Remantadin: instructions for use, indications and contraindications. Remantadin tablets, instructions for use.
Remantadin is an antiviral drug used for treatment and prevention.
Release form and composition
Remantadin released in the form of:
- Tablets containing 50 mg of rimantadine hydrochloride (10 and 20 pieces in a blister pack, 10, 20, 30, 40 or 50 each in dark glass jars);
- Capsules containing 100 mg of rimantadine hydrochloride (10 each in a blister pack).
Indications for use
Remantadin is prescribed for:
- Prevention of influenza in adults during epidemics;
- Early treatment and prevention of influenza in adults and children from 7 years;
- Prevention of tick-borne encephalitis viral etiology.
Contraindications
The use of rimantadine is contraindicated in:
- Acute liver disease;
- Chronic and acute kidney disease;
- Hypersensitivity to rimantadine and auxiliary components of the drug.
Remantadin is not prescribed:
- Pregnant women;
- Children up to 7 years.
Dosing and Administration
Tablets or capsules are taken without chewing inside, after meals. The drug should be started immediately after the first signs of flu. A more pronounced therapeutic effect is observed in cases of its use during the first 2 days of the disease.
Usually prescribed:
- 1 day - 3 times a day 100 mg (or once 300 mg);
- 2-3 days - 2 times a day, 100 mg;
- 4-5 days - once a day, 100 mg.
Before using the drug, children should consult a doctor. Typically, rimantadine children prescribed in a single dosage of 50 mg. The frequency of admission is determined by age:
- 7-10 years - 2 times a day;
- 11-14 years - 3 times a day.
Duration of treatment is 5 days.
For the prevention of influenza, adults are prescribed 100 mg of the drug once a day, the duration of the course is 10-15 days.
When a tick is detected, for prevention of tick-borne encephalitis, adults take 100 mg, 2 times a day, for 3 days. By appointment of the doctor in some cases, the course may be extended to 5 days. The drug should be taken immediately after the tick bite, but no later than 48 hours.
In elderly patients with arterial hypertension while taking rimantadine increases the risk of hemorrhagic.
With epilepsy in history and anticonvulsant therapy, the drug increases the risk of an epileptic seizure. In these cases, it is taken at 100 mg per day simultaneously with anticonvulsant treatment.
With influenza B virus, rimantadine has an antitoxic effect.
Prophylactic administration of the drug is effective in:
- The spread of infection in closed collectives;
- Contact with the sick;
- Increased risk of developing a disease (during a flu epidemic).
Perhaps the emergence of drug-resistant viruses.
Remantadin with simultaneous use lowers the effectiveness of antiepileptic drugs.
Absorption of the drug reduces enveloping and binding agents and adsorbents.
The effectiveness of rimantadine:
- Reduce - urine acidifying means (ammonium chloride, ascorbic acid);
- Strengthen - alkalizing means urine (acetazolamide, sodium bicarbonate).
Analogs
Analogues of rimantadine are:
- According to the active substance - Algirem, Orvirem, Rimantadin;
- The mechanism of action is Yodantipirin, Ladivin, Rebetol, Alloferon, Amiksin, Acyclovir, Valogard, Gepon, Imichimod, Tetraxolin, Citivir, Tamiflu and other antiviral agents.
Terms and conditions of storage
Keep out of reach of children, in a dry place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
The shelf life of the drug in the form of:
- Pills - 5 years;
- Capsule - 2 years.
INSTRUCTIONS
(information for experts)
on the medical use of the drug
REMANTADIN-BELMED
Agreed by the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus
Order No. 28 dated 1/19/2016
Tradename:Remantadin-Belmed.
International non-proprietary name:Rimantadine (Rimantadine).
Release form:pills.
Description:tablets of white color with a biconvex surface.
Ingredients: each tablet contains:
active substance: rimantadine hydrochloride, 50 mg;
excipients: lactose monohydrate, calcium stearate, potato starch.
Pharmacotherapeutic group:Antivirals for systemic use. Cyclic amines.
