Vomiting with intestinal infection of a child. Classification of intestinal infections. Meals during and after illness
The term "intestinal infection in children" in medicine refers to a group of infectious diseases of various etiologies. The causative agents of infection can be various pathogenic agents - viruses and bacteria, such as Salmonella, rotavirus, Shigella, Escherichia, Cambilobacteria and a number of other microbes. Sharp intestinal infections in children, hitting gastrointestinal tract, usually cause a toxic reaction and lead to dehydration. This condition of the child requires emergency medical care.
The source of infection by pathogenic microorganisms - viruses and bacteria that lead to the development of an intestinal infection, can be animals, a sick person or bacteria carriers. The highest infectiousness is observed in the first three days of the disease. During this period, an infected child is a threat to healthy people.
The mechanism of infection of acute intestinal infection in children
The infection mechanism is predominantly fecal-oral, and there may be several ways of transmission:
- alimentary;
- water;
- contact and household.
The main age group that is most often exposed to the development of intestinal infectious diseases is children from 2 to 5 years. Children under the age of one who are breastfed are practically not ill, as they are protected by the mother's immunity.
Often, intestinal infections are seasonal in nature, the peak of the incidence falls on a different period depending on the causative agent of the disease, but may not be associated with seasonality, such as, for example, rotavirus infection.
Microbes, pathogens of intestinal infections are released into the external environment along with feces, saliva, urine, and vomitus of a bacteriocarrier or a sick person. Pathogenic microorganisms, getting into the water, food, household items, children's toys, are stored on them for a long time, penetrating into the body of healthy people.
Infection with pathogens occurs as a result of pathogenic microorganisms entering into gastric tract child’s mouth with contaminated food, water, or toys.
All intestinal infections, regardless of their etiology and pathogen, cause the development of inflammatory process mucous membrane of the stomach, intestines and other digestive organs. Depending on the mucosa, which organ was affected by pathogen microbes, the following forms of intestinal infection develop:
- gastritis;
- enteritis;
- colitis;
- gastroduodenitis;
- enterocolitis.
Common intestinal infectious diseases
The manifestation of symptoms of intestinal infection in children depends on the type of disease and its pathogen. The most common diseases of the digestive tract caused by pathogenic microflora are the following:
- dysentery and shigellosis;
- colibacillosis;
- salmonellosis;
- yersiniosis;
- rotavirus infection;
- campylobacteriosis.
Violation of the stool in the form of diarrhea is the main characteristic feature of almost all intestinal infections.
Signs of intestinal infection shigellosis in children
Signs of intestinal infection in a child caused by bacteria of the Shigella genus, known as dysentery, or shigellosis first occur within 1-7 days from the time the pathogenic microflora penetrates the child’s body. That is how long the incubation period of dysentery lasts.
The disease begins acutely, the body temperature rises to 39-40 ° C, the feeling of weakness and weakness is growing rapidly, there is a decrease in appetite, vomiting is possible. With fever, symptoms of the disease can occur, such as:
- headache;
- chills;
- stomach ache;
- violation of the chair - the frequency of bowel movements can vary from 4-6 to 15-20 times a day;
- rave;
- convulsions;
- loss of consciousness.
Usually the chair contains impurities of mucus and blood. Severe forms of dysentery may be accompanied by hemorrhagic syndrome, up to intestinal bleeding.
Symptoms of acute intestinal infection escherichiosis in children under one year old
Escherichiosis is an acute intestinal infection caused by various serological groups of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Predominantly, the disease affects small patients under the age of 3 years.
In gastroenterology, the following types of escherichiosis are distinguished:
- Entero-invasive. This form of infection is characterized by acute onset, a sharp increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees, pain in the abdomen. The child has diarrhea with stool frequency up to 5-10 times a day, perhaps even with an admixture of mucus and blood.
- Enterotoxigenic. This type of escherichiosis is accompanied by frequent vomiting, liquid stool without any impurities, repeated up to 10 times a day, the consistency of a rice broth. This form of intestinal infection is characterized by dehydration of the isotonic type. An increase in body temperature during enterotoxigenic escherichiosis does not occur.
- Enteropathogenic. This form of intestinal infectious disease affects children under the age of one year. Development of toxicosis and exsicosis is noted, the disease proceeds in a rather severe form. Enteropathogenic colibacillosis may develop acutely or gradually. The excrements are most often watery, have a yellowish or orange tint, with a small amount of mucous impurities. The feces may be mushy, but necessarily frothy. Other symptoms of this form of colibacillosis in children include vomiting 1-2 times a day, regurgitation, loss of appetite, low-grade fever.
- Enteropathogenic colibacillosis type 2. The clinical picture is reminiscent of salmonellosis. The disease always begins acutely, with an increase in body temperature to 38-38.5 degrees. The characteristic symptoms of the disease is chills, loose stools up to 6 times a day without impurities. Child bother with cramping abdominal pain.
- Enterohemorrhagic. For this form of colibacillosis, liquid stool with a frequency of up to 10 times per day with blood admixtures, almost without feces, is characteristic. Usually on the 2nd-4th day of the course of an infectious disease, there is a marked deterioration in the condition of the patient. High body temperature is not characteristic of enterohemorrhagic escherichiosis.
Diarrhea and other signs of intestinal Salmonella infection in a child
Salmonellosis is an acute infectious disease of the digestive system caused by the action of the bacterium Salmonella. This bacterial infection may develop as isolated cases or as a whole outbreak of salmonella infection. The peak incidence occurs in the summer, when food storage conditions are violated.
Incubation period when salmonellosis is from several hours to 5 days. The main signs of Salmonella infection are:
- fever that lasts from 5-7 days to 2-3 weeks;
- frequent fetid stool;
- dryness of the mucous membranes and skin, indicating dehydration of the child’s body as a result of severe diarrhea.
Diarrhea during an intestinal infection in a child caused by the bacterium Salmonella usually goes away after 7-10 days.
This intestinal infection in children under one year is characterized by slightly different symptoms than in older patients. In babies, over symptoms of intestinal disorders are dominated by common signs of intoxication. Body temperature can remain normal, malnutrition is observed in infants, and during the course of the course of the illness, the babies hardly gain weight.
When salmonellosis in children in the first year of life, the following symptoms are observed:
- restlessness, tearfulness and moodiness;
- frequent regurgitation;
- bloating;
- cold limbs.
Dehydration with salmonellosis is manifested by dryness of mucous membranes, skin and tongue, oliguria, and retraction of the fontanel.
Gastrointestinal form of intestinal infection in a 2-year-old child
The most common is gastrointestinal form of salmonellosis. This intestinal infection in a child at 2 years old takes the form of gastritis and gastroenteritis. The disease is characterized by such signs:
- painful sensations in the field of epigastria;
- heat;
- malaise, general weakness;
- frequent vomiting;
- frequent loose stools with undigested food particles;
- tongue dry and covered with thick bloom;
- slight flatulence.
How long does intestinal infection of typhoid form in children last?
Typhoid form of salmonellosis is characterized by such signs as prolonged fever, headaches, vomiting, delirium, impaired confusion, enteritis chair. At the peak of infection, it becomes possible for the child to have a roseolous-papular rash on the child’s body. How long does the intestinal infection last in children of typhoid form? With proper treatment recovery occurs after 14 days, as with typhus.
