture in the initial period, the main symptom that forces you to see a doctor is pain.
Developed period. The main symptom of a developed period of cancer of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is pain of varying degrees of intensity. The pain can be local or radiating most often in the ear, the temporal part of the corresponding side. In this period, the oral cavity mucosa is subdivided into anatomical forms.
Papillary cancer may develop on the background of papillomatosis, verrucous leukoplakia. In this form, the tumor has the appearance of compacted tissue, towering above the surrounding tissue. Education may have the appearance of an elevated hemisphere or have a base in the form of a wide leg. In the thickness of the tissue, according to the projection of the tumor, an infiltrate is palpated without clear boundaries. The surface of the tumor may be hilly, covered with areas of keratinized epithelium, in some cases represented by a fine-grained surface, bleeding easily with a minor injury.
Infiltrative cancer is quite rare, but it is she who presents the greatest difficulties in diagnosis. The disease begins with the appearance of a low-painful infiltrate in the thick of the tissues, the mucosa covering it is most often hypermetered. Over time, an increase in infiltration occurs, which limits the function of the oral organs.
Patients complain of pain, difficulty in eating, talking. With further course of the disease, the infiltration ulcerates, complaints of pain increase, and bleeding may occur.
Ulcerative Infiltrative Cancer occurs more often than others, its share among other clinical manifestations of oral mucous membrane cancer is about 65%. The tumor is presented as a cancer ulcer, the shape and size of which vary widely and depend on the location and stage of the process. The edges of the ulcer are roller-shaped raised above the surrounding tissues. The bottom is either in the form of necrotic tissue, or covered fibrinous bloomafter removal of which is determined by the bottom of the ulcer krateobrazny form, made of fine-grained tissue, bleeding easily with a minor injury. At the base of the ulcer, a dense infiltrate is palpated, which, as a rule, exceeds the size of the tumor ulcer in size and often extends to adjacent anatomical structures.
Period of neglect. Depending on the location of the tumor, it spreads to the muscles of the floor of the mouth, the muscles of the cheek, and the skin grows.
Cancer of the mucous membrane of the alveolar part of the upper or lower jaw spreads to the bone tissue. With the localization of the tumor in the posterior oral cavity - on the palatine arches, lateral pharyngeal sections. Based on clinical observations, it should be noted that the cancer of the posterior oral cavity is more malignant and metastasizes to the regional the lymph nodes in more early terms. Histological examination of the posterior oral cavity has, as a rule, low differentiation of tumor cells.
Cancer of the mucous membrane of the tongue
Most often, the tumor process affects the middle and posterior third of the lateral surface of the tongue.
The most common symptom in this location is pain, which is often associated with trauma to the tumor on existing teeth. Earlier, functional impairment occurs (chewing, swallowing, speech), which is associated with both pain syndrome and limited mobility of the tongue with a pronounced infiltrative component of the tumor. The ulcer on the lateral surface of the tongue has a round or oval shape, at the base of which is determined the infiltrate. On palpation, as a rule, there is a discrepancy between the size of the tumor (ulcer) and the infiltrate, which exceeds its size and can spread both to the tissue of the floor of the mouth and to the muscles, going beyond the midline, to the root, up to a total lesion of the entire tongue.
Cancer of the oral mucosa
In the area of the floor of the mouth cavity, the ulcer-infiltrative form of the tumor is more common. In the anterior regions of the floor of the mouth, the ulcer has a rounded shape, in the middle and posterior third it is slit-shaped, and in some cases of observation, one part of the tumor is located in the region of the floor of the mouth, and the other on the lateral or anterior surface of the tongue.

In the initial period, patients complain of a feeling of a foreign body. A painful symptom appears at the accession of a secondary infection and in more late terms. Topographic and anatomical features of this localization determine the early spread to the tissues of the tongue, the mucous membrane of the alveolar part of the mandible. During the period of neglect, the tumor infiltrates the muscles of the floor of the mouth, submandibular salivary gland, destroys the alveolar part and the body of the mandible.
Cancer of the mucous membrane of the cheeks
Most often the tumor process is manifested in the form of ulcerative-infiltrative form. A typical localization of a tumor ulcer is the mucous membrane along the line of teeth closing, the retromolar region, the corners of the mouth, i.e. those anatomical areas of the cheek that are most often subjected to traumatization. In the initial period, patients complain of discomfort, foreign body sensation. More than half of patients noted that the disease began with the appearance of pain when eating, talking. With the progression of the disease, the tumor process extends to the muscles of the cheek, the skin, the mucous membrane of the transitional fold, the alveolar part of the upper or lower jaw. When the tumor is located in the distal parts and the process spreads to the chewing or internal pterygoid muscle, the opening of the mouth is limited. For tumors of the retromolar region, metastasis is observed earlier and the involvement of the tonsils and palatal handles in the process.
Cancer of the mucous membrane of the palate
The most frequent localization of squamous cell carcinoma is the soft palate. On the hard palate, tumors from the small salivary glands are more common: malignant - adenocystic carcinoma, adenocarcinoma; benign - polymorphic adenomas. For squamous cell carcinoma of the mucous membrane of the palate, the ulcer-infiltrative form is more characteristic. At this location of the tumor, one of the earliest symptoms is the appearance of pain, which causes patients to consult a doctor.
