Diseases of the blood system. Blood disorders in children
Malignant formations affect not only the adult population of the planet, but also children. It penetrates both into the cellular tissue and into the circulatory system. in children and adolescents can be attributed to a pandemic. Too often, doctors began to make a diagnosis of leukemia, who had not yet known life and defenseless patients.
Affected cells invade the entire body, circulating through it along with blood circulating through it. Unfortunately, this type of oncology is very difficult to identify. The tumor can not be palpated. It can be detected only by analyzing the bone marrow.
The reasons
Blood cancer in children, what are the causes of its occurrence? What causes cells to share uncontrollably? Before proceeding to this issue, you should know what the hematopoietic system is.
The human body is a complex mechanism in which each organ has its own role. This mission is performed by the cell, while it maintains an inextricable link with the whole organism.
The bone marrow is the blood-forming organ in which blood cells originate. This concept itself is extensive, since there are several types of such cells.
- Leukocytes - they act as a barrier against penetration of microbes, viruses, infections and other various microorganisms.
- Platelets. Their purpose is to preserve the integrity of the body tissue. In case of damage, blood clots appear. Thus, platelets close the damaged tissue and the blood stops circulating.
- Red blood cells - a kind of transport of the human body. They deliver oxygen to the cells.
Each of the above listed cells can degenerate into malignant. More than any other such anomalies are young cells. There are many reasons for such a metamorphosis. The most important factors are listed below:
- Radiation exposure - a sharp jump in pathology among the population occurred after the bombing of Hiroshima, Nagasaki and the explosion at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant.
- Bad environmental background. Technical progress has not only the positive side. With its leap forward, the ecology around the world has deteriorated sharply.
- Genetic predisposition. In a family where there were cancer patients, the risk of getting cancer is much higher.
- A weakened immune system, especially after chemotherapy.
Important! The main cause of leukemia in children is a weakened immunity after a serious illness. Scientists revealed an interesting fact. Children with allergies are less susceptible to oncological diseases. This is explained by the fact that the immune system is in constant tone.
In order to develop a disease, just one mutated cell is enough. It is rapidly beginning to divide, and the symptoms of blood cancer appear quickly. The less the patient's age, the more rapidly the cancer develops.
Symptoms
The symptoms of blood cancer in children and adolescents are almost identical, as are adult patients. At the beginning of the pathology, the disease is difficult to identify, but the following symptoms can be identified:
- Somatic symptoms - fatigue, drowsiness or insomnia, forgetfulness;
- Wounds and ulcers do not heal for a long time, fester;
- There are bruises under the eyes, swelling, skin color has a pale tint;
- The nose often bleeds, the gums bleed;
- Frequent viral and infectious diseases, acute respiratory infections.
The symptoms of a child’s blood cancer are similar to the symptoms of common diseases, for this reason it is difficult to diagnose the disease. Attention should be paid to the following:
- A slight increase in body temperature for no reason;
- Aching sensation in the elbows, knees. Bones become fragile.
- Lack of appetite - the baby refuses to eat, even his beloved.
- Frequent headaches, dizziness, fainting.
- Fatigue;
The above symptoms are found in respiratory and infectious diseases, for this reason they are not emphasized. They should cause wariness if such signs may appear in the complex to them:
- Sharp weight loss;
- The skin color has a yellowish tint and it becomes dry;
- The child has apathy, he wants to sleep constantly;
- Irritability appears;
- Increased sweating during sleep;
- A reddish rash appears on the skin;
- The entire group of lymph nodes is enlarged;
- In some cases, increases liver, spleen, stomach.
Important! If you find the signs mentioned above, the child must be urgently shown to the doctor. You should also not miss the signs of internal bleeding - vomiting with blood, severe weakness, tachycardia, hypotension, the discharge of blood from the anus, cough with dichorus, tarry stools and bloody urine. Such symptoms may be mild, but in no case can they be ignored or self-treated.
Diagnostics
If you suspect a blood cancer, the child is sent for examination, which will include a blood test. It is he who will accurately indicate whether there is pathology or not.
According to the condition of the blood, a preliminary diagnosis will be made, then more in-depth research will be required:
- Bone marrow biopsy;
- Radiography;
- CT scan;
- Immunohistochemistry.
With their help, experts get a detailed picture of the disease - the degree of damage to the organs and bone marrow, the type of education and the presence of metastases.
A biopsy is performed using a special syringe, which is used to puncture the bones of the sternum or pelvis and produce material. A cytologist on the analysis of the material is able to give an accurate conclusion.
Modern medicine for the diagnosis of blood cancer uses immunohistochemistry. This relatively new diagnostic method allows you to determine the number of proteins found in cancer cells. According to the obtained indicators, a conclusion is made about the nature of the disease. This method is very accurate. Therefore, it is used in very difficult cases.
Blood test:
- Hemoglobin is significantly lower than normal. Its performance is 60-20 g / l. In the early stage of blood cancer, anemia is absent, but it is always present in the later ones.
- The level of red blood cells is underestimated to 1.5 - 1.0 × 102 / l.
- Increase or decrease in lymphocytes. Such a fluctuation is possible in children. According to the level of lymphocytes determine the stage and form of pathology.
- The number of reticulocytes is reduced. Reticulocytes are young red blood cells that do not have a nucleus. Their level from a normal indicator can go down to 10% - 30%.
- Platelets have lowered their levels. At the onset of the disease, a deviation from the norm may be imperceptible, but further reduction reaches 15 g / l. Basophilic and eosiphilic leukocytes disappear from the blood.