The septic form of salmonellosis is distinguished, which is mainly diagnosed in weakened children of the first year of life and in premature babies. With this infectious bacterial disease the formation of purulent foci of various localization occurs - in the lungs, kidneys, meninges, joints and bones. There is a stool with a frequency of up to 5-10 times a day, liquid or mushy continuous with admixtures of greenery, mucus, white lumps with a sharp sour smell.
Complications of intestinal infection in an infant
After suffering an intestinal infection baby for a long time, it continues to excrete bacteria to the external environment, this lasts for about a month. If the carriage of the bacterium Salmonella lasts more than 3 months, the intestinal infection becomes chronic.
Salmonellosis for children, especially the first year of life, is dangerous with many serious complications:
- swelling of the brain and lungs;
- renal failure;
- peritonitis;
- reactive arthritis;
- abscess of internal organs.
If you suspect the development of salmonellosis in infants, parents should immediately show the baby to a specialist, because there is a danger of death.
Norovirus intestinal infection in children
Norovirus intestinal infection in children is one of the common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in a child. Pathogens act noroviruses.
The first signs of the disease appear 24-48 hours after the penetration of norovirus into the child’s body. The disease begins severe vomiting, which is soon joined by diarrhea, body temperature rises, muscle and headaches, general weakness occur.
Usually, these signs of norovirus intestinal infection disappear on their own after 12-72 hours, however, symptomatic treatment of the child is required to alleviate his condition. After the illness, an unstable immunity to the pathogen is produced, which persists for up to 8 weeks. After this time, the child may again become infected with norovirus infection.
Symptoms of acute intestinal infection yersiniosis in children
It is an infectious disease characterized by a toxic-allergic syndrome and lesion. digestive system. The causative agent of yersiniosis is motile bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica, in their form resembling short sticks. How many days does the intestinal infection in children last from the moment the pathogens enter the body? The incubation period lasts from days to 7 days, however in medical practice there are known cases of its increase up to 3 weeks. Full recovery with adequate therapy occurs after 10-14 days from the moment of infection.
For convenience, experts divide all symptoms of acute intestinal infection in children caused by the bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica into several groups. The following common toxic symptoms of yersiniosis occur:
- high body temperature - up to 40 degrees, such indicators can be maintained for up to 10 days;
- severe headaches;
- general weakness of the body, muscle and joint pain;
- significant loss of appetite;
- violation of the nervous system.
Regarding the defeat of a child's gastrointestinal tract bacterium, intestinal yersiniosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal discomfort of fuzzy localization;
- intermittent loose stools;
- runny nose, sore throat, tearing;
- redness and paleness of the skin;
- crimson color of the tongue a week after infection.
In some cases, children may experience allergic reactions –– Rashes on the skin in the form of small red spots, small dots and bubbles. The main places of localization of the rash are the soles of the feet and hands. Such dermatological manifestations of the disease are accompanied by dryness, itching and burning.
Incubation period of viral intestinal infection in children
Intestinal infections can have both bacterial and viral etiology. Rotavirus is a viral intestinal infection in children, which usually proceeds as acute gastroenteritis or enteritis. The incubation period of this intestinal infection in children lasts from 1 to 3 days. All the characteristic symptoms of the disease appear on the first day, while intestinal lesions are combined with catarrhal phenomena.
Observed symptoms of respiratory syndrome such as hyperemia of the pharynx, rhinitis, sore throat, cough. Simultaneously with the defeat of the oropharynx, there are signs of gastroenteritis - liquid, watery or frothy stools with a frequency of bowel movements from 4-5 to 15 times a day, vomiting, fever. So frequent stool leads to dehydration of the child’s body and increases the signs of intoxication. All these signs disappear within 5 days.
Symptoms of rotavirus intestinal infection in a child under 1 year: temperature and intoxication
Rotavirus intestinal infection in a child under 1 year old and always accompanied by vomiting, which lasts for 1-2 days. In children after a year, usually this symptom is observed only the first day.
With this intestinal infection in a child, the body temperature usually rises very much - up to 39̊ С, is held no more than three days.
Intoxication of the body is the first symptom of intestinal infection in children under one year old caused by rotaviruses. The baby becomes sluggish, he practically does not perform any movements, refuses to breast and constantly cries, there is increased sweating. To these signs of intoxication in children after a year, an intestinal infection may be accompanied by severe headaches and dizziness.
The pain in the abdomen is mild, and it may increase with palpation. All these symptoms may have varying degrees of severity, as a rule, the older the child, the easier the disease progresses. If these signs of viral infectious disease appear, you should immediately seek the help of a specialist.
Symptoms of Staphylococcal Intestinal Infections in Children
The causative agent of staphylococcal intestinal infection in children is Staphylococcus aureus and other pathogenic strains of this microorganism. Staphylococcus belongs to the conditionally pathogenic microflora, this means that it is present in many people, not making itself known, and only under certain conditions causes the development of the disease.
The provoking factors are:
- a weakened child’s immunity resulting from congenital immunodeficiencies, HIV;
- developmental pathologies of internal organs;
- children belonging to the category of frequently and long-term respiratory illnesses;
- the presence of chronic foci of inflammation in the body - tonsillitis, sinusitis, gastroduodenitis and others.
Often a child is infected with Staphylococcus aureus during his stay in the maternity hospital; then the signs make themselves felt in the first days of the baby’s life. During the course of a staph infection in newborns, the following signs are characteristic:
- bloating and intestinal colic;
- frequent liquid fetid stools, possibly with admixtures of mucus and greenery;
- in some cases, there is an increase in body temperature;
- violation of the general condition of the newborn - causeless crying, refusal to eat, lethargy and anxiety.
With prolonged diarrhea, signs of dehydration appear. It is manifested by dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, the crying of a newborn without tears, sunken spring. This condition requires an urgent hospitalization of the infant in the hospital.
In children younger than one year, the signs of a staph infection are slightly different from the characteristics of the manifestation of this disease in newborns. Usually in children under one year old, this intestinal disease is manifested by signs of toxicoinfection or gastroenterocolitis, an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine.
Experts identify the following main symptoms in children under one year, characterized by intestinal infections caused by staphylococcus:
- weakness, lethargy, lack of appetite;
- increase in body temperature to 38, 5̊ С;
- headache and dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weight loss;
- frequent loose stools with impurities of mucus, blood, foam, and greens;
- abdominal distention and pain in his area.
Treatment of symptoms of intestinal infection in children caused by the action of staphylococci is carried out by the combination method. antibacterial drugs and specific means. Therapy of light and moderate forms of staphylococcal infection is carried out with the help of such antibiotic groups:


semi-synthetic penicillins: oxacillin, ampioks;

macrolides: erythromycin, roxithromycin;

lincomycin.
In the case of severe forms of staphylococcal intestinal infection, aminoglycosides are given to children:


gentamicin, rifampicin, and


i generation cephalosporins - cefazolin.
Symptoms of intestinal infection campylobacteriosis in children under 2 years old
This is an infectious intestinal disease, the causative agent of which are Campylobacter - conditionally pathogenic microorganisms. The disease is mainly manifested by the defeat of the child’s gastrointestinal tract.
Campylobacteriosis usually occurs in debilitated infants and adults who suffer from tuberculosis, diabetes, hemoblastosis and other oncological diseases. Children of the first year of life are also at risk.
The incubation period of campylobacteriosis lasts 3-5 days. The disease is characterized by an acute onset, and soon after infection, an increase in body temperature to febrile indices is observed.
The child is concerned about muscle pain and general weakness. In most children up to 2 years, a symptom of campylobacter intestinal infection is also strong pain around the navel, which is especially enhanced with palpation.
The first days of the disease may occur vomiting, sometimes repeated. The main symptom of the disease, as with many other intestinal infections, is severe diarrhea - from 4-6 to 20 times a day. The feces are copious, watery, yellowish in color.
In infants, mainly developed generalized form of campylobacteriosis. Symptoms include severe fever with frequent daily fluctuations, vomiting, diarrhea, an increase in liver size, weight loss, anemia. Due to bacteremia in babies, organ purulent lesions can occur - purulent meningitis, meningoencephalitis, endocarditis, thrombophlebitis, septic arthritis, pneumonia.
Young children are most susceptible to intestinal campylobacter infection. Tactics of treatment of the disease depends on the severity of its occurrence in the children's body. With light and medium severe forms Campylobacteriosis medications are prescribed such pharmacological groups:
- antispasmodics;
- enzymes;
- biological bacterial preparations.
Such therapy is aimed at correcting intestinal dysbiosis and colonizing it with beneficial microflora. For this purpose, a special therapeutic diet and oral rehydration are also prescribed.
In severe forms of the disease, it becomes necessary to take antibiotics to which Campylobacter are sensitive. These are erythromycin, tetracycline, doxycycline, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, macrolides, metronidazole, furazolidone. The course of antibiotic therapy is 7-14 days, set by a specialist individually for each patient.
Methods of treating the symptoms of acute intestinal infection in children
Antibiotic therapy is the main method of treating intestinal infections in children, when the causative agents are bacterial agents. However, it is not always used, but only in the case of neglected, moderate and severe forms of defeat of the child's digestive tract.
Treatment of the symptoms of acute intestinal infection in children must necessarily be comprehensive and consist of several methods of therapy, such as:
- health food;
- oral rehydration;
- etiotropic therapy;
- pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy.
The treatment of acute intestinal infection in children is almost never complete without etiotropic therapy, which consists in taking antibiotics, chemotherapy, specific bacteriophages, enterosorbents, enteric immunoglobulins, lactoglobulins.
When an intestinal infection of various etiologies are usually prescribed such antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs as nalidixic acid (nevigramon, nergam), furazolidone, ercefuryl, gentamicin, anamycin sulfate, kanamycin.
Specific bacteriophages are recommended for use as monotherapy for mild and erased forms of the disease. Enterosorbents are necessarily prescribed for symptoms such as diarrhea. In light and moderate forms of infection, Smecta has proven itself well. The course of treatment with enterosorbents is 5-7 days.
Pathogenetic therapy consists of the following methods:


oral rehydration with rehydron, oralit, gastrolit;

enzyme therapy, which is prescribed Panzinorm Forte, Abomin-pepsin,
Pancreatin, Pankurmen,
Digestal, Festal,

Mezim Forte, Creon;
anti-allergic therapy method of taking antihistamines;
correction of dysbacteriosis by probiotics.
What to give the child with intestinal infections, accompanied by diarrhea?
Symptomatic therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms characteristic of an intestinal infection. What to give a child with intestinal infection, when there is severe diarrhea?
Specialists in this case, prescribe antidiarrheal drugs:
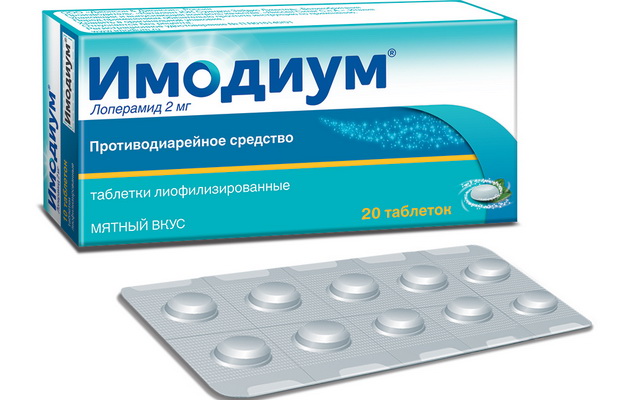

Imodium, Diarol.
In osmotic diarrhea, children under 2 years old are medications not assigned.
To eliminate the expressed pain syndrome, antispasmodics are used:
drotaverinum, papaverine,

spasmomemen 40 and some other drugs prescribed by a specialist.
Vitamin therapy is mandatory for all children, regardless of the type of intestinal infection, for a course of 14 days.
Treatment of intestinal infection in a 3 year old child
In the case of an antibacterial treatment of an intestinal infection in a 3-year-old child, antibiotics may be prescribed, such as:

Ciprofloxacin,
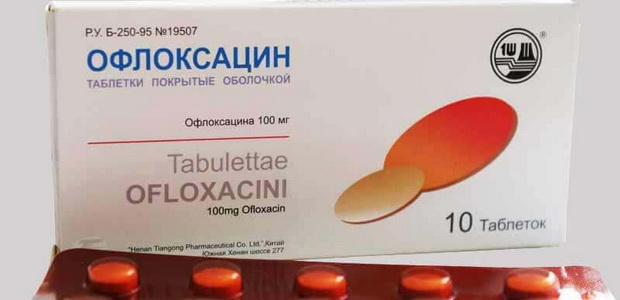
Ofloxacin,
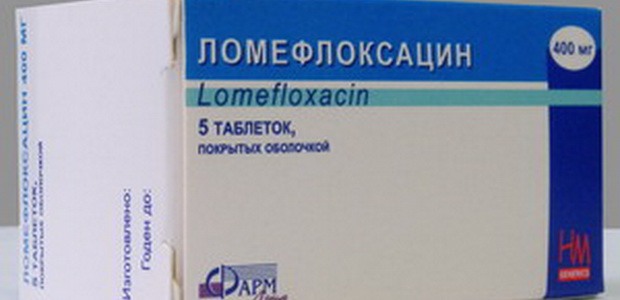
Lomefloxacin.
The dosage is determined by a specialist for each patient individually.
How to treat intestinal infection in children caused by such pathogenic agents as viruses? The goal of therapy is to remove viruses from the intestines, which are located on its machines and destroy their cells. For these purposes, sorbents are prescribed:

activated carbon - up to 4-6 tablets per dose several times a day;

Smectaor Neosmectin - 3-4 sachets per day;


Enterodezor Polysorb - 1-2 sachets per day.


In the fight against rotaviruses, the effectiveness of such antiviral drugs as Anaferon and Arbidol has been proven.
During rotavirus infection In the intestine, inevitably a significant portion of beneficial bacteria is destroyed, ensuring the healthy functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. That is why therapy must necessarily consist of receiving probiotics, children are prescribed:

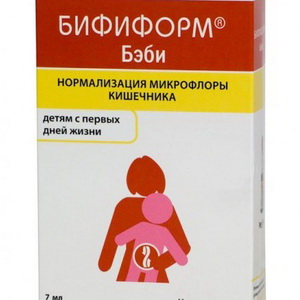
Laktofiltrum, Bifiform,


Linex, Bifidum,
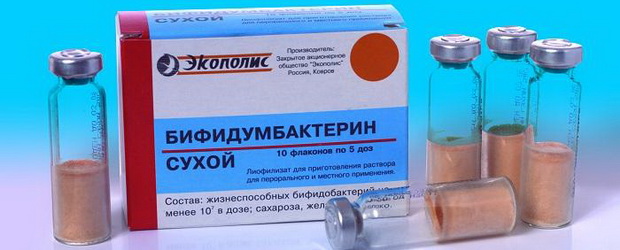
Bifidumbacterin.
Diet menu for intestinal infections in children: how to feed a child
Diet for intestinal infections in children is an obligatory method of therapy, allowing to restore the disturbed functions of the digestive system and speed up the healing process. Many parents are interested in what to feed the child with an intestinal infection.
The first day after infection, the baby is better to eat nothing at all. If the child has an appetite, he can be given a rice broth, older children - a cracker.
The diet menu for intestinal infections in children should consist of easily digestible and pureed food. Products such as whole milk, black bread, ryazhenka, yogurts, cream, porridge with milk, beetroot, legumes, citrus, meat and fish broths, fatty meats, poultry and fish are prohibited.
The menu for intestinal infections in children should be based on such foods as porridges on water - corn, rice, buckwheat, and lean meat - turkey, chicken breast, veal, rabbit meat. Then, fermented milk products are introduced into the diet, vegetables and fruits can be eaten after they disappear. unpleasant symptoms disorders of the digestive system. Recommended otpaivat child decoction of hips, weak tea, rice water, dried fruit compote, but without prunes.
About the menu might look like this:

Breakfast- semolina, cooked in water, a glass of unsweetened tea.

Snack - Steam soufflé from homemade low-fat cottage cheese.

Dinner - light broth from low-fat chicken meat, steamed veal meatballs, fruit jelly.

Afternoon tea - 200 g of wild rose broth, rusk bread.

Dinner - non-greasy steam fish, unsweetened tea.
Before bedtime You can give your child a glass of low-fat homemade yogurt.
Diet recipes for children after intestinal infection
A variety of diet recipes for children after an intestinal infection will allow parents to avoid problems with the choice of suitable dishes for the still weakened body of the child.

Steamed chicken soufflé
To prepare meals for this recipe for intestinal infections in children will require boiled chicken breast, egg, 4 tbsp. l chicken broth, 1 tbsp. l flour.
Follow the following sequence of making souffles after an intestinal infection for a child according to this recipe:
minced boiled chicken breast;
- combine minced chicken meat with egg yolk, whipped protein, add a spoonful of flour, salt and mix;
- stir the mass thoroughly, place it in a greased form, and steam.

Blueberry jelly
You can use this diet recipe for children with intestinal infections to cook blueberry jelly:
- 2/3 cup blueberries should be washed with running water.
- Pour 4 glasses of water into a saucepan, put on the fire, bring to a boil.
- Add 2 tbsp. l Sahara. In a glass of cold water stir 1 tbsp. l starch, gradually pour into the sugar syrup.
- Put washed blueberries in a saucepan, mix.
- Reduce heat, bring to a boil and remove from heat.
What to cook for a child with intestinal infection: diet recipes

Slimy soup
To prepare the mucous soup, use this recipe for intestinal infections in children:
- Put a saucepan with 2 liters of water on the fire, pour ½ cup of washed oatmeal there.
- Finely chop the onions and carrots, add to the soup, salt a little, boil for another 15 minutes and remove from heat.
- When the soup has cooled down a little, it should be rubbed through a sieve, if desired, you can add a spoonful of vegetable oil.