Cancer of the mucous membrane of the alveolar process
The tumor with the same frequency is located on both the lingual and buccal side. The upper jaw also does not determine the predominant lesion of any side of the alveolar process (palatine or buccal). More common ulcerative infiltrative form. In the developed period, the bottom of the tumor ulcer is the dirty-gray bone tissue, although radiographically bone-destructive changes may not be detected. During the period of neglect, bone destruction occurs and the process spreads to the body of the lower jaw, surrounding soft tissues. In the upper jaw, the process destroys the bone tissue of the alveolar process, followed by germination of the tumor in maxillary sinus. The tumor process manifests itself quite early and the main symptom is often pain, which increases with food intake.
Regional metastasis of oral mucous membrane cancer
The frequency of metastasis and localization of metastases depends on the location of the tumor in the oral cavity, its differentiation, and the characteristics of lymph circulation. In cancer of the mucous membrane of the lateral surface of the anterior and middle third of the tongue, metastasis occurs in the submandibular, middle and deep cervical lymph nodes. The frequency of metastasis in the defeat of the tumor process in these areas is 35-45%.
When the tumor is localized in the posterior third and root of the tongue, metastasis occurs much more frequently in the upper deep cervical lymph nodes and is about 75%.
With the defeat of the anterior process of the floor of the mouth cavity, the mucous membrane of the anterior alveolar part of the mandible, the mucous membrane of the cheek, metastasis occurs in the submandibular and submental lymph nodes. Cancer of the posterior regions of the floor of the mouth, the retromolar region, metastasizes mainly to the upper and middle jugular lymph nodes.
Tumors of the mucous membrane of the palate and the alveolar process of the upper jaw metastasize to the submandibular and posterior pharyngeal lymph nodes, sometimes metastasis is determined in the frontal ear nodes.
In cancer of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, there are cases of contralateral and bilateral metastases on the neck.
In some cases, in the diagnosis of regional metastases, palpation examinations alone are not enough, there may be cases of both hyper- and underdiagnostics. Great importance for the presence of enlarged lymph nodes and possible damage to the tumor process is attached to methods of radiation diagnosis: computed tomography, ultrasound. Important for the diagnosis of regional metastases is a cytological method for the study of punctate from enlarged lymph nodes, the reliability of this method is 70-80%.
TNM clinical classification.The classification is applicable only for cancer of the oral mucosa:
- TX - Not enough data to evaluate the primary tumor.
- T0 - Primary tumor is not detected.
- Tis - Preinvasive carcinoma.
- T1 - Tumor up to 2 cm in the greatest dimension.
- T2 - Tumor up to 4 cm in the largest dimension.
- T3 - Tumor more than 4 cm in the largest dimension.
- T4 - Oral cavity: the tumor spreads to the adjacent anatomical structures - the cortical bone, the deep muscles of the tongue, maxillary sinus, skin.
- NX - Not enough data to evaluate regional lymph nodes.
- N0 - No signs of metastatic lesion of regional lymph nodes.
- N1 - Metastases in one lymph node on the affected side up to 3 cm in the largest dimension.
- N2 - Metastases in one lymph node on the affected side up to 6 cm in the largest dimension, or metastases in several lymph nodes on the affected side up to 6 cm in the largest dimension, or metastases in the lymph nodes of the neck on either side or on the opposite side up to 6 cm largest dimension.
- N2a - Metastases in one lymph node on the affected side up to 6 cm in the largest dimension.
- N2b- Metastases in several lymph nodes on the affected side up to 6 cm in the largest dimension.
- N2c - Lymph node metastases on either side or on the opposite side, up to 6 cm in the largest dimension.
- N3 - Metastases in the lymph nodes more than 6 cm in the largest dimension.
- MX - Not enough data to identify distant metastases.
- M0 - No signs of distant metastases.
- M1 - There are distant metastases.
Grouping by stages
| Stage | Grouping by stages | ||
| 0 | Tis | N0 | M0 |
| I | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| II | T2 | N0 | M0 |
| III | T3 | N0 | M0 |
| T1 | N1 | M0 | |
| T2 | N1 | M0 | |
| T3 | N1 | M0 | |
| IVA | T4 | N0 | M0 |
| T4 | N1 | M0 | |
| Any T | N2 | M0 | |
| IVB | Any T | N3 | M0 |
| IVC | Any T | Any N | M1 |
Treatment of oral mucosa cancer
The main methods of treatment are radiation, chemotherapy and surgery, as well as their combination with each other. Cancer of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity belongs to moderately radiosensitive tumors, but despite this, the radiation method is the most common. It is used in almost 90% of patients. The most common in the treatment of this group of patients received remote gamma therapy, which is carried out as an independent method of treatment, and in combination with other antitumor methods.
As an independent method of treatment in patients with cancer of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, it is more often used for palliative purposes. In some cases, especially with low differentiation of tumor cells, with the prevalence of the tumor process T1-T2, it is possible to obtain a complete regression of the tumor. However, the clinical observations of many authors and their own allow us to conclude that radiation treatment as an independent method of treatment does not give a stable result. The best results were achieved with combined treatment, when surgery was included in the plan of antitumor methods, which can be performed after preoperative radiation treatment (the second stage of the combined treatment) and before the radiation treatment (the first stage of the combined treatment).