- A large number of blast cells in the acute form of leukemia, up to 99% of the total. In the chronic form of the disease, they are completely absent or present in small amounts - up to 10%. Children rarely have a chronic form.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate or ESR is sometimes reduced.
- Anisocytosis is leukocytes of different sizes.
The same blood test may show an increased activity of bilirubin, urea, gamma globulin, LDH, AST. And the level of fibrinogen, glucose and albumin is reduced.
Treatment
Doctors around the world never stop working to create more effective and safe methods of cancer treatment. But for today, there are only two of them:
- Chemotherapy;
- Bone marrow transplantation.
Chemotherapy is a method of treatment in which high doses of a very toxic drug are injected into the blood of a sick baby. The purpose of such medicines is the complete destruction of malignant cells in the blood.
The main drawback in this method is the non-selectivity of the effect of the administered drug - together with the oncological cells, healthy ones die. First of all, rapidly developing tissues suffer from chemotherapy:
- Hair bulbs;
- Bone marrow;
- Cells of the gastrointestinal tract.
For this reason, patients lose their hair, nausea occurs and diarrhea begins. Appetite decreases and anemia, leukopenia appears.
After such treatment, patients are prescribed blood transfusions to fill in the lost red blood cell and platelet counts.
Important! Chemotherapy in children and adolescents is much easier to tolerate than adults. And out of ten patients, seven are recovering.
During bone marrow transplantation, the patient is injected with a concentrate of this substance, withdrawn from a healthy donor. But before this operation is performed, the patient’s destruction of the “native” bone marrow is carried out with the help of chemotherapy. From this die and healthy and diseased cells.

This method of treatment of children is used in very extreme cases, when the tumor is extremely malignant. Donors for the operation often become close relatives. It can be brothers, sisters.
During the operation and before the bone marrow begins to function, the patient is in the intensive care unit. This is due to the fact that at this moment he is very vulnerable to any infection.
Parents should remember, the main thing in the treatment of any cancer, it is time. The later treatment begins, the greater the likelihood that the result will be ineffective.
Due to the fact that the body of children recovers much faster, the therapy in children is much easier than in adults.
Important! In any oncology, and in particular in cases of blood cancer, one should not resort to the help of traditional healers and homeopaths. The only thing that is allowed. This is a reception of vitamins and herbal decoctions that can normalize the work of the gastrointestinal tract.
Forecast
The end result of hemoblastosis in children depends on the type of education and the stage of the disease. Acute leukemia is known for its transience and aggressiveness. For this reason, the prognosis for this type of oncology is unfavorable.
In the chronic form of the pathology, a benign progression of the disease is characteristic and the prognosis is much more positive.
With acute lymphoblastic leukemia, a positive result of treatment reaches 75%, with acute myeloblastic -40 - 50%.
Blood cancer for babies - babies is considered very dangerous. Their bodies are underdeveloped and cannot fight the disease on their own. Diagnosis in such patients is more difficult. Unlike babies and teenagers, babies cannot talk about their condition. For this reason, many parents notice the symptoms of the disease too late and consult a doctor even when the pathology passes into a more aggressive stage. Infants with blood cancer lag behind in their development, early refuse breast, suffer from lack of appetite, do not gain weight, sleep poorly.
Cancer treatment with Mishin's coil:
The device, developed by Russian scientists, allows you to effectively deal with cancers with an electrostatic field. A huge number of tests and studies of doctors confirmed the positive effect of the device on ...
Treatment of tumors with Mishin's coil (video):
ORDER MISHIN'S COILS
Do not pull with the diagnosis and treatment of the disease!
Choose the best medical center for you from the list below and register for a PET-CT study!
With anemia, the number of red blood cells is less than 3.5 * 10 12 / l, and hemoglobin is lower than 110 g / l.
According to the etiological principle, anemia is classified as follows:
1) deficient (iron, protein, vitamin deficiency);
2) post-hemorrhagic (acute, chronic);
3) hypo-and aplastic (congenital, acquired);
4) hemolytic (congenital, acquired).
By the level of the color index of blood, anemia is divided into hypochromic - a color index of less than 0.85; normochromic - color index 0.85-1.0; hyperchromic - color index above 1.0. By the number of reticulocytes in the blood, anemia is divided into hyperregenerative - reticulocytosis is above 50%; regenerative - reticulocytes more than 5%; hyporegenerative - reticulocytes less than 5%. According to the average volume of red blood cells, anemia is divided into microspherocytic - the volume of red blood cells is less than 50-78 fl; normocytic - erythrocyte volume up to 80-94 fl; macrocytic - volume of erythrocytes 95-150 fl.
Iron deficiency anemia is most common in children and adults; depends on the social conditions of life, quality of nutrition, iron content in the diet.
The main cause of iron deficiency anemia is iron deficiency in food. The need for iron in the child is covered by natural feeding, the correction of artificial mixtures of iron. The iron contained in the female milk is enough for a child up to 3 months, further correction of the nutrition for the gland is necessary. Therefore factors predisposing to iron deficiency anemia are: late introduction of complementary foods and improper feeding; insufficient supply of iron (prematurity, multiple pregnancy, maternal anemia during pregnancy); iron absorption disorders (dyspepsia, intestinal and other diseases); increased iron loss (blood loss, helminthiasis); increased need for iron (frequent infections).