Vegetable salad
At the end of the course of the disease, when the symptoms of intestinal infection begin to gradually disappear, fresh vegetables can be introduced into the diet of the child. If you do not know what to cook for a child with an intestinal infection, this recipe diversifies the baby’s diet menu:
- Boil carrots, cauliflower and zucchini.
- Cut all the vegetables into small cubes, salt a little, mix well, season 1 tbsp. olive oil.
Prevention of intestinal infections in children
Prevention of intestinal infections in children, primarily consists of the formation of personal hygiene skills. Parents should teach the child to eat fruits and vegetables only after they are washed, and also do not forget to wash hands thoroughly with soap and water before eating.
Other preventive measures are to thoroughly process food and boil water. In addition, the prevention of intestinal infections is the observance of such rules:
- Never eat foods that you doubt, especially if they have already expired.
- Observe the temperature and cooking time of raw foods. Boiling completely destroys almost all pathogens.
- Be sure to wash the eggs before breaking them for cooking. Such actions will save from infection with salmonellosis.
- For the preparation of raw foods, you must use different cutting boards.
- Before use, boil ready-made soup or soup.
- Pathogenic microorganisms multiply rapidly in salads made from raw vegetables, especially seasoned with sour cream. That is why it is recommended to fill them immediately before serving and to cook at one time.
- If there are pets in the house, they should be regularly degelmentized and vaccinated.
All food and water consumed by people, unfortunately, are very far from sterility. Every day and every hour, billions of different bacteria enter our bodies. Nothing wrong with this happens, because nature has come up with effective ways to neutralize germs. "Good" bacteria, saliva with bactericidal properties, poisonous gastric juice do not allow strangers to settle down in the body and destroy it.
But the child's body is very gentle and receptive, so miracles do not always happen to him. Unfortunately, Dr. Komarovsky argues, intestinal infections are radiated with children almost as often as ARVI. What should parents do when they suspect an intestinal infection in their karapuz, and are there ways to prevent dangerous infection? We will try to figure it out.
Cause of intestinal infection
There is not a single person who has never caught an intestinal infection. This is so because there are many ways to neutralize a huge amount of body defenses: neutralizing acidic gastric juice with an alkaline drink, destroying your own microbes with antibiotics, swallowing food without chewing it, and many others.
Still, these pests get into the body quite often, says Dr. Komarovsky. Intestinal infections really do not need any adult, let alone a child. Their main reason was, is and will be the failure to comply with the simplest hygienic norms: unwashed hands, improper storage of food, flying between the toilet and the dining table a flock of flies. No matter how great defensive forces the human body possesses in general and the baby in particular, there will always be microbes, which cannot be neutralized.
Intestinal infection in any family member is a huge alarm for everyone else. The patient needs a separate dish, and the rest - often wash their hands, organize the perfect cleanliness, all the dishes should be boiled, not sparing disinfectants.
The main principle of assistance in receiving an intestinal infection is to make up as soon as possible the loss of salts and fluids. Compote of dried fruit, green tea.
Infectious agents
Like many others, intestinal infections in babies can be viral and bacterial. By their name it is clear that the difference in the nature of the pathogen. Among the huge number of children the most common is rotavirus.
In addition, there are still the most common infections in babies: dysentery, enterovirus and salmonellosis.

Every year (according to WHO statistics) about 2 million children under the age of 5 years die from a disease called intestinal Komarovsky believes that if all the necessary measures were taken, this figure would be much lower.
Self-medication or experience of professionals?
But parents should not be afraid and despair. Not the worst thing that can happen to their baby, is an enteric intestinal infection. Komarovsky asserts that over 90 percent of all cases of infections can be overcome without the use of special medicines. But the remaining 10% - the most insidious and terrible. This is exactly the case when self-medication cannot be applied in any case! The most important thing in the current situation - as soon as possible to bring the baby to infectious diseases.
Indications for calling a doctor
Urgent doctor care is needed for the following symptoms in your child:
- there are blood clots in the vomit of the baby or his stool;
- the child cannot be drunk - he either spits up the water, or cannot swallow it;
- there are clear signs of dehydration - “dry” tongue, the baby does not pee for the last 5-6 hours, there is dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, no sweat and tears;
- on the body of the child made a rash;
- the crumb complains of a headache;
- body temperature rises sharply and severely;
- in case of diarrhea or vomiting, parents can see that the baby’s skin is rather pale and is much shaky.
Signs and symptoms of intestinal infection in babies
All the above signs and symptoms describe a situation in which intestinal infection in children (Komarovsky declares this with full responsibility) has already acquired a rather severe or even deadly form. Fortunately, such situations are not frequent.

Most cases of infection are usually expressed by several universal symptoms:
- baby refuses to eat;
- have vomiting or diarrhea;
- body temperature rises slightly;
- the baby is sleepy, lethargic and pale.
Who brings the infection to the body?
Not in all cases, intestinal infection in children is terrible and dangerous. The treatment (Komarovsky is convinced of this from the height of his professional experience) must be timely and accurate.

The causative agents of intestinal infections include bacteria (vibrio cholera, stick typhoid fever, staphylococcus) and some viruses. They can well reproduce in the intestines and lead to disruption of the digestive process. They contribute to the inflammation of all the cells of the intestinal mucosa. A common and characteristic consequence of these processes is diarrhea as the main symptom in a situation where Komarovsky is observed, explaining that from the very beginning the very concept of a disease obtained by infection differs. For a person not versed in medical terms, diarrhea is a guarantee of infection in the body. For the doctor, it is not the symptoms themselves that are important, but the ways of infection.
Part of the symptoms is not a disease.
"Any disease in children, transmitted through the mouth (the so-called fecal-oral route of infection) and shows what intestinal infection in infants" (Komarovsky). The most obvious example is Botkin's disease. The virus enters the gastrointestinal tract, diarrhea in most cases is not, and the liver is affected. That is why it is not necessary to focus only on diarrhea. After all, there are also other signs of the disease - pain in the tummy of the baby, high body temperature, nausea and vomiting, the child is weak. Such signs are quite common, but they do not always indicate that intestinal infection is present in children. Symptoms, treatment (Komarovsky, as a representative of the clan of talented doctors, is convinced that the result will be much better than before the parents went to the doctor) should be: first - well studied, and second - applied according to the doctor's instructions.
Dehydration of the child's body
Only an insignificant part of the diseases called “intestinal infection”, treatment (Komarovsky, as a doctor with many years of experience is convinced of this), which does not require any thought, should be carried out with the help of antibiotics. And the rest pass without such intervention, accompanied by the immune system of the baby. After a few days, she begins to develop the necessary protection against this disease. The main task of any baby is to hold out for these few days. And the most dangerous risk for this period for a child is the most common dehydration, reports Dr. Komarovsky. Intestinal infections contribute to the fact that when diarrhea or vomiting fluid leaves the body. Therefore, it is so important to renew it.

If mom and dad know exactly how to protect the body of their child from dehydration, their intestinal infection is not terrible for their toddler.
Features in babies: fever and antibiotics
Intestinal infection in children - symptoms, treatment (Komarovsky stopped at this point in detail in his programs) when the situation arose - must first be detected on time and then eliminated with the help of properly prescribed drugs.
It is usually considered that if a baby has a body temperature of about 38 ° C, then it should not be knocked down (the body fights itself). But according to Dr. Komarovsky, intestinal infections are dangerous, therefore, it is not only possible but also necessary to bring down the temperature. This follows from the fact that the heat removes huge reserves of fluid from the body, and in fact it is especially dangerous for children to dehydrate with intestinal infections.