Surgical treatment of patients with cancer of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is an important step, the features of which depend on the prevalence of the process and localization. Surgery is performed according to all the rules adopted in oncology, i.e. the tumor should be removed within healthy tissues, some distance from the defined boundaries 2.5-3.5 cm. As an independent method, the operation in this group of patients is practically not performed due to the high probability of recurrence. For T1 tumors after radiation therapy, it is possible to remove the tumor within the organ. An example is the operation of a half-resection of the tongue. Locally common tumors require combined operations when adjacent anatomical structures are included in the tissue to be removed.
Combined operations in the maxillofacial area lead to disfigurement of the patient, significantly violate such important body functions as the ability to eat, breathe, speak, etc. In this regard, an important component of surgical intervention is the restoration of lost organs and partial or complete restoration of function . Restoration of organs and functions can be performed during the operation in full, if this is not possible due to various circumstances, then the restorative part should be preparatory for subsequent interventions to restore lost organs and tissues and impaired functions.
Chemotherapy in patients with tumors of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is indicated for a common process, the presence of metastases or relapses. Antitumor regimens of combination drugs with a different mechanism of action significantly increase the effectiveness of treatment. The use of chemotherapy before radiation treatment has a radiosensitizing effect - hypoxia is reduced, the blood supply to the tumor tissue improves, the size of the tumor decreases.
The most rational approach to the treatment of patients with cancer of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is the use of a complex chemotherapy - radiation treatment - surgery.
"Diseases, injuries and tumors of the maxillofacial region"
by ed. A.K. Iordanishvili
The concept of "oral cancer" includes the appearance of tumors or lesions on any surface of the mucosa: tongue, cheeks, gums, palate. These can be ulcers, papillomas, bumps or growths. It is an insidious disease, quickly giving metastases and requiring immediate treatment.
Despite the frequent cases of late seeking help, Israeli doctors have achieved some of the highest results in this area of oncology. A complete set of diagnostic equipment, robotic operating rooms, a skilled staff of radio, otorhinolaryngological, and other surgeons defeat oral cancer every day.
The team of doctors affects the affected areas:
chemotherapy;
ray method;
surgically.
When performing minimally invasive operations, surgeons try to preserve the tissue surrounding the neoplasm and all its functions. Irradiation and chemical action is directed precisely at the tumor, and does not affect healthy tissue and excess radiation load on the body as a whole. Thus, the patient has a high chance to continue the quality life after recovery and not to feel disabled.
Free consultation of Israeli doctors: jaw cancer treatment in Israel .
 Israeli medicine has achieved high results in the prevention and treatment of oral cancer
Israeli medicine has achieved high results in the prevention and treatment of oral cancer Among the causes that cause cancer of the oral cavity, experts identify various factors that affect the mucous membrane, and as a result lead to the appearance of precancerous formations (atrophy, hyperplasia, leukoplakia):
- General condition of the body. It may reduce the ability of the mucosa to resist. The disease is easier to develop in the human body, in which there are any or disruption of other organs. These pathologies often include improper work. gastrointestinal tractor hormonal balance disorder.
- Syphilis transferred. This disease, as the cause, is determined by some doctors, as when collecting the anamnezasifilis was once transferred in 7.8% of patients with oral cancer.
- Changes in the teeth, inflammation of the salivary glands, various kinds of chronic infections. The sharp edges of the teeth, poor quality dentures can lead to permanent mechanical injury oral cavity, which in turn will precede the onset of cancer. Directly these reasons provoke this malignant formation.
- Tobacco, alcohol, hot food. Especially strongly affects the origin of such tumors, in which the mucous membrane for a long time washed with juice from tobacco. 57% of people who suffer from cancer of the gums, use tobacco. Eating too spicy or hot foods, lack of vitamin A, also contribute to tumors.
- Poor oral hygiene and irregular dental visits.
- Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays can cause lip cancer.
- The papilloma virus plays an important role among the factors of oral cancer.
Prevention
Prevention of oral cancer should be to eliminate the factors that contribute to its appearance. First, you should constantly monitor oral hygiene and regularly undergo examination by a dentist. Secondly, every person, regardless of whether he wishes to prevent cancer or not, needs to eat right. Food should not be too hot or hot, it should contain the necessary amount of vitamins and minerals. Thirdly, if a person is sick chronic diseasesHe needs to constantly monitor the state of his health and the progression of diseases, be monitored regularly by a doctor.
The first symptoms of oral cancer
The first and main symptoms of the fact that a malignant formation in the mouth area lives in the body are painful and very discomfort in the zone where it begins to occur - in the outbreak.
They are present somewhere in 25% of patients, but usually the majority associate them with diseases of the teeth or diseases of the throat, for example, with angina. In addition, ulcers begin to form on the mucous membrane, and over time they do not disappear.
Possible symptoms of oral cancer
But such symptoms are not observed at all and not always. There is a group of other additional features. These include white or red spots that appear on the mucous membrane of the skin, directly in the mouth or throat, and do not disappear for some time. There may also be swelling or thickening in the mouth and on the lip. With cancer, it is difficult and very painful to swallow food and fluids, to talk and chew. Sometimes the mouth itself may become numb or even bleed. Suddenly, teeth begin to fall out for no apparent reason. A slight swelling in the neck also becomes a signal that malignant processes occur in the body. A person can noticeably lose weight in a very short time, while the reasons for this are also incomprehensible. Another important symptom is bad breath.
