Streptococcus and infectious diseases caused by it. What is Streptococcus - groups, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment with antibiotics and prevention
Streptococcus is a spherical bacterium. Today, 27 types of streptococci are known. Some of them are harmless to humans. Others, such as beta hemolytic streptococcus, can cause many dangerous diseases in person.
The group includes streptococci pneumococci. Pneumococcus is the main cause of bronchitis, community-acquired pneumonia, pleurisy, middle ear disease (25% of all otitis) and sinusitis. They cause endocarditis and arthritis, meningitis and peritonitis.
General characteristics of the pathogen
Streptococci constitute about half of the normal microflora of the oropharynx. The desquamated epithelium and food remains are a good nutrient medium for them. Bacteria colonize also gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, genitals, a large number of them lives on the skin.
Reduced immunity contributes to the development of serious infectious diseases. In such a situation, streptococci begin to acquire pathogenic properties. Especially many patients with quinsy, pharyngitis, rhinitis and other diseases of the streptococcal nature of the upper and lower respiratory tract are recorded in the cold season and after acute respiratory viral infections and measles. Low temperature and high humidity are optimal for the life and reproduction of bacteria.
Fig. 1. In the photo streptococcal angina.
Ways of transmission
Distributors of infection are sick and bacteria carriers. Carriage among maternity hospital employees is especially dangerous.
- Airborne droplet is the main (up to 96%) in the spread of infection. The spread of microbes by contact and with dirty hands is somewhat less common.
- Streptococci in the genital tract can get to the partner during sexual intercourse.
- A pregnant woman can transmit an infection to a newborn during childbirth.
- Enterotoxin of the pathogen that has accumulated in food can cause severe food toxicosis.
Products affected fecal streptococci, become lazy and get unpleasant taste. At the forefront of the clinic toxemia fever and the appearance of loose stools. Nausea and vomiting are much less common.
Streptococci are capable of staying in the human body for a long time. With a decrease in immunity, they become the cause of exacerbation with and.
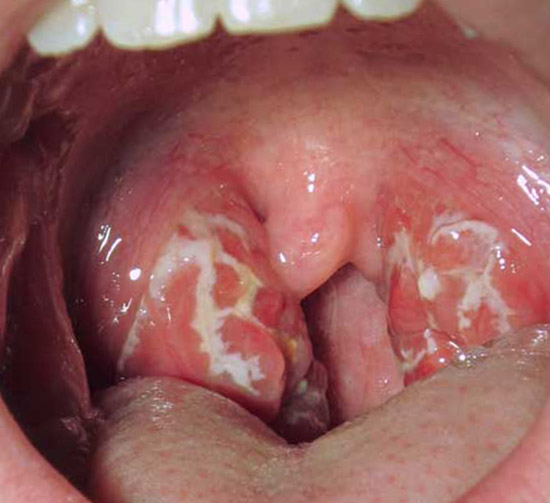
Fig. 2. The cause of sore throats is often beta-hemolytic streptococci.
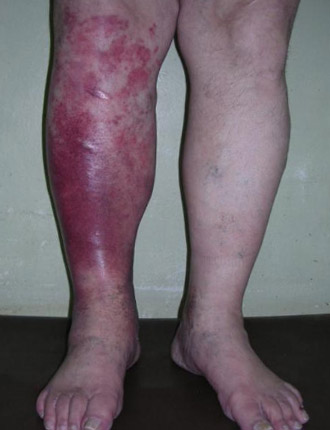
Fig. 3. In the photo erysipelas of the leg. The main cause of the disease is streptococcus.
Features Streptococcus
Streptococci are able to produce toxins.that damage the tissues of the human body and contribute to the spread of infection throughout the body. Inflammatory foci in the internal organs are purulent-necrotic in nature. Excreted toxins cause severe toxicosis, accompanied by high temperature body, vomiting, headache and even impaired consciousness.
Feature streptococcal infection cause an autoimmune response, leads to serious complications from the internal organs:
- rheumatic heart muscle damage;
- joint damage (arthritis);
- kidney damage (glomerulo - and pyelonephritis).
When microbes enter the bloodstream and their massive reproduction, sepsis and meningitis may occur.
Immunity after diseases caused by streptococci is not produced. The exception is scarlet fever, after which immunity is for life.