Karapazu (if the body temperature has risen) must be given a febrifuge so that there is no dehydration and intoxication. You should constantly give your baby a drink.
Parents, remember: the higher the temperature of a baby’s intestinal infection, the more it needs to be watered!
It has already been said that only a small percentage of intestinal infections require the use of antimicrobial agents to cure. And the use of any antibiotics in this case is strictly regulated by WHO.
According to Dr. Komarovsky, intestinal infection in children is dangerous, but not fatal. It is only necessary to adhere to all the recommendations of the doctor and not to self-medicate. Antibiotics can be used in cases of diarrhea, which has lasted for several days, hemocolitis (when there is an admixture of blood in the feces or vomit) and in severe forms of cholera. Only in these cases is the use of antibiotics for babies justified and fairly effective.
Treatment of intestinal infections in babies: sorbents
Indeed, there is a certain reason in the use of sorbents for intestinal infections of babies. They can absorb poisons, toxins and other harmful substances inside the gastrointestinal tract, will eliminate the excess gas. Practicing pediatricians are convinced that to some extent sorbents protect the child's body from dehydration and intoxication. No one has yet been able to prove that the use of such tools poses a threat to the child.
Baby food after getting rid of an intestinal infection
So, what is the diet after an intestinal infection? Komarovsky reminds that during the illness the baby had a temporary enzymatic deficiency. After an illness, it does not last long. This is important to consider when drawing up the baby’s menu.
In the first days after the illness, it is necessary to restrain the appetite of the recovering child.