If the above signs of oral cancer appear, you should immediately contact the doctor who is treating you or your dentist. If you diagnose cancer in time and begin immediate treatment, the chances of a full recovery can be increased.
But the most important occurrence of signals that indicate the occurrence of diseases is not a sentence and a guarantee that it is the malignant tumor that develops in the body, since these symptoms can be a signal not only about this disease.
Required survey
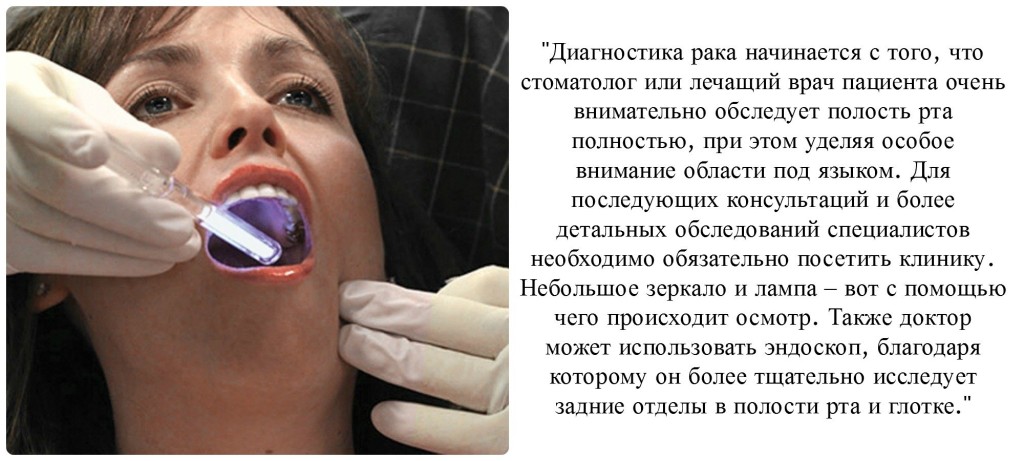
In order for the doctor to put the patient a detailed and correct analysis in this case, you need to undergo a biopsy procedure. This is a process during which a physician selects a small piece of tissue from a patient in order to examine it later under a microscope. Biopsy occurs with the use of anesthesia, as a rule, is common, and requires a mandatory short-term presence from the patient in the clinic.

Also, to establish the general health of a person, blood tests and X-rays of organs chest. In addition, when establishing a diagnosis of oral cancer, doctors may use other methods. For example, to detect bone lesions, he may prescribe an x-ray of the facial area of the skull or neck. In order to assess the condition of the jaws and teeth, the doctor may use a special type of radiography - orthopantomogram. also used to obtain detailed images of tissues and organs. For some patients, special dyes are injected intravenously. It improves the clarity and quality of images. In the diagnosis of malignant tumors of the oral cavity, computed tomography can also be used; it is absolutely painless and takes 10–30 minutes to complete. Bone scan is one of the studies that helps to see the pathology in the bones.
What to do if you have been diagnosed with Oral Cancer?
If the doctor has diagnosed oral cancer, this is not a sentence. The most important thing is not to panic. Moreover, if the diagnosis was made at the initial stage of the disease, then there is a chance to cure it completely.
Healing is a must. The doctor may offer the patient different types of treatment: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and biological therapy. Usually, the patient is attributed the method that is most suitable for the degree and type of his disease and can accurately cope with cancer in a particular case. In this case, the attending doctor should discuss with the patient all possible consequences after the therapeutic procedure. Doctors should observe the entire treatment process, so the patient must obey what they say.
Regular visits to the polyclinic and medical examinations are also very important, especially after undergoing therapy. They include x-rays, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, if necessary. Such surveys can be carried out even for several years.
Also, with the diagnosis of “oral cancer”, the patient should try the use of traditional medicine. But only with them should be treated very carefully, as this is not something professional and proven. In addition, it is not known how the interaction between traditional and popular means will occur. But, regardless of the type of treatment, a psychological attitude and a great desire to get rid of the disease forever is very important.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy: all the pros and cons
(Video: the choice of tactics of complex treatment)
Each patient, depending on the type and stage of his illness, doctors prescribe a particular therapy, that is, treatment, which can be of several types. Two of the main ones are chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
In radiation therapy or radiotherapy, high-energy X-rays are used. Therefore, slight damage may occur to those tissues that remain healthy. In the early stages of the disease, such treatment is used as an independent method. It can be assigned before the operation. This will reduce the chance of cancer recurring.