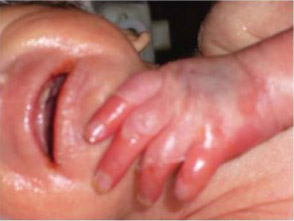
Fig. 4. Streptococcus - the cause of sepsis in a newborn.
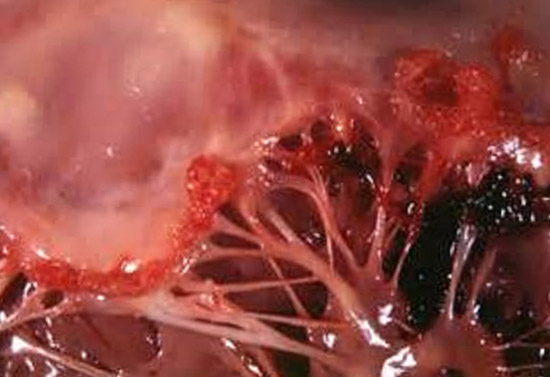
Fig. 5. Heart failure in rheumatism.

Fig. 6. The defeat of the joints with rheumatism.
Structure and Streptococcus
- Streptococci have a rounded shape. Arranged in chains or in pairs. Breed by dividing in two.
- They die quickly at high temperatures, in sunlight and from the action of disinfectant solutions.
- In the external environment (in dust, sputum, pus) persist for months. It tolerates low temperatures and freezing.
- Bacteria are sensitive to a range antibacterial drugs. Resistance to them is developed gradually.
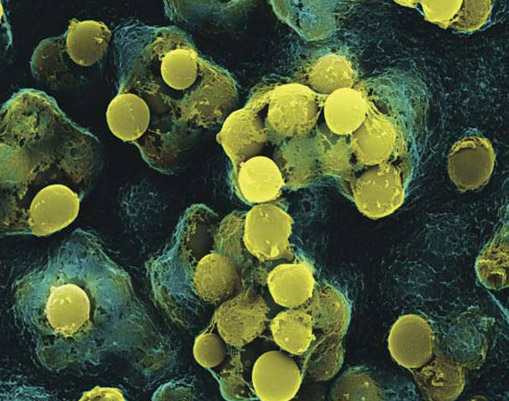
Fig. 7. In the photo streptococci (computer visualization).
Pathogenicity factors of streptococci
The damaging effects of bacteria are caused by endo- and exotoxins and a number of enzymes that they secrete.
- Protein M streptococci directly acts on phagocytes, reducing their activity, and on the humoral mechanisms of the immune response. When its effects develop autoimmune reactions. C5a-peptidase also suppresses the activity of phagocytes and the humoral mechanisms of defense of the body. Streptococcus capsule protects bacteria from phagocytes and provides adhesion (adhesion) to the epithelium. With the penetration of streptococci into the tissue, they are able to destroy their own capsule.
- Hyaluronic acid, from which the capsule is formed, is similar in structure to hyaluronic acid of the connective tissue of the human body, due to which streptococcus is not recognized as a foreign agent.
- The place of introduction of bacteria is fenced off from surrounding tissues slowly, which allows microbes to multiply and move throughout the body, causing the development of serious diseases.
- Streptolysin O is capable of destroying red blood cells and heart muscle cells.
- Streptolysin S destroys red blood cells and phagocytes, which are absorbed by bacteria.
- Erythrogenic toxins are able to expand small vessels. They cause the appearance of a rash (for example, with scarlet fever).
- Cardiohepatic toxin causes damage to the heart muscle, diaphragm and liver.
- Streptokinase promotes the dissolution of fibrin and facilitates the movement of bacteria through the connective tissue.
- Hyaluronidase promotes the breakdown of connective tissue cell membranes, contributing to the spread of infection.
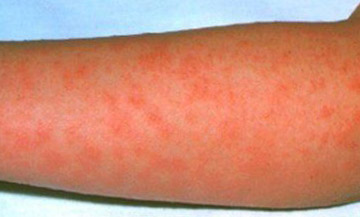
Fig. 8. In the photo there is a punctate rash with scarlet fever.