PBX code:J05AC02.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Rimantadine hydrochloride (hereinafter referred to as rimantadine) is effective against various strains of influenza A virus (especially A 2 type). Active against tick-borne encephalitis viruses (Central European and Russian spring-summer), which belong to the group of arboviruses of the Flaviviridae family.
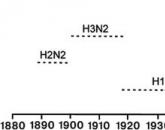
Rimantadine inhibits viral replication in the early stages of the cycle, possibly disrupting the formation of the viral envelope. Genetic studies have shown that the specific protein M2 of the virion has an important antiviral effect on rimantadine against the influenza A virus. Invitrorimantadine inhibits the replication of all three antigenic subtypes of the influenza A virus isolated from humans - H1N1, H2N2 and H3N2. Rimantadine does not affect the immunogenetic properties of inactivated influenza A vaccine. Correlation between the sensitivity of influenza A virus to rimantadine invitroand the clinical efficacy of the drug has not been established.
Rimantadine has an antitoxic effect against influenza caused by virus B. It is not effective for other acute respiratory viral infections.
As a result of the use of rimantadine, the appearance of strains of influenza A virus resistant to the action of rimantadine is possible. These resistant strains can cause the development of influenza with typical clinical symptoms in people from the contact group.
Development of resistance to rimantadine was observed in strains of seasonal and pandemic influenza viruses in patients receiving rimantadine. Substitution in at least one of the five amino acids in the transmembrane domain M2 causes the development of resistance to rimantadine. The most frequent substitutions that cause the development of resistance of H1N1 and H3N2 viruses to rimantadine are associated with S31N, less often they are caused by substitutions in A30F, V27A, V30A and L26F.
It was shown that influenza viruses A (H1N1) (S-OIV), which were resistant to rimantadine, contained substitutions in S31N. Consider local recommendations on the resistance of influenza viruses to antiviral agents.
Pharmacokinetics
Rimantadine is well but slowly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Communication with plasma proteins is about 40%. The maximum plasma concentration when taking 100 mg 1 time per day is 74 ng / ml (from 45 ng / ml to 138 ng / ml), and when taking 100 mg 2 times a day - 416 ng / ml. Most of the drug is extensively metabolized in the liver.
The elimination half-life from blood plasma is 24-36 hours. Excreted in the urine: less than 25% of the dose - unchanged, about 20% - in the form of hydroxyl metabolites. In renal insufficiency, the half-life increases by approximately 2 times. In patients with renal insufficiency and in elderly people it can accumulate in toxic concentrations, if the dose is not adjusted in proportion to the decrease in creatinine clearance.
Indications for use
Early treatment and prevention of influenza in adults and children over 7 years old; prevention of influenza during epidemics in adults.
Method of application and dosing regimen
Accept inside after food, washing down with water. Treatment of influenza should begin within 24-48 hours after the onset of symptoms.
As a remedy for influenza Remantadin-Belmed prescribed by one of the following schemes:
Scheme 1: Adults: on the 1st day - 100 mg 3 times a day; in the 2nd and 3rd days - 100 mg 2 times a day; in the 4th and 5th days - 100 mg 1 time per day. On the 1st day of the disease, it is possible to prescribe the drug in 150 mg 2 times a day or 300 mg per dose.
Scheme 2: Adults: 100 mg (two tablets of 50 mg) 2 times a day for 7 days.
Children aged 7 to 10 years appoint 50 mg 2 times a day; 11-14 years old -50 mg 3 times a day; The course of treatment is 5 days.
For flu prevention Remantadin-Belmed is prescribed 50 mg 1 time per day for 10-15 days. The prescribing physician may increase the dose for adults up to 100 mg twice a day.
In patients with severely impaired liver function, severe impaired renal function (creatinine clearance from 5 to 29 ml / min) or renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance ≤ 10 ml / min) and elderly patients, a dose reduction to 100 mg per day is recommended. Because of the possibility of accumulation of rimantadine metabolites in patients with impaired liver and / or kidney function, it is necessary to control side effects.