According to the level of hemoglobin in the blood emit mild, moderate and severe forms of anemia. Most often, anemia occurs in children under 3 years.
With mild iron deficiency anemia, paleness of the skin and mucous membranes, irritability, lethargy, and loss of appetite are observed. Hemoglobin level 110-90 g / l.
Moderate anemia is characterized by an even more pronounced paleness of the skin and mucous membranes; the child has pale nail beds, the skin has a waxy shade. Weakness, lethargy, apathy develop, appetite decreases. In language, signs of papillae atrophy. The hemoglobin level is 90-70 g / l.
Severe anemia is manifested by inhibition. The child is lethargic, adynamic. The skin and visible mucous membranes are pale, the skin is dry with a waxy shade; there are angular stomatitis, flattening of the nails (thinning), thinning, brittleness and dryness of the hair. Children have no appetite, there is a perversion of taste. Cardiac changes are detected: tachycardia, systolic murmur at the apex of the heart, development of myocardial dystrophy and heart failure is possible. Hemoglobin below 60 g / l.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of a clinical examination and data from the study of peripheral blood on the content of serum iron. In severe iron deficiency anemia, there is a decrease in its level to 12 mmol / l, an increase in the total iron-binding ability of blood serum above 78 µmol / l, an increase in transferrin level over 4 g / l and a decrease in ferritin concentration.
Therapeutic measures are aimed at correcting the diet, especially in the gland. Iron preparations are widely used in a dose of 5-8 mg / kg per day, which is divided into three doses. Parenteral iron is administered to children with severe anemia in the absence of the effect of its oral intake.
In acute and severe post-hemorrhagic anemias, when the hemoglobin level is below 70 g / l, the erythrocyte mass and washed erythrocytes are injected intravenously.
In children from 2 months of age who are breastfed, anemia is prevented with iron supplements at a dose of 1 mg / day. When artificial feeding evaluate the mixture on the content of iron in it.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis
The disease is characterized by disorders of the vascular component of the hemostatic system.
As a result of exposure to infection, vaccination, drugs, food allergies in the body produces immune complexes that act on the vascular endothelium. Violating the surface of the endothelium, these factors cause intravascular thrombus formation on the background of platelet hyperactivation. The child develops thrombovasculitis with simultaneous hypercoagulation. Small vessels of the skin, joints, gastrointestinal tract and kidneys are systemically affected.
Vasculitis is distinguished by the extent of vascular lesions. Depending on the predominant localization, skin, abdominal, renal, articular syndromes may occur, and mixed forms of the disease are observed. They distinguish mild, moderate and severe vasculitis; phases of activity and subsidence; acute, subacute and chronic relapsing course of the disease.
In children with vasculitis, allergy history is often burdened. The disease begins with the appearance on the skin of a child (usually the legs) of a symmetrical maculopapular rash. At first, the rash resembles an urticarial rash, then it becomes crimson, often has a flush character. Rash is located symmetrically, a favorite location - extensor surfaces of the limbs and buttocks. Angioedema, polyarthritis can develop. There are abdominal pains (abdominal syndrome), bloody vomiting and even melena.
Often associated with renal syndrome in the form of hematuria. Sometimes the disease is complicated by intestinal invagination, which requires the advice of a surgeon.
In children under 5 years of age, fulminant hemorrhagic vasculitis occurs with a fatal outcome.
Diagnosis is based primarily on the clinical picture. In the study of blood is determined by hypercoagulation. There is an increase in blood levels of circulating immune complexes. Often revealed inhibition of fibrinolytic activity.
Treatment of hemorrhagic vasculitis in children is carried out in the hospital. Sanitize possible foci of infection. Prescribe a hypoallergenic diet with the exception of all food allergens, enterosorbents and antihistamines. For severe skin syndrome and mixed forms of the disease, anticoagulants are used - heparin, chimes in combination with aspirin. Prednisolone is prescribed in cases of complicated, severe, prolonged vasculitis.
60-70% of children recover. Prognostically unfavorable is kidney damage. Children who have had hemorrhagic vasculitis should be under dispensary observation for 5 years. Vaccinations are carried out no earlier than 2 years after the last exacerbation.
Thrombocytopenic purpura
When the disease is formed hemorrhagic syndrome, caused by a decrease in the number of platelets (thrombocytopenia), enhanced by their destruction or insufficient education. Most often, thrombocytopenia develops as a result of immunization of the body.
Alloimmune and transimmune thrombocytopenia is associated with the transport of anti-platelet antibodies from mother to fetus (thrombocytopenia during the first days of life). Heteroimmune thrombocytopenia occurs as a result of the formation of antibodies in response to changes in platelets under the influence of viruses or drugs. Most thrombocytopenia and idiopathic thrombocytopenia (ITP) are among the autoimmune.
The flow is divided acute and chronic ITP with rare, frequent relapses or continuously recurring.
ITP is considered a disease with a hereditary predisposition. It manifests itself in children with a hereditary platelet defect. The implementation of this defect is possible under the influence of a viral disease, preventive vaccinations, physical or mental trauma, insolation, hypovitaminosis. These factors affect the immune processes in the body, causing the synthesis of anti-platelet antibodies by sensitized lymphocytes.