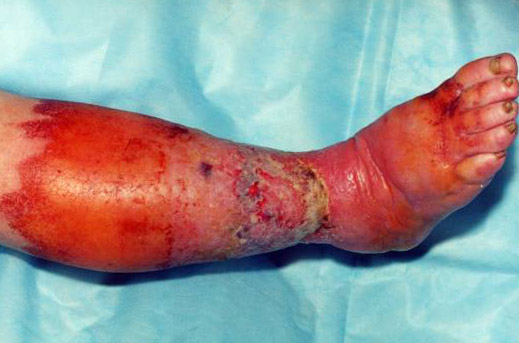
Fig. 9. In the photo erysipelas of the leg.
Streptococcus groups
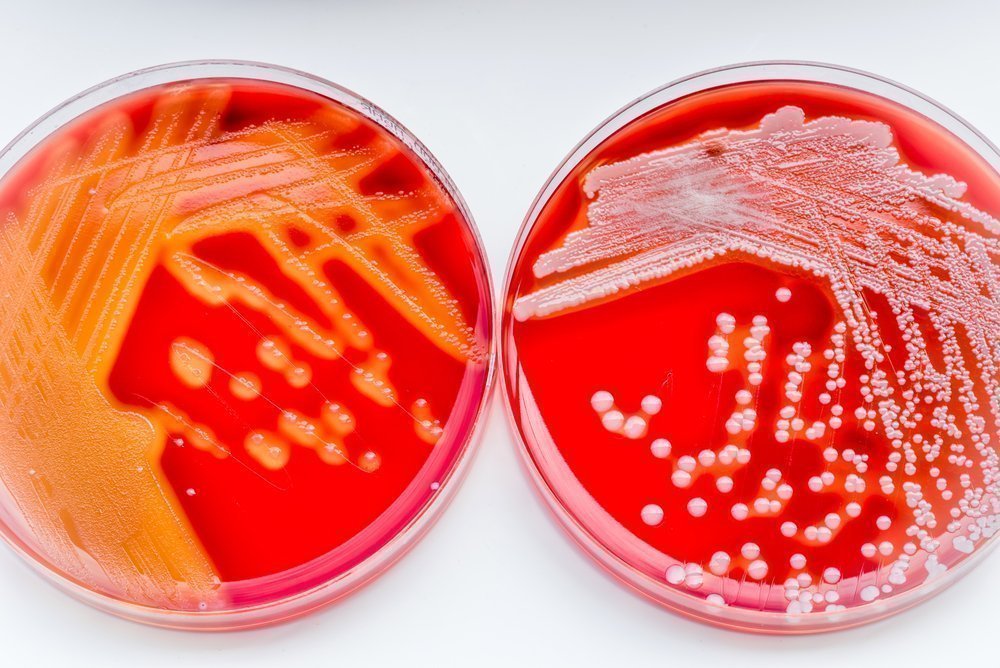
According to their ability to destroy red blood cells with the growth on the “blood agar” nutrient medium, streptococci are divided into 3 groups (Brown's classification, 1919):
- 1st group - alpha - hemolytic streptococci. They cause the oxidation of iron in the hemoglobin molecules of erythrocytes, which gives a greenish color with the growth of bacteria on blood agar. Streptococci of this group are called "green".
- 2nd group - beta - hemolytic streptococci. They cause complete hemolysis (destruction) of red blood cells. Bacteria of this group cause many dangerous diseases in humans. There are 20 types (serogroups) of streptococci, which are denoted by capital Latin letters (Rebecca Lansfield classification. 1933). The most significant of these are bacteria serogroups A, B, C, D and G.
- 3rd group - gamma - hemolytic streptococci. They are not able to cause visible hemolysis of red blood cells.
Characteristics of beta-hemolytic streptococci
Beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A (Streptococcus pyogenes, GABA)
Pyogenic (purulent) bacteria cause a number of diseases: pustular diseases of the skin and soft tissues (abscesses, cellulitis, boils, osteomyelitis), sore throats and pharyngitis, bronchitis, rheumatism, scarlet fever and toxic shock. Feature cause an autoimmune response, leading to the occurrence of serious lesions of the internal organs - heart, joints, kidneys.
Finding out the type of microbe that caused the disease is necessary to decide on the course of treatment with antibiotics. Diseases caused by beta-hemolytic streptococci must be treated with antibiotics.
Streptococcus is a conditionally pathogenic bacterium that is found in the human body in large quantities and in most cases does not harm it. However, in some cases, while reducing the protective forces of the immune system, it can cause serious diseases that require immediate treatment. What are streptococci, what diseases cause, how are they tested for the detection of this microorganism and what are the main methods of treatment?