Side effect
From the side of the central nervous system: reduced ability to concentrate, insomnia, dizziness, headache, nervousness, irritability, excessive fatigue, ataxia, depression, gait disturbances, euphoria, increased physical activity, tremor, hallucinations, convulsions.
From the digestive system: dry oral mucosa, anorexia, nausea, gastralgia, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea.
On the part of the respiratory system: dyspnea, bronchospasm, cough.
From the senses: tinnitus, disturbance or loss of taste, disturbance of smell.
Since the cardiovascular system: heartbeat, tachycardia, arterial hypertension, cerebrovascular disorders, heart failure, syncope.
Other: hyperbilirubinemia, allergic reactions (skin rash).
The incidence of adverse reactions, especially those associated with the gastrointestinal tract and the nervous system, increases significantly when taking the doses higher than recommended.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the drug, acute liver disease, acute and chronic kidney disease, thyrotoxicosis, pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding should be discontinued for the period of treatment), children under 7 years of age.
Carefully. Epilepsy, arterial hypertension, cerebral arteriosclerosis, chronic renal and / or liver failure.
Overdose
With the use of rimantadine-Belmed in high doses, there is an increase in side effects.
An overdose of amantadine (a remedy like rimantadine) was manifested by the development of arousal, hallucinations, cardiac arrhythmias, and death is possible. If you have symptoms of overdose, you must stop taking the drug and consult a doctor.
Precautionary measures
When treating patients with renal and / or liver failure, a lower dose of the drug is necessary.
With the use of rimantadine-belmed, exacerbation of chronic concomitant diseases is possible.
Elderly patients with arterial hypertension increase the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Patients with a history of epilepsy and anticonvulsant therapy during treatment with rimantadine-belmed increase the risk of developing an epileptic seizure. In such cases, Remantadin-Belmed is recommended to be administered in a dose of up to 100 mg / day simultaneously with anticonvulsants. In the event of a convulsive seizure, Remantadine-Belmed should be stopped.
The drug should not be taken in patients with rare congenital galactose intolerance, Lapp deficiency of lactase, or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Remantadin-Belmed is not a substitute for early flu vaccination in accordance with the recommendations of national health authorities. Doctors need to consider local recommendations when deciding on the appointment of rimantadine-Belmed for the prevention or treatment of influenza.
The effectiveness of the use of Remantadin-Belmed for the prevention of influenza virus A. has been proven. Remantadin-Belmed does not completely suppress the development of the immune response to the infectious agent, therefore, individuals who have taken Remantadine-Belmed can develop an immune response due to the disease or vaccination, which is of importance in subsequent contact with viruses with similar antigenic composition. If influenza vaccination is carried out during an influenza epidemic, rimantadine-belmed can be used on the recommendation of a physician for prevention during the period required for antibody production (2-4 weeks).
The effectiveness of the appointment of rimantadine-Belmed children for the treatment of influenza has not been definitively established. If prescribed within 48 hours of the onset of the disease, Remantadin-Belmed reduces the duration of the fever and other flu symptoms. At the discretion of the attending physician, rimantadine-Belmed for the treatment of influenza may be prescribed to children over 7 years old with comorbidities (diabetes, heart disease, sickle cell anemia, etc.) who are at high risk of developing complications.
Use during pregnancy and lactation. Contraindicated use during pregnancy and lactation (for the period of treatment should stop breastfeeding).
Influence on ability to steer the car and potentially dangerous mechanisms.
When using Rimantadine-Belmed, it is impossible to exclude the likelihood of reduced ability to concentrate, therefore driving vehicles and other activities that require increased attention and speed of reaction are not recommended.
Interaction with other drugs
Enhances the stimulating effect of caffeine. Reduces the effectiveness of antiepileptic drugs. Adsorbents, binders and coating agents reduce the absorption of rimantadine. Means, acidifying urine (ammonium chloride, ascorbic acid, etc.), reduce the effectiveness of rimantadine (due to the increase of its excretion by the kidneys). Means alkalizing urine (acetosalamide, sodium bicarbonate, etc.), enhance its effectiveness (due to a decrease in the excretion of rimantadine by the kidneys). Paracetamol and acetylsalicylic acid reduce the maximum plasma concentration of rimantadine by 11%. Cimetidine reduces the clearance of rimantadine by 18%.