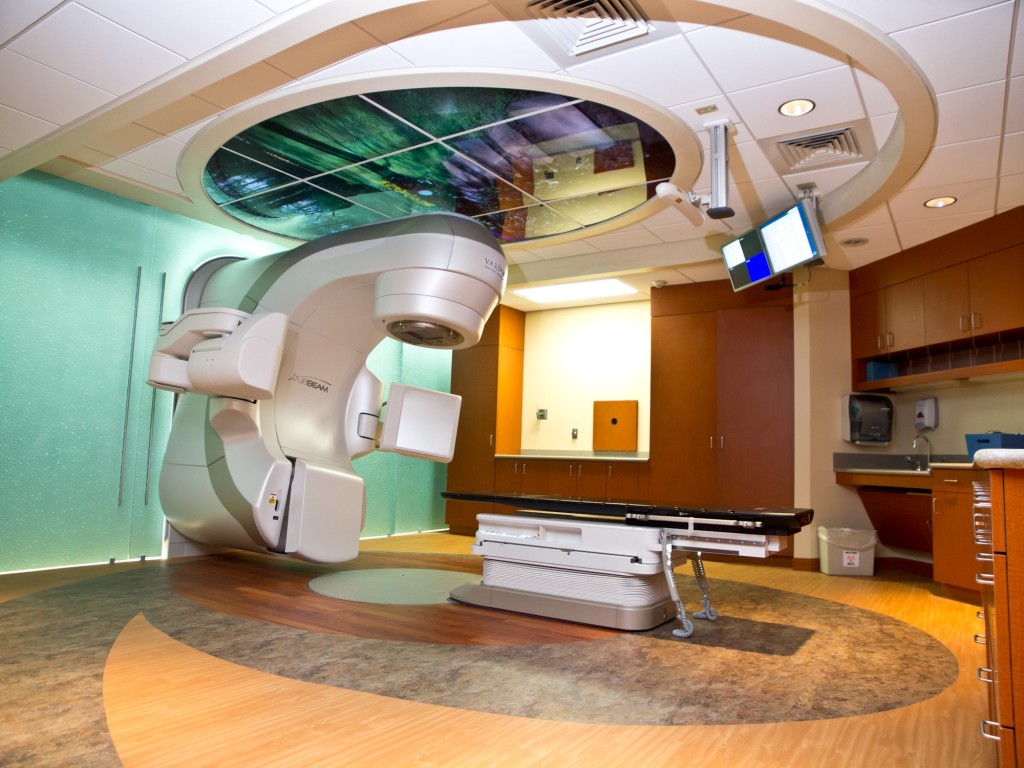
Radiation therapy is actively used in the defeat of the lymph nodes of the neck. In some cases, this treatment can be given in combination with chemotherapy. But this method has side effects. It can blush, darken or even hurt the skin in those areas that have been irradiated. This usually occurs during the second week of therapy and may last a month after it. Also, the skin can peel or burst, so you need the right care, which tells the doctor. Often the voice hoarses, taste changes. Eating can be difficult, swallowing can be painful. Because of this, additional drugs are prescribed. Often, radiation treatment affects the amount of saliva. It becomes less. In such cases, it is recommended to use sprays with artificial saliva. But most of these effects disappear quickly after cessation of therapy.
Chemotherapy destroys cancer cells. Such drugs are prescribed before radiotherapy or surgery, together with radiation treatment, after it, or when cancer spreads to other organs. If chemotherapy is prescribed after surgery, the risk of recurrence is reduced. malignant tumor.
It is usually used in the treatment of lip cancer. Medicinesusually administered intravenously. But they can cause a decrease in the number of blood cells, which can cause all sorts of infections. Therefore, during chemotherapy, the patient needs to undergo blood tests.
Also, the side effects of chemotherapy include nausea, vomiting, pain in the mouth of the company, baldness and fatigue. If any of this appears, you must immediately inform your doctor.
Folk ways to combat cancer
Among the variety of methods for the treatment of oral cancer pathologies are highlighted and folk methods. Various kinds of compresses are widely known, for example, from dry grass of celandine. 3 tbsp. l chopped herbs are poured 300 ml of boiled water. All this together is brought to a boil and left for 3 hours. Then, I put the gauze in three layers, moisten it in this liquid and apply it to the tumor for an hour. The procedure is repeated at least three times a day.
A compress from urine also helps. If the wound is not open, it is recommended to apply grated carrots mixed with the juice of celandine or hemlock tincture. They are taken in a 1: 1 ratio. If the wound is already open, then next to the use of this mixture should drink a glass or two of carrot juice. You can also apply wipes soaked in this juice to the wound (5 times per day). 
Productive and compresses out. You can use a mixture of ointment prepared from one hundred grams of fresh unsalted melted pork fat and twenty grams of camphor in powder form. It is used as a compress, which is applied for two to three hours.
Oral cancer can also be treated with ointments. Mix, for example, 10 grams of herb powder ground into powder, 40 grams of petroleum jelly and 10 milliliters of carrot juice. It is also recommended to water the wound with a thick solution of yeast, and then apply wipes soaked in it.
There are tinctures that help with oncopathology. In cancer, lips are advised to take hemlock tincture, starting with a few drops and increasing to a daily rate of 30 drops. If no side effects appear, you can increase the dose to 40 drops. The entire course of such treatment should occur within 90 days. also in traditional medicine Many other means of fighting cancer are widely used.
Oral cancer is a malignant tumor that affects any part of the oral mucosa, including cheeks, throat, gums, tongue, lower and upper jaw, lips.
The reasons
Currently, the exact cause of cancer is not known. Experts point to factors that provoke the emergence of this serious illness.
Smoking. Tobacco smoke contributes to the constant irritation of the cells of the oral mucosa. About 90% of patients suffering from cancer of the oral mucosa, smoke or use chewing tobacco.
Alcohol abuse. Alcohol also irritates the oral mucosa. The combination of smoking with alcohol significantly increases the risk of disease.
Irritation of the mucous membranes with dentures for a long time. Improperly matched dentures lead to more significant absorption of tobacco or alcohol. As a result, the negative impact on the oral mucosa is enhanced.