In children of early and preschool age, ITP develops, as a rule, after the infection has been transferred. A spotted-petechial hemorrhagic rash appears on the skin and mucous membranes, bleeding from the mucous membranes of the nose, gums, alveoli of the teeth is observed, internal bleeding is rare. Polychromic rash, polymorphic, asymmetric, resembles "leopard skin". Splenomegaly is found in 10% of children.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of a decrease in the level of platelets in the peripheral blood less than 140 * 10 9 / l. The retractions of the blood clot are disturbed, the bleeding time is extended, positive tests for capillary resistance appear. In the myelogram, the number of megakaryocytes is usually increased, but it may be normal.
If thrombocytopenic purpura is suspected, patients are hospitalized. If there is a pronounced hemorrhagic syndrome, glucocorticoids are prescribed. When bleeding is administered intramuscularly, амино-aminocaproic acid, dicine, adroxone, ATP, inside the drugs magnesium.
In case of a protracted, chronic course of ITP, the issue of splenectomy, indications for which are the duration of thrombocytopenia for more than 6 months, severe bleeding, not controlled by therapy, and suspicion of hemorrhagic stroke, is indicated.
Hemophilia
This is a hereditary disease that is inherited in a recessive manner; the gene is linked to chromosome X. In this disease, there is increased bleeding due to the insufficiency of coagulation factors. There are three types of hemophilia: A, B, C. With hemophilia A there is a deficiency of factor VIII, with hemophilia B (Christmas disease) there is a deficiency of factor IX, and with hemophilia C (Rosenthal disease) there is insufficient activity of factor XI. In addition, there is parahemophilia associated with a deficiency of the V factor.
Hemophilia in children appears more often after stopping breastfeeding and is manifested by hematomas and bleeding. Their severity depends on the concentration of a particular coagulation factor. Hemophilia A is the most severe form of the disease, its manifestations are observed at the level of factor VIII below 25%. Hemorrhages occur at the slightest injury, when changing teeth. Especially dangerous are hemorrhages in the brain.
Diagnosis is based on laboratory blood tests. Determine the levels of coagulation factors.
All patients with hemophilia are under the supervision of a hematologist. Ambulance for bleeding they enter the missing clotting factor. In hemophilia A, these are cryoprecipitate and PPSB concentrate. For stopping bleeding, 15–20 U / kg is used, for bleeding from the tongue, neck, and oral cavity, the dose is 25–50 U / kg, and if intracranial hemorrhage is threatened, 50 U / kg is administered. In case of hemarthrosis in the first days, the immobilization of the joint is shown, followed by physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises on the affected joint.
Leukemia
In children, acute leukemias most often prevail, and up to 75% of them are lymphoblastic leukemias. Less common non-lymphoblastic leukemia - up to 15-20%, even less often - chronic myeloid leukemia - 1-3%. The remaining forms are non-differentiable variants of acute leukemia. Boys get sick more often than girls.
The etiology of these diseases is still unknown.
Leukemia usually proceeds typically. Against the background of anemization, an intoxication symptom complex develops: an increase in peripheral lymph nodes, hepatosplenomegaly, hemorrhage. Signs of lesions of the skeletal system, brain. Join secondary infections.
For diagnosis in addition to clinical data, timely examination of peripheral blood to detect anemia, blast cells, and thrombocytopenia is necessary. A microscopic examination of the bone marrow is conducted in order to identify blast elements.
Children are treated in specialized departments according to anti-leukemic and anti-relapse therapy schemes.
Children, along with adults, often suffer from various blood diseases. Some of the ailments are treatable, and others in some cases are fatal. One of the key factors for successful control of the disease is timely diagnosis and the development of an effective treatment strategy. The most common blood disorders in children are anemia, hemorrhagic vasculitis, and leukemia.
Causes and consequences
All childhood blood disorders occur for specific reasons. Consider in detail the features of ailments.
Anemia
The occurrence of anemia is directly related to iron deficiency or vitamins, and its development is triggered by the destruction of red blood cells, bleeding, as well as a number of other factors. In addition, various acquired or genetic afflictions affect the deterioration of the condition.
In the absence of proper treatment, the patient is faced with a number of consequences.
- reduced immunity, low resistance to viruses; infectious diseases develop;
- the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, mouth, respiratory tract become sensitive to mechanical stress;
- decreases the intensity of absorption of nutrients in the digestive tract;
- cardiomyopathy develops; due to lack of oxygen, the heart begins to work more intensively, doubling the load, resulting in heart failure;
- swelling of the lower limbs;
- liver increases.
Another unpleasant consequence of anemia, in some cases, becomes a violation of the nervous system.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis
Schoenlein-Henoch Purpura is characterized by vascular lesions in the joints, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and epidermis. A feature of this blood disorder in children is that it occurs much more often in boys than girls.
For many years of study, experts have failed to identify the exact cause of this blood disease in children. The most likely option is a failure of the immune system, as a result of which the body begins to produce antibodies that infect healthy cells. Due to the autoimmune process, the vascular walls become thinner and petechial hemorrhages appear.
The exacerbation of this blood pathology in children can be caused by recent acute allergic reactions, infections, injuries, vaccinations, hypothermia, and other stressful situations for the body.
Leukemia
As in the case of many diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs, a number of aspects of the development of leukemia in children are still not fully known. Today, experts are confidently saying that the factors that provoke leukemia are:
- radiation;
- hereditary indicators (predisposition);
- immune and hormonal disorders;
- oncogenic viral strains;
- various chemical factors.
In addition to the reasons described above, leukemia can develop after undergoing a course of radiation or chemotherapy, through which malignant tumors and other oncological diseases are treated.