Intranasal live attenuated flu vaccine should not be given until 48 hours after discontinuation of rimantadine-belmed. Remantadin-Belmed is not recommended for two weeks after the administration of the intranasal live attenuated vaccine, since rimantadine may inhibit the replication of virus strains contained in a vaccine.
Storage conditions
In the place protected from moisture and light at a temperature not higher than 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package.
Packaging
10 tablets in blisters. One, two blister strip packagings together with the instruction for application are placed in a pack from a cardboard.
Pharmacy holidays
Over the counter.
Drug registration information
1 tablet contains rimantadine hydrochloride 50 mg; in the package 20 pcs.
Mode of application
Individual, depending on the evidence, age of the patient and the treatment regimen used.
Indications for use
Prevention and early treatment of influenza in adults and children over 7 years of age, prevention of influenza during epidemics in adults, prevention of tick-borne encephalitis of viral etiology.
Contraindications
Acute liver diseases, acute and chronic kidney diseases, thyrotoxicosis, pregnancy, children under 7 years old, hypersensitivity to rimantadine.
Pharmacological properties
Antiviral agent derived from adamantane. The main mechanism of antiviral action is the inhibition of the early stage of specific reproduction after the virus enters the cell and prior to the initial transcription of RNA. Pharmacological efficacy is ensured by inhibiting the reproduction of the virus in the initial stage of the infection process.
It is active against various strains of influenza A virus (especially type A2), as well as tick-borne encephalitis viruses (Central European and Russian spring-summer), which belong to the group of arboviruses of the Flaviviridae family.
Pharmacokinetics
After ingestion is slowly, almost completely absorbed in the intestine. Plasma protein binding is about 40%. Vd in adults - 17-25 l / kg, in children - 289 l. Concentration in nasal secretion is 50% higher than plasma. The value of Cmax when taking 100 mg 1 time / - 181 ng / ml, 100 mg 2–416 ng / ml. Metabolized in the liver. T1 / 2 - 24-36 h; excreted by the kidneys (15% - unchanged, 20% - as hydroxyl metabolites). With chronic renal failure, T1 / 2 increases by 2 times. In patients with renal insufficiency and in elderly people, it can accumulate in toxic concentrations, if the dose is not adjusted in proportion to the decrease in CC.
Pregnancy and lactation
Contraindicated in pregnancy.
Side effects
From the digestive system: epigastric pain, flatulence, increased bilirubin in the blood, dry mouth, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, gastralgia.
From the side of the central nervous system: headache, insomnia, nervousness, dizziness, impaired concentration, drowsiness, anxiety, irritability, fatigue.
Other: allergic reactions.
Interaction with other drugs
With simultaneous use of rimantadine reduces the effectiveness of anti-epileptic drugs.
Adsorbents, binders and coating agents reduce the absorption of rimantadine.
Means, acidifying urine (ammonium chloride, ascorbic acid), reduce the effectiveness of rimantadine (due to the increase of its excretion by the kidneys).
Means alkalizing urine (acetazolamide, sodium bicarbonate) increase its effectiveness (reduced excretion by the kidneys).
Paracetamol and acetylsalicylic acid reduce rimantadine Cmax by 11%.
Cimetidine reduces the clearance of rimantadine by 18%.
special instructions
Rimantadine is used with caution in cases of arterial hypertension, epilepsy (including history), and atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels.
When using rimantadine may exacerbate chronic comorbidities. Elderly patients with arterial hypertension increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. With indications of a history of epilepsy and anticonvulsant therapy, the risk of developing an epileptic seizure increases with the use of rimantadine. In such cases, rimantadine is used in a dose of up to 100 mg / simultaneously with anticonvulsant therapy.