Leukoplakia. An entity called a precancerous condition. This is a limited spot of whitish color, the size of which does not exceed 1 cm. Such formations are most often solitary, usually do not rise above the mucosa. Found on the mucous membrane of the cheeks or tongue.
Erythroplasty Another form of precancerous condition. It is a formation of reddish color, developing on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
Human papillomavirus. In some cases, it is a provoking factor for the appearance of cancer of the oral mucosa.
Symptoms
Symptoms of oral cancer depend on the period of the disease.
1. The initial period. The most common symptom of the disease is an unusual feeling in the affected area. When examining the oral cavity, you can see various changes - white spots, papillary tumors, superficial ulcers, compaction of tissues and mucous membranes.
In the initial period of the development of the disease, pain in the oral cavity is noted in 25% of patients. Most often, pain occurs in case of cancer of the posterior half of the mouth or alveolar jaw. However, in half of the cases of pain associated with diseases of the teeth, tonsillitis.
In the initial period of development of cancer of the oral mucosa, there are three anatomical forms:
- ulcerative form - the most common; in one half of the patients, ulcers develop quickly, in the other, slowly;
- nodular - manifested by hardening in tissues or compaction in the mucous membrane, which is surrounded by whitish spots; seals are clearly limited and develop much faster than ulcers;
- papillary form - characterized by the formation of dense processes on the mucous membrane, which are usually covered with undisturbed mucous membrane; develop very quickly;
2. Developed period. The patient has numerous symptoms of oral cancer. In most cases, patients suffer from oral pain. Although there are cases of the absence of pain. Pain may have a local character or give to a specific area of the head, for example, in the temporal region, in the ear. In many patients, there is an increased saliva secretion, fetid odor from the mouth. This occurs as a result of disintegration and infection of the tumor.
There are two forms of advanced cancer:
- exophytic form - may be papillary (the tumor has the shape of a fungus with papillary or plaque outgrowths) and ulcerative (superficial ulcer with a limiting roller of tumor growth);
- endophytic form - sometimes ulcerative-infiltrative (the ulcer is located on a large tumor infiltrate) and infiltrative (diffuse organ damage); the mucous membrane of the oral cavity with these tumors has no ulcers;
Endophytic forms, diffusely damaging organs, are more malignant than exophytic forms having a limited type of growth.
3. The period of neglect. Symptoms of oral cancer are greatly exacerbated. The disease spreads rapidly, destroying the surrounding tissues. At this stage, the tumor is extremely aggressive and malignant.
Treatment
The therapy of this disease is carried out by standard cancer treatment methods - surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy. The method used depends on a number of factors: the general condition of the patient, the size of the malignant tumor, the degree of its germination in nearby tissues and organs, the stage of development cancer tumor, the existence of regional and distant metastases. Often in the treatment of oral cancer combine several methods of therapy. Usually, a tumor is irradiated before or after surgery. Often also used surgery and chemotherapy. All this can significantly increase the chances of successful treatment.
Radiation therapy is the effect of ionizing radiation on the cells of a malignant tumor. But, in addition to affecting cancer cells, radiation also affects healthy cells. However, cancer cells, however, are more sensitive to ionizing radiation.
Radiation exposure is carried out by contact or remote method. In the contact method, special objects are applied to the tumor for a certain time, which emit radiation. With the remote method, the irradiation is carried out in a special chamber. A beam of radiation is directed to the area of the tumor.
A side effect of radiotherapy for oral cancer is thyroid irradiation. Therefore, before starting treatment, the function of the thyroid gland is checked by examining its hormones.
Chemotherapy - the use of chemotherapy drugs that suppress livelihoods cancer cells tumors and destroying them. Chemotherapy drugs come in different groups. The doctor selects the type, method and duration of use, the dose, depending on the type of tumor, its size, stage of development and the presence of metastases. Chemotherapy is carried out before surgery or radiation therapy to reduce the size of the tumor. Or after surgery and radiation therapy to destroy the remaining cancer cells.
Chemotherapy is injected directly into the bloodstream of the patient, resulting in their effect on the organs and tissues of the body. Related to these are the side effects of their use.
Treatment of oral cancer with surgical intervention. The type of surgical treatment depends on the size, location of the tumor, the degree of germination in the surrounding tissue, the presence of metastases. With minimal consequences for the patient, the doctor can remove a malignant tumor that has not sprouted into neighboring tissues or organs.
Sometimes the surgeon is forced to remove part of the palate or lower jaw. With the development of regional metastases in the lymph nodes of the neck, they are also subject to removal.
The prognosis of oral mucosa cancer depends on the form of the disease. The papillary form can be cured most successfully. The ulcer form is one of the most difficult and unfavorable for treatment.
Attention!
This article is posted solely for educational purposes and is not a scientific material or professional medical advice.
4.75
4.75 out of 5 (4 votes)Sign up for an appointment with the doctor
Cancer is an uncontrolled proliferation of cells that invade neighboring tissues and interfere with their normal development and functioning.
Cancer is dangerous diseasewhich, if not detected and eliminated in time, can lead to death. Cancer treatment is a complex process involving multiple procedures.