Streptococcus in adults
Streptococcus in men
Streptococcus in men is detected most often in smears from the pharynx, nose, or when taking a urinalysis. He is a normal inhabitant of the nasal cavity, mouth and intestines, therefore, the diagnostic value is played by the combination of his high titer with the clinical manifestations of an infectious disease.
Streptococcus in women, as well as in men, is most often detected in smears from the pharynx and nose. The most dangerous is a positive result in the study of urine in a pregnant woman, because streptococcus agalactia can cause serious illness in a child if infected during the passage of the genital tract during childbirth.
Streptococcus in children
Respiratory diseases in babies are the most frequent reason for going to a pediatrician. Examination of a throat or nose smear is a very common type of analysis, because streptococcus in children often causes serious infectious diseases. The strength of local and general immunity in preschool children is much weaker than in adults, therefore bacterial complications develop in them more often and behave more aggressively. Streptococcus in children, as well as in adults, is normally present in the nasal cavity, oropharynx and intestines, however, in severe viral infections, they often cause complications in the form of otitis, sinusitis, and even pneumonia and meningitis.
If streptococcus in children is detected in a throat, nasal or urine smear in high titers, treatment with antibacterial drugs is necessary, taking into account age, the nature of the pathology and weight.
What are Streptococcus bacteria?
Streptococci are microscopic examinations that look like balls or ovals. However, they usually live not one by one, but united in pairs or chains, vaguely resembling beads with not buttoned ends. There are various groups of streptococci, each of which has its own characteristics, causes specific diseases in humans and is an indication for the appointment of a specific type of antibiotics. The most common streptococcus bacteria are conditional pathogens, since they live on the skin or in the body of almost every person from the first day of life, but in most cases do not cause the development of infection. They are waiting for the creation of favorable conditions, which is a decrease in the protective forces of the immune system, and then they can become the cause of quite serious diseases.
Each cell is an autonomous organism with a certain type of vital activity. Streptococcus bacteria cannot move independently, since they do not have any devices for this (flagella, cilia). Therefore, they move exclusively due to the influence of an external force: the movement of blood flow, urine, with inhaled or exhaled air, through the contaminated surface of the hands from one place to another. Streptococcus bacteria multiply very quickly when they are in conditions that are favorable for them (high humidity, heat, glucose solution and blood) by division, and two of them are obtained, each of which is also divided in half. As a result, their number grows exponentially in a short time.
Streptococcus groups
Various groups of streptococci are isolated, depending on their ability to cause hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells). Carry out this study on blood agar in a clinical laboratory, because the type of this bacterium will determine further medical tactics and influence the course of the disease. Non-hemolytic, alpha hemolytic and beta hemolytic streptococci are distinguished, each of which has its own characteristics.
Alpha hemolytic streptococcus has another name "greening." The Latin version of this bacterium is Streptococcus viridans. It received its name due to the fact that during the analysis it gives not complete hemolysis (destruction) of red blood cells, which gives the blood a green tint. However, in itself it does not have that color. Alpha hemolytic streptococcus is one of the most favorable types of these microbes, as it rarely causes the development of diseases.
Beta hemolytic streptococcus
Beta hemolytic streptococcus is determined by complete hemolysis (destruction) of erythrocytes on blood agar during microbiological research. A characteristic difference from the previous one is that it does not show the appearance of a green hue around these cells. Beta hemolytic streptococci in turn are subdivided into several small subgroups, each of which has its own specific features in the structure of the cell wall.
Beta hemolytic streptococcus groups A, B, C, D, and so on, are distinguished up to U, that is, their diversity is simply impressive. Group A includes pyogenic streptococcus, group C - streptococcus agalactia, group D - enterococci, and so on. Determining the specific type of this microorganism is extremely important for doctors, because they all behave in a special way in the human body and this affects the course of the disease. In determining the treatment tactics, it will be easier for the doctor to make a choice among the whole variety of antibacterial drugs in order to help the sick person as quickly as possible.
Hemolytic streptococcus
Nonhemolytic streptococcus does not cause erythrocyte hemolysis on blood agar. For this and other reasons, they pose no danger to humans. They do not cause bacterial infectious diseases and are not of medical interest.