With influenza B virus, rimantadine has an antitoxic effect.
Prophylactic administration is effective in contacts with patients, in the spread of infection in closed collectives and at high risk of developing a disease during a flu epidemic. Perhaps the emergence of drug-resistant viruses.
Remantadin - synthetic, which, in fact, is derived from adamantane. The drug was first obtained as a result of chemical synthesis in 1963 in the United States, and the resulting formula was significantly improved in the Soviet Union in 1969 — this final version of the drug under consideration is now being produced by the pharmacological industry.
Note: There is another name for the considered antiviral agent - rimantadine. Each of them is actively used among doctors and patients.
Remantadin: how the drug works
The drug under consideration has an antitoxic effect, and scientists have detected its activity against the virus and tick-borne. But the main purpose of rimantadine is a destructive effect on type A.
The principle of rimantadine in the body:
- prevents the penetration of the virus into healthy cells - this gives reason to consider the drug under consideration as an effective prophylactic agent;
- blocks the release of viruses from the cell - this contributes to a significant reduction in the total number of viral agents in the body.
Important: Remantadin is effective not only as a preventive measure against influenza A, but also at an early stage of the disease - the expected result of non-proliferation of the virus will be obtained if no more than 18 hours have passed from the appearance of the first signs of pathology.
The considered drug can be taken with type B flu - the virus is unlikely to be blocked, but rimantadine’s antitoxic effect will be fully manifested.
Rimantadine - indications for use
The considered drug is indicated for use for the prevention of influenza during epidemics, early treatment of already diagnosed and progressive influenza in adults and children over 7 years old.
Remantadin is also used as a prophylactic agent aimed at preventing tick-borne encephalitis virus infection.
Remantadin - instructions for use

The considered antiviral drug should be taken after consultation with the doctor, but in the official annotation to rimantadine there are general recommendations:
- In the first two days after the first signs of flu appear, rimantadine should be taken in an amount of 300 mg per day - this dose can be taken at a time, divided by 2-3 times.
- On the second and third day, the daily dose of rimantadine should be 200 mg - it is divided into two doses.
- On the fourth and fifth day of the disease, it is enough to take 100 mg of the preparation in a single dose a day.
Note: The above general guidelines for the use of rimantadine apply only to adults and adolescents (from the age of 14).
If you plan to treat the flu in childhood, you should follow the following recommendations:
- for children between the ages of 11 and 14, the daily dose of rimantadine should be 150 mg, 50 mg three times a day;
- children aged 7 to 14 years per day are advised to use 100 mg of the antiviral agent in question — 50 mg twice a day.
When carrying out flu prevention, adults are advised to take 50 mg of rimantadine 1 time per day, children up to 10 years old - 5 mg / kg 1 time per day.
Features of treatment and prevention of influenza:
- The treatment of influenza with the medication in question is 5 days.
- Rimantadine is taken only inside.
- Tablets of the drug are taken after meals with a large amount of water.
- The prophylactic course of taking rimantadine is 10-15 days.
In order to prevent tick-borne encephalitis of viral etiology, 50 mg twice a day should be taken. Reception duration - 15 days.
In the case of an already accomplished tick bite, a person should take rimantadine 100 mg twice a day to prevent the development of tick-borne encephalitis. Reception duration - from 3 to 5 days.
Remantadin - contraindications
We recommend to read:The official instructions for use of rimantadine are unconditional and conditional contraindications. They need to be known to adults when choosing this antiviral drug as a drug for children in the event of illness of the flu - this will prevent the development of side effects, the strongest allergic reaction.
Unconditional contraindications to the use of rimantadine are:
- impaired absorption of glucose-galactose;
- lactase deficiency;
- galactosemia;
- severe impaired liver and kidney function;
- thyrotoxicosis.
 note: rimantadine in children under the age of 7 years is strictly prohibited to appoint and accept. It is forbidden to take rimantadine and during pregnancy!
note: rimantadine in children under the age of 7 years is strictly prohibited to appoint and accept. It is forbidden to take rimantadine and during pregnancy!