Symptoms
In the late stages, all childhood blood diseases are accompanied by pronounced symptoms. However, in the initial stages to determine the presence of a serious illness, it is often quite difficult. In order not to "start" the disease, you should not ignore the alarming signals, but promptly seek the help of a specialist.
Symptoms that may be caused by anemia include fainting during physical exertion, rapid heartbeat, pallor of the skin, chronic fatigue and weakness, and rapid fatigue.
If the hemoglobin level is not high enough, the integuments take on a sallow tint. Children under 1 year of age are at risk of mental retardation. Therefore, if a child sleeps a lot, refuses to eat, breathes heavily and gets tired very quickly, these symptoms should be described to a doctor.
In addition, hemorrhagic vasculitis is accompanied by more pronounced manifestations:
- abdominal pain (seizures or mild);
- the skin of the child becomes pale, the eyes sink, the tongue dries out;
- small episodes of hemorrhage appear on the epidermis;
- increased pressure, swelling of the face;
- hemorrhages over the joints, pain and inflammation.
In some cases, it can be difficult to identify the disease due to symptoms similar to the manifestations of anemia.
In turn, leukemia in children, regardless of the form of the disease, provokes one set of symptoms. An insufficient amount of oxygen enters the tissues of the body, from which the skin becomes very pale or becomes bluish. The child gets tired quickly, eats badly, and in the case of even a minor injury, he has severe bleeding, which is very difficult to stop.
From the above, it can be understood that all hematological diseases in children affect the overall well-being.
Diagnostics and types
Features of blood diseases in children are directly dependent on the degree of neglect and the type of leakage.
There are several types of anemia, and their separation depends on the value of the color index (PCP), which reflects the hemoglobin content in one red blood cell:
- hyperchromic (RFP - above 1.05); It is divided into three types: drug or vitamin deficiency anemia, and myelodysplastic syndrome;
- normochromic (RFP - from 0.75 to 1.05); There are four types: neoplastic, hemolytic, aplastic, post-hemorrhagic;
- hypochromic (RFP - below 0.75); subdivided into thalassemia and iron deficiency anemia.
In the process of diagnosing this disease, the doctor conducts a comprehensive examination and takes blood for analysis, the results of which are the decisive factor in the diagnosis. If necessary, for a final confirmation of the diagnosis, a hematologist may prescribe a histological examination of the bone marrow.
The process of diagnosing rheumatic purpura includes an examination, collection of family medical history, as well as a number of studies, including: tests, endoscopy, skin and kidney biopsy, ultrasound, and immunological research.
Depending on the characteristics of the flow, Schoenlein-Henoch purpura is divided into several types: articular, dermal, abdominal, renal and combined.
If the pediatrician notes signs of leukemia in a child, a blood test is assigned to confirm the diagnosis. Alarming indicators in the results are high ESR, thrombocytopenia, blastomy, leukocytosis or leukopenia, the absence of intermediate forms between blast and mature cells.
Mandatory procedures are sternal puncture and myelogram examination. If the results do not give 100% certainty, the doctor prescribes an ileal puncture.
Treatment
A number of different characteristics directly affect the treatment process; The doctor takes into account the type, degree of development of the disease and many other indicators.
The decisive factors in the treatment process is the timely diagnosis and prescription of an effective technique, including the necessary procedures and medications. That is why one should not engage in self-treatment, use traditional methods or look for information about preparations on the Internet. Only a qualified doctor who knows what kind of blood diseases in children can develop a strategy that will lead to complete deliverance from the disease.
Prevention
Most diseases of the blood system can be prevented by adhering to the advice of specialists and avoiding serious negative effects on the body.
First, exposure to ionizing radiation and toxic dyes that contribute to the development of hematological disorders should be avoided.
Secondly, it is necessary to abandon unreasonable blood transfusions and serious stress, which can provoke a number of serious ailments.
In addition, hypothermia, infection and other hazards that may have a negative effect on the child’s bone marrow should be avoided.
You can find out information about what kind of blood diseases in children, as well as select an experienced highly qualified specialist who will become the attending physician, on our website or by calling the help desk (the service is free). Experienced staff will provide detailed advice and answer all your questions.
Blood cancer in children and blood cancer in adolescents is not a rare disease, statistics and forecasts, which are not at all comforting for relatives or doctors. The whole world is trying to fight this pandemic. For some reason, cancer of the blood takes children from two to five years old, mainly because boys get sick with blood cancer more often (according to extras). In general, in medical terminology, the definition of blood cancer means various tumors.
A malignant tumor belonging to, can affect not only the cellular tissue of a living organism, but also the human circulatory system. This disease is called blood cancer. The saddest thing is that it is very difficult to determine this tumor by palpation, only when examining the bone marrow, one can understand that a person is sick.
In modern times, more and more the diagnosis is heard, which they began to put the most defenseless and not yet knowing life - blood cancer in children. Cancer cells affect the entire body, moving through it, circulating with the influx and outflow of blood. Unfortunately, blood cancer in children and adolescents has become a systematic disease.
The main causes of blood cancer in children is rapid cell division. Cells begin to form and function so quickly that the body ceases to cope with its tasks. For each cell in a certain period of life, its own role and its place.
Uncontrolled cell division in the body causes cancer. Cancer cells begin to compete with healthy ones for food, forming their settlement in new places, disrupting and breaking the work of the organism as a whole.
Blood cancer in children originates in the bone marrow, because the most important moments occur in this organ, which affect human life. is the progenitor of the entire circulatory system. In this small area of the body, blood is born, which then begins to circulate.