It often happens that after the recovery phase begins, the baby’s condition improves and appetite comes. Here are parents (especially grandmothers) and are happy to try - they put all the tasty things on the table - fatter and thicker. But purely physiologically, the child’s body is not yet ready for such excesses: it does not yet have enzymes that would digest all this taste.
You should not feed him "heavy" and fatty foods. It is better to prolong the therapeutic diet, which include vegetable soup, cereal porridge on the water, cookies, fruit puree. This is only 5-7 days, until the activity of the enzymes is restored.
Be sure to follow the diet of the child after an intestinal infection. Komarovsky advises that it is possible to act in a different way: for some time, to give the recovering baby special enzymes. Although many pediatricians believe that the prolonged diet is better than “feeding” the child pharmacy enzymes.
Health to you and your children!
According to WHO, annually in the world about 5 million children die as a result of acute intestinal infections (AII). Moreover, more than 10% of them die as a result of rotavirus infection - the so-called "intestinal flu."
Oka is infectious diseases with an enteric mechanism of transmission, characterized by diarrhea, vomiting, dehydration of the patient's body and general intoxication. The causative agents of acute intestinal infections in children are bacteria, viruses or protozoa.
Infection with intestinal infections is associated with the use of poor-quality or improperly stored food, unboiled water, and violations of personal hygiene. Some pathogens of OKA, for example, rotavirus, are highly contagious, so get infected " intestinal flu»Possible even with the observance of sanitary standards.
Please note that OCIs pose a threat to children due to the nature of their body, therefore, a doctor should treat intestinal infections. Below you will find information about first aid that you can provide to your child before the arrival of the doctor, as well as therapeutic measures that can be performed at home for medical purposes.
Oka: symptoms
Diarrhea (diarrhea) is the most common specific sign of intestinal infections in children. Liquid stools more than three times a day, noted in a child, should make parents suspect OCI.
Note that breastfed babies have a higher stool frequency than older children.
In addition to increasing the frequency of stool and its liquid consistency, changes in its color may indicate an intestinal infection. For example, in case of viral hepatitis A, a stool discoloration is observed, and in case of dysentery, impurities of blood, mucus and greenery can appear in it.
Vomiting is another specific sign of OCI. Even a single vomiting in a child can talk about the development of the disease.
In most cases, children with OCI will have a higher body temperature. Depending on the pathogen and the severity of the disease, it can reach 41 ° C or remain subfebrile. Also, the child may experience the following signs of intoxication and gastrointestinal lesions - nausea, general weakness, weakness, abdominal pain, painful urge to defecate (tenesmus).
Dehydration (dehydration), which develops as a result of diarrhea, vomiting and fever, is the main danger in acute intestinal infections in children. Correction of severe dehydration is possible only in a medical hospital, so consult a doctor immediately if you suspect an intestinal infection in a baby.
Treatment of acute intestinal infections in children
As noted above, with OCI in a child, you should immediately consult a doctor. This is due to the threat of dehydration, which can develop in young children within a few hours after the onset of the disease. Before the arrival of the doctor, you should help the child yourself.
OCI therapy includes etiological, pathogenetic and symptomatic methods. The first are aimed at the destruction of the causative agent of the disease. The second affect the mechanism of the development of the disease, and the third eliminate its individual symptoms. Please note that first aid for intestinal infections in children should be provided using pathogenetic methods of therapy.
Pathogenetic treatment of OKA
As noted above, the severity of a child’s condition in acute intestinal infections is usually caused by dehydration — loss of fluid due to diarrhea, vomiting, and accelerated evaporation through the lungs at elevated temperatures. In addition, the body suffers as a result of the accumulation of toxins in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting from inflammatory damage to the intestinal walls, impaired digestion and the breakdown of bacteria.
Thus, the main objectives of pathogenetic therapy are:
- Rehydration of the body - replenishment of fluid and minerals lost as a result of diarrhea and vomiting.
- Removal of toxins from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Remove toxins from the baby’s blood.
The fight against the dehydration of the organism is the most important task in the development of AII in children. The child should drink as much as possible in order to avoid severe dehydration, which is a life-threatening condition. In the first hours of the disease, water the child with boiled water and special preparations for oral rehydration - Oralit, Regidron and others.
You can independently make a solution for oral rehydration at home. To do this, take 1 liter of cold boiled water, add to it one and a half tablespoons of sugar, half a teaspoon of salt and a quarter of a teaspoon of baking soda. Mix thoroughly - the solution is ready.
?>Intestinal infections often affect young children. This is facilitated by the still imperfect work of the immature digestive tract, violation of the standards of personal hygiene and improper storage and handling of products. Children's intestinal infections can be quite acute and lead to serious complications. If you do not have crumbs proper help they are capable of causing serious damage to his health.
How does the intestinal infection in the smallest?
There is diarrhea (diarrhea) - this is frequent stools, which can be from two to ten times a day. At the same time, the consistency of faeces can vary from porridge to completely liquid. You can find an admixture of mucus, foam, greenery, and in some cases, blood.
- There are signs of general intoxication, expressed in general weakness, the crumb becomes sluggish and drowsy, somewhat apathetic. He may complain of pain in the head.
- Appetite disappears completely or deteriorates. This is how the body protects itself, directing all its energy into fighting the infection, instead of digesting food.
- Vomiting occurs - single or multiple. Emetic masses initially contain some amount of food debris, after they become scarce and may include bile.
- The body temperature rises and sometimes to 38C, chills may occur on the first day.
- Cramps and pain appear in the stomach.
Children's intestinal infections are usually characterized by an acute onset. Each infection has its own characteristics and characteristics. Parents need to carefully fix them and everything that happens, since after the story about these manifestations it will be easier for the doctor to make a diagnosis and choose the right treatment. If the signs of infection have appeared in young children, then there is no need to pull on a doctor’s call, he should be called as soon as possible.
Be sure to think about whether there are adults or children with similar symptoms in the kid's environment. Often, intestinal infections are widespread, since early age children are constantly in contact with unwashed hands, toys, etc. Remember what a crumb ate in the last two days. Meals should be as fresh as possible, but perhaps after such an analysis, you will identify the pathogen by exclusion.
Causes of illness
Often the disease occurs due to meat, fish, dairy and vegetable dishes of dubious quality. Because of them, a staph infection can develop. Poorly washed fruits, vegetables and herbs, as well as raw eggs and boiled sausages lead to Salmonella infection.
First aid for children with intestinal infection
The first thing the crumbs need to wash the stomach. After each attack of vomiting, let the one-year-old baby have about a hundred grams of normal boiled water of cool temperature. For each year of the child add a hundred milliliters of fluid. In order to provoke vomiting yourself, press a finger on the root of the tongue with your finger, while wiping the finger with a sterile cloth. You can also resort to a cleansing enema (half a liter of cool water should be mixed with one teaspoon of salt). Be sure to make sure that all the water poured into it comes out of the intestines, so that it heats up to body temperature and is absorbed into the body, which will lead to repeated intoxication. If you are a little unsure of your abilities, seek medical help.
After the enema, cover the baby with a blanket and put him to bed.
To prevent dehydration, give it a special mixture - Regidron, Electrolyte, Glukosolan. They need to be purchased at a pharmacy and diluted with boiled water. This tool can be prepared independently, dissolved in a liter of water (boiled or mineral) in half a teaspoon of soda and salt and a tablespoon of sugar. This drink should be given to the baby in small sips, but not in a gulp to prevent a new attack of vomiting. You can also use weak green tea, dried fruit compote, canteen or mineral water without gas. In the development of an intestinal infection in a sick baby with toxins excreted from the body, it is important to ensure abundant drinking.
It is not necessary to give crumbs drugs that suppress the symptoms - binding and eliminating loose stools. These medicines may create the impression that the child’s condition has improved, but at the same time, intoxication will only increase.
Food for intestinal infections
The first day is better for the baby to eat nothing at all. But if he asks for one, give him some rice broth or a toast. Further be guided by indications of the doctor and a condition of the child. You can gradually introduce light soups on vegetable broth, water pots, chamomile tea, mashed potatoes without adding oil, a little dried bread, compote of dried fruits.
For about two weeks, eliminate from his diet fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, fresh bread, sweets, spicy, salty, fried and fatty foods.
Rules for the prevention of intestinal infections
Need to follow the rules of personal hygiene. Most often, wash hands, handle toys, cut nails, clean the apartment.
- When going to the nature, it is worth using only pre-stored water or sanitary napkins for washing hands.
- Treat berries, fruits and vegetables before eating.
- Buy only quality products that have passed the sanitary and hygienic test.
- Do not give the baby food that you forgot to put in the fridge. After all, many microbes do not affect the taste, but, nevertheless, multiply rapidly.
Be attentive to what your crumb eats and how, and intestinal infections will bypass your side.
Catherine, www.site
An intestinal infection is a disease that is localized in the gastrointestinal tract and is accompanied by general and local symptoms. Pathogenic viruses and bacteria are the causative agents of pathology. The disease is severe in childhood, often causing serious complications. Therefore, treatment of an intestinal infection in a child should be timely and effective.
The incidence of intestinal infections in the world, including in Russia, is quite high. Intestinal infections are in the next place after SARS and influenza in frequency of occurrence. Almost every person knows their signs, as many have had intestinal infections in childhood.
What is important to know about intestinal infection in children?
Intestinal infections in children can be caused different species viruses and bacteria. All these pathogens are resistant to negative environmental factors, they can maintain their activity for a long time at low temperatures outside the human body.
They live on food, household items and dirty skin of the body. Bring infectious pathogen in the gastrointestinal tract is very easy, infection occurs through the mouth. The process of treating intestinal infections in children will take a lot of nerves from parents and cause even more suffering to the child.
Intestinal infections are divided into the following diseases:
- Bacterial intestinal infections: salmonellosis, dysentery, colibacillosis, yersiniosis, campylobacteriosis, cholera, botulism, typhoid fever, acute intestinal infection caused by Klebsiella, clostridia, blue prickly stick, staphylococcus and others.
- Viral intestinal infections that cause rotaviruses, enteroviruses, adenoviruses and others.
- Fungal intestinal infections caused by Candida fungi.
- Protozoal intestinal infections: amebiasis, giardiasis.
Treatment of intestinal infections in children is complicated by the fact that specialists need about 3 days to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. During this period, the pathogenic microflora begins to be active in the biological material collected from the patient. While the analysis is being conducted, the child receives treatment with drugs that are effective against the overwhelming number of pathogens.
Symptoms
The symptoms of intestinal infection in children are divided into local and general.
Common signs of the disease:
- intoxication: fever body, headache, general weakness;
- dehydration: rare urination, dark color urine, dry mucous membranes and skin, violation of skin turgor.
Local symptoms of intestinal infections in children:
- by type: stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- by type: pain in the stomach and umbilical region, vomiting, watery stools with mucus;
- by type of gastroenterocolitis: persistent abdominal pain of diffuse nature, vomiting, loose stools with blood, not bringing relief;
- according to the type of colitis: pain in the lower abdomen, pain during stool, loose stools mixed with mucus and blood, false desires to the toilet.
Severe disease can cause the following complications, each of which has its own signs:
- neurotoxicosis: restless behavior, disorder of consciousness, delusions and hallucinations, convulsive syndrome;
- impaired blood circulation: low blood pressure, cyanosis of the skin, weakness of the heart;
- renal failure: pain in the lumbar spine, a decrease in the volume of urine excreted or its complete absence;
- hypovolemic shock resulting from dehydration: retraction of the eyeballs, weight loss, sharpening of facial features.