With great caution, the considered antiviral drug is prescribed during lactation - it is understood that doctors should relate the risk of developing the flu to the health of the mother with possible problems if the baby is not breastfed. Important!If taking rimantadine is inevitable, then the mother should stop feeding the child.
The conditional contraindications include previously diagnosed:
- heart disease;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- heart rhythm disorders;
- epilepsy.
Note: some patients had allergic reactions while taking rimantadine - prior to the start of a course of treatment or prophylaxis, hypersensitivity and / or individual intolerance to the drug should be avoided.
Side effects
In general, rimantadine is well tolerated by patients, and the occurrence of side effects is extremely rare. But against the background of the intake of the considered antiviral drugs may appear:
- dizziness and concentration disorder;
- low intensity and insomnia;
- nervousness and unmotivated fatigue;
- dry mouth, nausea and vomiting;
- increased gas formation;
- classic allergic reaction - urticaria, pruritus.
If at least one of these side effects appears, you should immediately stop taking rimantadine and consult with your doctor about the appropriateness of a further course of taking the antiviral in question. Most often, experts either carry out a complete replacement of the drug, or adjust the dosage.
Overdose of rimantadine
Some patients deliberately overestimate the recommended daily doses of rimantadine in order to obtain a speedy effect of recovery and / or relief of well-being. But this can lead to an overdose, and this condition will be characterized by pronounced side effects.
There is no directional treatment for overdose with rimantadine, doctors recommend washing the stomach and consult a specialist.
Note: rimantadine analogs (rimantadine actitab, rimantadine-STI) have similar instructions for use.
Interaction with other drugs
There were no complicated side effects while taking the drug in question and other medicines at the same time. But you need to know some of the nuances of this combination:

Remantadin for children: scientific research
The considered antiviral drug according to the instructions is strictly prohibited to children up to 7 years. But doctors recently conducted a study Orvirem - a drug developed in St. Petersburg Research Institute. In the composition of this tool the main active ingredient is rimantadine, but it is supplemented with sodium alginate. It is an additional component that has adsorbing and detoxifying properties - this significantly reduces the anti-toxic activity of rimantadine.
Such a pharmacological form of release of the considered drug provides a gradual flow of the active substance into the blood, its accumulation and prolonged circulation. Orvirem can be prescribed to children aged 1 year, it has a powerful opposition to the development of the most common complications of influenza.
In the course of the research, the expediency of administering Orvirem to children diagnosed with acute respiratory viral infections, influenza A and B type, and respiratory infections of viral and bacterial etiology was highlighted and confirmed.
Orvirem, which includes rimantadine, can be safely prescribed to children aged 1 year, even with diagnosed cardiac pathologies - such treatment leads to a reduction in the intoxication period, a reduction in the risk of bacterial complications, and significantly reduces the length of stay of the child in hospital.
Rimantadine is an antiviral drug that has proven itself both as a prophylactic and as a remedy. In a period of increased epidemiological risk of the spread of influenza, the agent in question will be appropriate for both adults and children. It is only necessary to strictly follow the instructions for use, to comply with the recommended dosage and to prevent the development of side effects.
Yana Alexandrovna Tsygankova, medical reviewer, general practitioner of the highest qualification category.
Antiviral .
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Rimantadine, from what are these pills? This antiviral agent, the main mechanism of which is to inhibit the early stage of virus reproduction after it enters the cell, blocks the transmission of the genetic material of the virus into the cytoplasm of the cell.
It affects the virus influenza a and virus tick-borne encephalitis (arbovirus). Effective when taken in the initial stage of infection (6-7 hours), which reduces the incidence of influenza and the severity of symptoms.
Pharmacokinetics
Slowly, but completely absorbed in the digestive tract. 40% bound to blood proteins. The concentration of the active substance in the nasal secretion is higher than plasma, by 50%. Metabolism occurs in the liver. The elimination half-life is 24-30 hours. Excreted by the kidneys. In patients with renal insufficiency accumulates in toxic concentrations in the absence of dose adjustment.