Children with blood cancer patients were exposed to radioactive substances, their cells go through a mutation stage, as a result of which accelerated cell growth cannot be controlled, this is what later leads to abnormal maturation. The cells begin to form a tumor, they stop giving the necessary elements to the body and work on themselves.
Uncontrolled cell division
The cellular structure is diverse, there are three main types:
- Leukocyte view. Blood cells are composed of leukocytes, this element performs a protective function.
- Platelet type. Platelets affect the integrity of the tissue, usually the damaged cell turns into a blood clot, the bleeding stops at that moment.
- Erythrocyte view. Red blood cells perform the nutritional function of the body, supplying cells with oxygen.
These cell structures can mutate into a cancer cell. Scientists have conducted a lot of research on this topic and found such a regular dimension that young cells are most vulnerable.
The most important causes of blood cancer in children:
- radiation (Chernobyl accident);
- ecology (in the period of technical progress, the ecology of the whole world has sharply decreased);
- predisposition at the gene level;
- weakening of the immune system (especially after chemical treatment)
Still, it is worth noting the most important cause of blood cancer in children - weakening of the immune system. After serious illness. But there is a very interesting fact, children with allergies are less susceptible to cancer, because their immune system is constantly in a state of heightened vigilance.
The signs of blood cancer in children and the signs of blood cancer in adolescents, as well as in adults, are almost the same. In the initial stage of this disease is very difficult to detect any signs. But you can still highlight a few signs:
- somatic signs (increased drowsiness or, on the contrary, it is not possible to fall asleep - insomnia, fatigue, forgetfulness);
- suppuration of wounds;
- poor and long healing of wounds;
- pale skin;
- bruises and bags under the eyes;
- blood from the nose;
- weakened immunity (frequent infectious diseases, frequent diseases of acute respiratory infections, etc.).

Blood from the nose, pale look
Signs of blood cancer in children and signs of blood cancer in adolescents are usually detected by laboratory tests.
Unfortunately, the symptoms of blood cancer in children and the symptoms of blood cancer in adolescents are similar to the symptoms of common diseases. This is the complexity of the diagnosis of blood cancer in children. When children are ill, the following symptoms may be noticed:
- change in body temperature (body temperature slightly increased to 37 degrees);
- aching sensations in the bony parts of the body (knees, elbows, etc.);
- no desire to eat (no appetite);
- headache;
- rare syncope;
- quick fatigue.

Lack of appetite
Since the above symptoms occur in acute respiratory infections, in infectious diseases, then, as a rule, these symptoms do not attach special importance. But besides all of the above, it is worthwhile to look at the child, since children can also have the following changes in the body:
- weight (weight loss);
- nervousness, irritability;
- drowsiness;
- dry and yellow skin.
The formation of blood cancer in the lymph tissue is caused by small seals in the groin, neck, underarms and over the clavicles. If seals are detected, it is necessary to consult a doctor; after certain examinations, the doctor will refer the child to an oncologist if he suspects cancer.
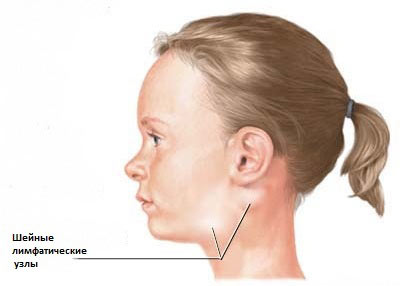
Lymphatic swelling
In general, doctors distinguish two - acute and chronic
Treatment of blood cancer in children and adolescents
Treatment of blood cancer in children and adolescents proceeds practically, as well as in adults. Scientists and doctors around the world are focused on creating a safe drug that could help many people (children, adolescents and adults) in the treatment of this terrible disease. But at present there are only two main ways: chemical therapy and changing the bone marrow with its transplant.
Chemical therapy is very toxic, the purpose of this treatment is the reducibility of toxic and dangerous drugs in the human body to combat tumor cells. Unfortunately, these drugs are so toxic that healthy ones die together with diseased cells. The hair starts to fall out, as the hair follicles die off, the gastrointestinal tract suffers.
Such treatment greatly undermines the body of a teenager and a child, further baldness occurs, loss of appetite, not uncommon nausea. Treatment with chemical therapy for blood cancer is much easier for children and adolescents than for adults; this is due to the fact that the children's organism, because of its youth, is restored more quickly and efficiently. Also, according to forecasts, the child's body perceives chemical therapy better and out of 10 children, as a rule, according to statistics, 7 are recovering.
During treatment, patients are isolated from the environment, because at this moment the body is so weak that the immune system can stop any breathing from the outside as an infection. Therefore, children and adolescents with cancer are under the strict supervision of doctors, parents, guardians.
Treatment with a bone marrow transplant occurs as follows: a donor is sought (as a rule, relatives are the donor), and the components of a healthy person are administered to a patient with a dropper. This treatment is very dangerous. With its use it is necessary to comply with all prescriptions of doctors. During the main treatment, you can use as a minor - taking vitamin complexes, drugs aimed at restoring the gastrointestinal tract.
Cancer prevention
Of course, it has not been fully revealed where it came from - a disease and, to the great regret, of all the inhabitants of the world there are no prophylactic agents for a blood cancer disease.
The only way to protect yourself and your children is to try to distance themselves from cancer-forming factors, such as radiation, try to improve immunity as before, hardening, use more natural food products, exercise a lot and actively engage in sports, train patriotism and reduce their excitability and nervous perception of life.