How to distinguish a viral intestinal infection from bacterial?
To make a correct diagnosis and choose effective treatment, it is important to find out why an intestinal infection arose, what became its basis - a bacterial or viral infection?
Bacterial intestinal infections develop as a result of the ingestion of bacteria such as salmonella, dysenteric bacillus, etc. It is possible to distinguish such an infection from a viral infection by the following features: the disease begins by poisoning with a simultaneous rise in body temperature from 37 to 38 °.
In most cases, the child develops abundant vomiting and colitis symptoms - intestinal spasms. Fecal masses can be colored green and contain mucus. With severe course infections in feces can be noticed blood. The urge to stool is extremely painful. Treatment of a bacterial intestinal infection requires antibiotics. Most often, the child is hospitalized for the period of treatment in an infectious diseases hospital.
Viral intestinal infections are also not uncommon. Experts identify 10 groups intestinal viruses. Rotaviruses and enteroviruses are the most common causative agents of the disease.
Rotavirus infection is called intestinal flu, it occurs in half of patients with a viral intestinal infection. Viral infections develop acutely, like a cold or flu, the body temperature suddenly rises to critical levels - from 39 ° and above, the stool becomes watery and profuse, painted in yellow. The treatment tactics for intestinal infections of viral origin is different from the treatment of a bacterial form of the disease.
What to do before the arrival of the doctor?
How to treat an intestinal infection in a child, the doctor will tell.
Before his arrival, you can help your child in the following ways:
- Offer as much drinking as possible. Even babies need to be given boiled water from the nipples to combat dehydration.
- From 6 months child can be given Enterosgel or Activated charcoal. Dose calculation is simple: 1 tsp. gel or 1 tablet of coal per 10 kg of child's weight.
- It is important not to give children any food. Food products, getting into the digestive tract irritated by the infectious process, irritate it even more and aggravate the signs of an intestinal infection in a child. Only babies under one year old can still be offered breast milk if they are breastfed.

What can not be done?
When symptoms of intestinal infection in a child are prohibited from doing the following:
- Give painkillers. Analgesics can blur the picture of the disease, with the result that the doctor can make the wrong diagnosis and postpone the provision of the necessary specialized care for an indefinite period.
- To give astringent or fixative preparations, for example, Loperamide or Imodium. It is impossible to stop diarrhea, as the pathogens and their toxins leave the intestines together with feces. If you stop the diarrhea, the bulk of pathogenic microflora will remain in the body, aggravating the situation.
- You can not do enemas at home.
- You can not hesitate with calling a doctor and self-medicate a child. Acute intestinal infections may hide surgical pathology, so ambulance must be called immediately, otherwise the consequences may be sad. The younger the child, the more dangerous for him intestinal infection.
Drug treatment
Treatment of intestinal infections in children should be comprehensive, suggesting the organization of oral rehydration, symptomatic, etiotropic and pathogenetic treatment, diet therapy.
Diet in children in the treatment of intestinal infections is based on reducing the volume of food and increasing the frequency of feedings, with the use of products in an easily digestible form or artificial formulas in infants with protective factors.
The basis of the treatment of symptoms of intestinal infection in children is oral rehydration of the body with special solutions of salts and glucose (drugs Regidron, Cytroglukosolan). You should also pay attention to drink plenty of water. If a sufficient amount of fluid cannot be consumed, the child is given infusion therapy with intravenous albumin solution, glucose and others.
Etiotropic treatment of symptoms of intestinal infection in children is carried out using the following drugs.:
- antibiotics: Gentamicin, Polymyxin;
- intestinal antiseptics: furazolidone, nalidixic acid;
- enterosorbents: Smecta;
- bacteriophages of specific importance: salmonella, klebsielle, dysenteric and others;
- immunoglobulin: antirotavirus and others.
Pathogenetic treatment is carried out with intestinal infections in children, the symptoms of which require the appointment of enzyme preparations (for example,) and antiallergic drugs (for example, Suprastin, Loratadin).
Symptomatic treatment of intestinal infections in children includes taking antispasmodic (for example, Drotaverin, No-spa) and antipyretic drugs (for example, Paracetamol, Panadol).
Nutrition
After a medical examination and appointment of all therapeutic measuresaimed at eliminating the symptoms of intestinal infection in children, treatment must be continued with proper diet therapy.
Babies under one year of age who are breastfed need to offer their breasts more often and give boiled water from the nipples so that the baby can quickly recover the fluid lost by the body. Babies who are bottle-fed during treatment and for a period after recovery are recommended to give a low-lactose or lactose-free mixture.

Children older than a year should receive the most sparing food that is easily digestible, for example: vegetable puree, vegetable and rice soups, low-fat dairy products, fruits and berries, porridge and cereals cooked in water, freshly squeezed juices without sugar. Also need to remember about drinking regime: To prevent dehydration, your child needs to drink frequently. As a drink, you can offer boiled water, black tea, chamomile decoction, fruit drink, non-carbonated mineral water.
Prevention
In order not to think about how to treat intestinal infections in children, you need to pay attention to the prevention of this disease. General recommendations reduced to the observance of personal hygiene, compulsory hand washing after the toilet and the street, careful processing of food, especially washing fresh vegetables and fruits.
If one of the family members or the child has symptoms of an intestinal infection, treatment should be carried out in a separate room where disinfection should be carried out. The sick stand out separate bedding, towels, dishes and cutlery. After each visit to the toilet you need to handle a toilet bowl or a children's pot with any disinfectant, if the child goes into it.
Detection of signs of intestinal infection in a child is an urgent reason to seek medical attention. There is no question of any self-treatment in this case. It is necessary to consult a pediatrician, undergo a proper examination and receive adequate medical care.
Useful video about the treatment of intestinal infections in children
Popular
- What is the name of the Scottish skirt
- What women like a man archer
- Dosage and use of doxycycline when tick bite
- Sinupret - complete instructions
- Number of antennae in arachnid and insect crustaceans
- Help for enterobiasis for the pool, how much is valid
- Ceftriaxone suspension. What is ceftriaxone?
- Third degree breast cancer: prognosis and treatment
- Salt Scrub for the scalp
- Do girls how many centimeters to the uterus