Oncological diseases of the oral cavity are a group of characteristic tumors in the area of the mouth. Unlike the oncology of other organs, oral cancer can be diagnosed at an early stage, and therefore, treatment can be started as soon as possible. In this case, the patient does not always pay attention to the signs of oral cancer, which may indicate the presence of a tumor. As a result, the treatment is prescribed out of time, and, as a result, the corresponding complications can occur. The forecast in this case is much less favorable.
Who can get sick?
At risk are:
- older men are sick 7 times more often than women of the same age group;
- for smokers, oral cancer is 6 times more common;
- with the use of chewing and snuff tobacco, the risk of developing the disease increases 50 times;
- people who use excessive amounts of alcohol are 6 times more likely to suffer from oral tumors;
- people who have a genetic predisposition;
- people spending a lot of time in the sun.
Causes of disease

Research scientists oncological diseases, found that the causes of tumors in the mouth are the following factors:
- use of tobacco products (both ordinary smoking and the consumption of snuff and chewing tobacco);
- frequent and heavy drinking of alcohol, especially in combination with smoking;
- contact with harmful substances;
- type 16 papilloma virus can cause oral cancer;
- inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity.
Cancer symptoms
The disease proceeds in several stages, each of which is characterized by certain signs.
First stage
At this stage, the patient feels strange sensations in the mouth, and these sensations are not always painful. Visually, in the oral cavity one can detect small formations, colorless spots, ulcerative lesions of the mucosa, seals on the mucosa, indicating cancer of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Accordingly, at the first stage of the development of the disease, 3 groups of neoplasms are distinguished: ulcers, nodes, papillaries.
Ulcerative form occurs in patients most often. It is characterized by the formation of small ulcers in the oral cavity, which grow over time (the rate of increase in the formation may be different).
The nodular form is characterized by the presence in the oral cavity of specific seals, which are characterized by clear forms and a rapid rate of increase. Seals can have a natural color or whitish color.
Papillary form is a specific outgrowth that forms on the mucous membrane. Formations quickly increase in size, as a rule, do not give painful sensations.
Stage of development
Symptoms of oral cancer at this stage may be the following:
- availability pain sensationswhich can be both local and spread to neighboring tissues and organs;
- presence of unpleasant stench from the mouth. This is due to the process of infection of the formation and oral cavity;
- increased salivation.
Running stage
The disease is more intense, there is a sharp increase in the number of tumors, and their increased growth. Symptoms of oral cancer increase, become more pronounced.
Cancer Varieties
Tongue cancer
The tumor most often develops in the area of the root of the tongue. Rarely noted the presence of formations in the lower part and at the tip.
Cancer of the floor of the mouth
A bottom tumor develops in about 20% of cases. A bottom tumor may form together with tumors of other parts of the oral cavity. The prognosis of oral cavity cancer may be different, depending on the degree of tumor development and on what stage it was detected.
Cancer of the mucous membrane of the cheeks
The development of ulcerative tumors on the inner side of the cheeks is characteristic of this case.
Sky cancer
Malignant tumors form on the surface of the sky, affecting mainly the small glands of salivation.
Cancer of the alveolar membrane of the jaw
This species is characterized by pain. In this case, the sensations may resemble a toothache.
Gum cancer
The tumor can be located anywhere in the gum area. Observed frequent metastases.
Stage of the disease
There are several stages in which oral cancer occurs:
Stage 1 involves the presence of small tumors whose cells do not yet spread to the region of the neighboring tissue. The forecast in this case is quite favorable.
Stage 2 is characterized by an increase in the formations of about 2 times, while the tumor cells have not yet penetrated the lymph nodes and other organs.
At stage 3, the tumor continues to grow, its cells have penetrated into the lymph node area. Metastases are absent. They manifest in other organs (most often, in the lungs), only in 4 stages.
Diagnostic methods
In order to detect cancer of the oral cavity, it is necessary to undergo an examination at the dentist. The doctor carefully examines the oral cavity for abnormal formations and areas, probes the throat, face, neck, determines the presence of tumors in these places.
When abnormal areas are found in the oral cavity, a biopsy is taken (a smear taken from a suspicious area). In the process of biopsy, the doctor determines the quality of the cells taken material.
In the event that oral cancer is started, other studies will be required to identify the presence of metastases in various organs.
Treatment
Depending on the type of tumor and the stage of its development, appropriate treatment is prescribed. The most common options: surgical treatment, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Surgical intervention can be carried out without excision of the tissue, if the tumor is mobile. Otherwise, for example, if there is cancer of the jaw, the tumor is removed along with its part. Lip cancer is also surgically removed. In this case, the tumor is removed in layers, which allows you to save the lips. With a significant degree of spread of tumors, surgical removal of the lymph nodes (if they are affected), as well as tracheal dissection (if the presence of a tumor makes breathing difficult) can be performed.
Radiation therapy can be used as an independent method of treatment (in the presence of numerous small tumors), and as an addition to the surgical method (if the tumor is large enough, it must be removed by surgery, and radiation can be used for final destruction of cancer cells). Most often, exposure is external, but in some cases it is more appropriate to use internal exposure when a particle of a radioactive metal is injected into the body of a tumor.
Chemotherapy. This method is the use of special medications that inhibit the growth and development of the tumor. This method is used before surgical and radiation treatment, or in combination with them.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent the onset and development of cancer are fairly simple and standard.