Video: causes of blood cancer in children!
Pallor in children is not necessarily a sign of anemia. It can be a consequence of poor blood supply to the skin, which is caused by constitutional features, inadequate exposure to fresh air, and slowed blood flow in the skin of rapidly growing children with labile circulation. Pallor can also be a symptom of a beginning infection. All these factors do not change the blood picture.On the other hand, with many complaints of a general nature (blood circulation lability, tachycardia, fatigue, loss of appetite, weakness of concentration, headache, shortness of breath during exercise), in many cases they are looking for the cause that caused them before taking a blood test and detecting anemia. Most often, it is iron deficiency anemia caused by recurrent infection or insufficient iron intake. Other forms of anemia in children are relatively rare.
Diagnostics: for diagnosis, it is necessary to determine the concentration of Hb (g / 100 ml) and the number of red blood cells in order to calculate the average content of Hb in a single red blood cell. After determining the hematocrit, it is possible to calculate the average concentration of hemoglobin in a single erythrocyte. By these indicators, hypochromic anemia can be distinguished from normochromic and hyperchromic. In rare cases, such as spherocytosis, the average red blood cell volume is of interest.
An accurate diagnosis of the form of anemia is a prerequisite for successful treatment. In some cases, the correct diagnosis is made only by a clinician, hematologist.
Leukocytosis
Leukocytosis most often indicates a bacterial infection. Exceptions: typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, septicemia caused by gram-negative pathogens, miliary tuberculosis. Bacterial leukocytosis is characterized by toxic changes in neutrophils: pycnotic nuclei, toxic granulation, Dele inclusion bodies, vacuolization of the cytoplasm.Leukocytosis, not caused by bacteria, may be associated with acute blood loss, metabolic acidosis, diabetic coma, and uremia.
Lymphocytosis
With age, the prevalence of lymphocytes in the blood formula, characteristic of small children, disappears, but as a pathological symptom it can be in pertussis and during recovery, especially after viral diseases. The relative content of lymphocytes sometimes reaches 90%. If leukopenia still occurs, pronounced lymphocytosis may be the reason for the erroneous diagnosis of lymphoblastic leukemia.The absolute increase in the number of lymphocytes occurs in acute infectious lymphocytosis (up to 100,000 leukocytes in 1 mm3, of which 85-95% are lymphocytes). The lymphocytes in this case, like other blood components, are not morphologically modified, which facilitates the differential diagnosis of lymphoblastic leukemia, especially if a mild upper respiratory tract infection is not accompanied by other characteristic symptoms: an increase in lymph nodes or spleen. In acute infectious lymphocytosis gastrointestinal disorders are frequent.
Leukopenia, agranulocytosis, lymphopenia
Syndromes, accompanied by a violation of antibody production:Bloom syndrome;
Glanzmann-Rinnicer's syndrome;
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome;
Chediaka-Steinbrinka-Higashi syndrome.
Leukopenia in febrile diseases indicates their viral etiology.
Agranulocytosis. If the number of neutrophilic granulocytes in the peripheral blood decreases to their complete disappearance, then the cellular immunity reactions are violated. When agranulocytosis after, as a rule, oligosymptomatic onset with an unclear temperature, necrosis of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity is soon discovered, ulcers, pyoderma and symptoms of sepsis appear. With acquired agranulocytosis, which is more common, changes in erythro- and thrombocytogenesis are absent or insignificant. Such a picture of the disease can suddenly develop after a viral infection or as a result of an allergic or anaphylactic reaction of the bone marrow to medicines. It is rarely possible to confirm the diagnosis by detecting leukocyte antibodies. Since a number of drugs are prescribed for febrile diseases, especially antipyretic, analgesic and sedative substances, it is difficult to ascertain the etiology of agranulocytosis, especially since many medications may be accompanied by leukopenia and agranulocytosis.
Leukocyte antibodies. In case of leukopenia in newborns, the possibility of transplacental intake of leukocyte antibodies, which may be the cause of transient inhibition of leukocyte maturation in the bone marrow, should be excluded, resulting in an increased susceptibility to bacterial infections for approximately three months.
Familial granulocytopenia. Large differential diagnostic difficulties are chronic granulocytopenia. Among them are rare benign familial hereditary forms that are discovered only by chance. Kostmann's hereditary pediatric agranulocytosis is detected in infancy due to recurrent febrile bacterial infection, especially skin infection. This disease is characterized by the almost complete disappearance of granulocytes from peripheral blood, while the bone marrow rich in cells indicates immature myelopoiesis or hypoplasia, which determines the unfavorable prognosis.
Periodic neutropenia. During the first 3 years of life due to recurrent infections, a stable or periodically increasing neutropenia suddenly appears, which, due to compensatory lymphocytosis and the preservation of the total number of leukocytes, is not always diagnosed. This chronic granulocytopenia has a good prognosis due to the maintenance of normal antibody production. However, this possibility should be remembered and differentiated this condition in young children with agranulocytosis and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. In doubtful cases, examine the bone marrow.
Syndromes, accompanied by a violation of antibody production. Lymphopenia may be a symptom of impaired lymphopoiesis and immunity reactions with antibody deficiency.
Bloom syndrome: body weight at birth is less than 2500 g, lag in growth, sometimes to nanism, hypogenitalism, telangiectatic erythema in the form of a butterfly on the face and on the hands, spots of the color of coffee with milk, photosensitivity and insufficiency of antibody formation.