Indications for use rimantadine
- treatment flu in the early stages;
- flu prevention in epidemics;
- prophylaxis caused by ticks.
Contraindications
- kidney disease;
- liver disease;
- age up to 7 years;
- pregnancy;
It is prescribed with caution when hypertension . Elderly people with elevated blood pressure increases the risk hemorrhagic stroke . With epilepsy in the history of possible development of epileptic seizure.
Side effects
- pain in the stomach, anorexia bloating, dry mouth, nausea;
- headache, nervousness, insomnia, anxiety, decreased concentration, irritability, drowsiness;
- allergic reactions.
Instructions for use rimantadine (method and dosage)
Rimantadine tablets, instructions for use
Tablets are taken by mouth, after meals. For treatment of influenza, take the following scheme: 1st day - 100 mg three times, in the 2nd and 3rd day - 100 mg twice, 100 mg on the 4th day. For the purpose of prevention, 50 mg per day for 10 to 15 days.
How to take the drug with a tick bite? During the first 72 hours, take 100 mg 2 times a day.
Instructions for use rimantadine STI
For the treatment of influenza, take the following scheme: 1st day - 100 mg three times, on the 2nd and 3rd day - 100 mg twice, on the 4th day - 100 mg 1 time. For the purpose of prevention, 50 mg per day for 10 to 15 days. Remantadin Aktitab has the same indications and is used in the same dose regimen.
Children from 1 year prescribed rimantadine in syrup. Syrup for children is issued under the name Orvirem and Algirem . The dosage method will be indicated below.
Overdose
Overdose is manifested by nausea, the appearance of metal taste in the mouth, the urge to vomit. Characterized by psychedelic trip, accompanied by fear, panic, delusions, hallucinations, intense thought process. Administered intravenously
Shelf life
Remantadine for children
Instructions for rimantadine for children: tablets of 50 mg twice are intended for children of 7-10 years old, 50 mg three times a day from 10 years old. In severe cases, children can be given 3–7 years old, but at a dose of 1.5 mg / kg / 2 doses.
Syrup Algirem (rimantadine + matrix carrier alginate ) can be used for children from 1 year. has an adsorbing and detoxifying effect, which enhances the antitoxic activity of the drug. Reduce its dosage and reduce the risk of unwanted reactions allows a longer time circulation Algirem in the blood. A teaspoon of syrup contains 10 mg of rimantadine, taken after meals, according to the scheme.
From 1 to 3 years: 2 tsp. syrup three times a day on 1 day; 2 tsp. twice a day, 2 and 3 days; 4 day - 2 tsp. syrup 1 time.
From 3 to 7 years: 3 tsp. three times a day on 1 day, 3 tsp. twice a day, 2 and 3 days; 4 day - 3 tsp. 1 time.
Effective in the case of admission in the first two days from the onset of the disease. Goes well with antiviral drug
which inhibits virus reproduction. It is a "long-liver" in the market of antiviral drugs - used since 1975. His prophylactic administration is effective in influenza epidemics in closed collectives, as reported in many reviews. However, in recent years, most influenza A viruses (up to 50%) have become resistant to this drug, so it has lost its relevance. It is not effective in other respiratory viral diseases and the A / H1N1 virus that causes pandemics is resistant to it. In this connection, the Ministry of Healthcare and Social Development of the Russian Federation does not recommend the use of rimantadine in the pandemic period.
The sensitivity of viruses to class II drugs remains:, zanamivir, peramivir. Class III drugs (, kamostat) appeared recently and occupy a leading position in the treatment of influenza.
Popular
- Blood disorders in children
- What can not drink a pill
- Blood disorders in children
- Blood disorders in children
- Bones: structure, composition, types of bones, types of connections and their characteristics
- How many live with lung cancer
- Influenza in children: how to treat, what can and cannot be done to parents, what medicines will help?
- "They are people too ..." - you say
- What helps "Prednisolone"
- How are menstruation for endometriosis?