Being formed from mucosal cells, oral cancer affects the surrounding tissues, manifesting itself as ulcers and germination. I must say that oral cancer includes a number of cancers, including cancer of the lips, soft and hard palate, tongue, throat, and buccal mucosa. In all cases, early diagnosis of the disease gives a chance for a positive outcome of treatment.
Five-year survival of patients with oral cancer is 41%, three-year - 56%, and the average annual survival, regardless of the type of oral cancer, is 81%. In general, this type of cancer takes a small percentage of all human cancers, it accounts for 1.5% of all malignant tumors. The most susceptible to this disease are men aged between 40 and 60 years old, while women get sick 4 times less often. Interestingly, this type of cancer among the oncological diseases of the male takes the 6th place.
As it develops, oral cancer is divided into three periods, it is initial, developed and running.
Early Signs of Oral Cancer
Cancer at the initial stage of development manifests itself a sense of mild discomfort in the field of their education. During the inspection, you can see white spots, seals in the mucous membrane, papillary tumors, tissue seals.
Often, patients come to the primary examination due to the occurrence of pain, which, I must say, the patient begins to disturb at the very beginning of the development of cancer only in a quarter of cases. Such pain is often mistaken for a symptom of other diseases, such as tonsillitis.
Oral cancer can be divided into three main forms, it is ulcerative, nodular and papillary. Each form of cancer also has its own symptoms.
The most common form of oral cancer is the ulcerative form, which is manifested by characteristic ulcerative formations on mucous tissues.
When nodular form specific seals occur inside the mucosa. This type of cancer develops more rapidly than the previous one and may be accompanied by the appearance of white spots around the seal.
The presence of dense outgrowths above the mucous membrane indicates a papillary form of cancer. Such a tumor also tends to progress very quickly.
It is worth noting that cancer of the oral cavity at the initial stage of its development is always formed first in the outer layer of the mucous membrane, and later on it grows either further outward or into the tissues.
Oral cancer during development
Along with the development of a cancer in the oral cavity, new brighter symptoms appear. First of all, it is a growing neoplasm itself, which begins to deliver considerable discomfort to the patient. Interestingly, even with a developed stage, pain may not occur. However, in most cases, the pain is still present and becomes quite painful. In addition, they can irradiate to other areas of the head, for example, in the ear.
In addition, a characteristic symptom of a developed stage of oral cancer is bad breath, which indicates the disintegration of the neoplasm and its infection.
In addition, in medicine, such a cancer is divided into two of its anatomical forms, each of which is also divided into several types.
The exophytic form is divided into papillary, in which the neoplasm takes on a mushroom or plaque-shaped form, and ulcerative, when the ulcer that has formed develops into a crater over time.
The endophytic form is also divided into two groups; these are ulcerative infiltrative tumors and infiltrative tumors. The first are ulcers localized on a massive infiltrate that grows into tissue. At the same time, ulcers may look like rather deep cracks. The second group includes tumors that are not related to ulcers, while there is a diffuse lesion of the mucous membrane.
Symptoms of advanced oral cancer
First of all, it should be said that oral cancer is considered one of the most aggressive and malignant cancers, among other cancers. It grows pretty quickly, rapidly destroying the tissue located near it.
Most aggressively behaves cancer of the root of the tongue, in which the tumor quickly affects the palatine arches and pharynx. However, cancerous lesions in the posterior region of the mouth are much more aggressive and difficult to treat than cancer in the anterior part.
Like many other types of cancer, the process of metastasis is characteristic of malignant neoplasms in the oral cavity at more advanced stages of development.
Metastases for this type of cancer are mostly spread to the lymph nodes of the neck. However, the site of metastases is directly dependent on the location of the primary malignant tumor. For example, cancer of the tongue, located in its anterior part, most often spreads not only to the lymph nodes of the neck, but also to the submandibular lymph nodes.
It must be said that oral cancer metastases very rarely reach distant areas of the body.
Most often, patients seek help from a doctor already at fairly advanced stages of the development of the disease, when an infection joins the most malignant neoplasm. At the same time, in one third of patients at the time of the initial examination, the tumor had already metastasized.
In cancer of the mucous tissues of the cheeks at the advanced stage of the disease, the tumor infiltrates from the skin, tonsils and lips. With the defeat of the mucous sky, there are quite strong pain and significant discomfort.
In the case of the appearance of a tumor of the minor salivary glands, patients seek help for painful sensations in the oral cavity, which are usually caused by the addition of an infection and the formation of a site with ulcerations.
Considered what is meant by external otitis. What are the symptoms, causes and treatment of the disease. Presented how the treatment of otitis externa in children. Recommendations for the prevention of otitis externa are given.
If you recognize the disease at the very beginning of its development and take proper measures, then a quick cure is possible. Recipes for the treatment of throat for 1 day. Methods of use.
As part of the article, we will learn more about the reasons and find out why nose bleed and how to stop it. Because this knowledge can be useful in the most unexpected circumstances.
Popular
- Breast cancer is curable at any stage.
- The remedy for the cold Sinupret
- Azitrox - official instructions for use
- Chicken-bjaka: allowed antibiotics were found in Russian chicken
- Oral Cancer: Symptoms and Treatment
- Dark and thick blood during menstruation.
- Modern analogues of doxycycline tablets
- Is it possible to die from pneumonia
- What earwax will tell all about your health
- Tussin: instructions for use