Glanzmann-Rinikera syndrome: severe hypotrophy as a result of recurrent diarrhea, polymorphic rash, progressive lymphocytopenia, hypoplasia of the lymphatic apparatus, thrush.
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: hemorrhagic purpura and melena, allergic dermatitis with secondary infection, recurrent bacterial infections, chronic lymphopenia and thrombocytopenia.
Chediak-Steinbrinka-Higashi syndrome: anemia, leukopenia with typical bluish giant granules in the cytoplasm of leukocytes, thrombocytopenia, reduced resistance to bacterial infections. This disease is also characterized by partial albinism, photophobia, and hepatosplenomegaly.
Hemorrhagic diathesis
In the differential diagnosis of increased bleeding should be borne in mind three large groups of reasons:1. Violation of humoral coagulation factors, such as hemophilia, lack of fibrinogen, consumption coagulopathy.
2. Violation of the number, structure or function of platelets (thrombocytopenia, Verlgof disease, thrombopathy).
3. Violation of the vascular wall (for example, Schönlein-Genoch disease).
Flat asymmetrical bruises in combination with petechial hemorrhages indicate a violation of humoral coagulation factors.
Petechial hemorrhages are characteristic of thrombopenia, and with an increase in the deficiency of platelets in the future, flat hemorrhages appear.
Symmetric punctate hemorrhages indicate toxic or allergic damage to the vascular wall, about Shenlein-Henoch purpura.
The picture of the disease is often a combination of symptoms.
Impaired humoral coagulation factors. In some cases, the history allows differentiation between hereditary coagulopathies (hemophilia A and B, congenital fibrinogen deficiency), acquired coagulation disorders (lack of prothrombin in liver diseases, vitamin K deficiency) and consumption coagulopathy associated with acute or subacute disease (sepsis, Waterhouse-Frideriksen syndrome).
Platelet damage. Disorders of hemostasis are easily diagnosed, since they are usually accompanied by thrombocytopenia: Verlgof's disease or symptomatic forms of thrombocytopenia.
Bleeding due to thrombopathy (platelet dysfunction) can be diagnosed using special studies. Thrombopathies include hereditary thrombasthenia, in which flat petechial hemorrhages in the skin and mucous membranes are observed with a normal number of platelets. Bleeding time is extended, retraction of the blood clot does not occur.
Damage to the walls of blood vessels. Among hemorrhagic diathesis in children, the most common anaphylactoid purpura is Schönlein-Genoch, based on
acute hyperergic vasculitis of arterioles and capillaries lies. Histologically, changes in the blood vessels are almost the same as those for periarteritis nodosa. From the 2nd year of life, the picture of the disease is very characteristic: exanthema symmetric petechial skin hemorrhages and ecchymosis, urticaria, rheumatoid pain in the joints, pain throughout the body, hematuria, bloody stools. In infants, the disease proceeds with an even more pronounced urticaria. All blood coagulation tests (platelet count, clotting tests) are normal.
Secondary vascular purpura occurs in severe infections (eg, meningococcal sepsis), severe renal failure (uremia), severe form of vitamin C deficiency.
Rarely, children may have increased capillary fragility with recurring severe nasal bleeding - Randyu-Weber-Osler syndrome, which can be diagnosed by identifying visible angiomas and telangiectasias in other places. The number of platelets and coagulation factors are normal.
Leukemia
Increasing pallor, normochromic, in older children, sometimes hypochromic anemia with a reduced number of reticulocytes, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia with a progressive tendency to bleeding - all this may be hematological symptoms of incipient leukemia, accompanied by unclear fever, increased fatigue, anorectomy, anorectomy. long tubular bones or joints, as well as enlarged lymph nodes, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly.Often, acute leukemia begins when the number of cells is less than 10,000 (aleukemic form), of which 80-90% are abnormal lymphoid cells. ESR significantly increased, blood clotting due to a decrease in plasma coagulation factors II, VII, IX, X and platelet deficiency is disturbed, which is manifested by severe bleeding. In the bone marrow, a more or less homogeneous population of leukemic cells is formed, displacing normal cells.
The prognosis in children over 10 years of age with hepatosplenomogalia (the number of cells in the peripheral blood is more than 20,000 per 1 mm3) and with acute myeloid leukemia is unfavorable. It is important to differentiate between immature and mature leukemic cells, because depending on this, the treatment must be different. In principle, in connection with dystrophy of cells in leukemia, continuous transitions from completely immature hematoblasts to almost mature cells in chronic myeloid leukemia are observed, excluding such rare forms as eosinophilic leukemia or monocytic leukemia. About 85% of acute leukemias occurring in children are “lymphoblastic” leukemias with reborn hemocytoblasts. They are determined morphologically by a narrow, sharply basophilic border of the cytoplasm and a large peculiar lobular nucleus; nuclei and cytoplasm vacuolation.
The differential diagnosis of latent leukemia with diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, osteomyelitis, bone tumors, lymphosarcoma, Hodgkin's disease, bone metastases in neuroblastoma, is difficult.
Popular
- Blood disorders in children
- What can not drink a pill
- Blood disorders in children
- Blood disorders in children
- Bones: structure, composition, types of bones, types of connections and their characteristics
- How many live with lung cancer
- Influenza in children: how to treat, what can and cannot be done to parents, what medicines will help?
- "They are people too ..." - you say
- What helps "Prednisolone"
- How are menstruation for endometriosis?