Often you can find this situation: a person in the analysis revealed non-hemolytic streptococcus, the symptoms of any disease are absent. However, he is extremely worried about this fact and he asks the doctor to prescribe him a treatment. And, nevertheless, there is no need for this.
Staphylococcus and streptococcus are two microorganisms that are most often found in humans in the analysis of urine, blood and various smears. Usually, people are alarmed by the positive result of the study, despite the fact that they have no unpleasant sensations and deviations in their state of health. And, nevertheless, staphylococcus and streptococcus can cause serious diseases that develop with adverse circumstances and the deterioration of the immune forces of the body.
Common in streptococcus and staphylococcus is their structure. They are Gram positive facultative anaerobic bacteria that cannot move on their own, but reproduce well under favorable conditions. The difference is that they are often found one at a time, and streptococci are combined in pairs, groups or long chains. And those and others live on the skin, mucous membranes, in the mouth, airway and sometimes they cause the development of angina, otitis, pyelonephritis, endocarditis, meningitis, skin inflammatory processes and even sepsis.
What streptococci are most dangerous
Some groups of streptococci, under unfavorable circumstances, can cause very serious diseases that require mandatory treatment with antibacterial drugs.
It is important for the physician to send the material of a person to a study on time, among which most often a smear is taken for streptococcus (from the pharynx, nose) in order for a specialist to determine whether the pathogen belongs to a particular species. In addition to smear, urine, blood, breast milk, etc. are suitable for bacteriological examination.
Streptococcus viridans (green streptococcus)
Streptococcus viridans or greening streptococcus is a normal inhabitant of the oral cavity of most people. Its favorite localization is the enamel of the teeth, the gums, which can be explained by its structure: there is a special protein on the surface of this bacterium that allows it to be fixed securely to the tooth enamel. If a person abuses sweet food and has a constantly favorable environment in his mouth, then Streptococcus Viridance secretes special substances that convert glucose into lactic acid, which in turn destroys enamel. As a result, caries or pulpitis develops.
If the strength of a person’s local or general immunity is reduced (viral infections, use of cytostatics, corticosteroids, severe hypothermia, HIV infection or other immunosuppressive diseases), then in addition to caries streptococcus viridans can cause angina, pneumonia, meningitis, endocarditis. In the most severe case, there is a risk of sepsis - spreading from a microorganism throughout the body.

The most common beta hemolytic streptococcus group A is a pyogenic streptococcus. In addition to it, there are a number of other bacteria (Streptococcus equisimilis and Streptococcus anginosus), but they are much less common. Therefore, at present, beta hemolytic streptococcus group A and pyogenic are synonymous with physicians.
Normally, it is present in the oral cavity in most people, without causing them harm. But under certain circumstances (severe viral infection, trauma, hypothermia, reduced immunity with various drugs (cytostatics, corticosteroids), chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer), it penetrates into the tonsils, causing the development of angina. Hemolytic Streptococcus group A, which caused acute tonsillitis, is extremely dangerous, because without treatment it spreads more easily with blood to the kidney parenchyma, the inner lining of the heart and joints. Therefore, untreated angina can provoke the development of pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, myocarditis, endocarditis and rheumatism.
If a patient has an acute tonsillitis clinic ( sharp pains in the throat, aggravated by swallowing or making it impossible at all, fever and symptoms of general intoxication) in combination with a positive result for group A streptococcus in a smear - a course of antibiotics is vital. No alternative treatment options in similar situation are not allowed. If the smear for streptococcus of this group from the pharynx turned out to be positive, but does not bother the person, then he does not need any special therapy to eliminate it - this is a variant of the norm.
Beta hemolytic streptococcus group b (streptococcus agalactia)
Among the beta hemolytic streptococci of group B, the only representative of interest to doctors is streptococcus agalactia. Despite its name, this microorganism is not related to the absence of milk in puerperas. He was called so solely for the reason that he was first found in cows that had mastitis.
Streptococcus alaktaktia is also a conditionally pathogenic microorganism, because it lives in the intestines of more than half of people, without causing any unpleasant symptoms. The presence of a large number of these microbes in the vagina can cause the development of vulvovaginitis and cystitis, and it gets there from anus. Sexually, a woman can infect a man who has an infection of the urethra and bladder.
In general, for an adult person, streptococcus agalactia does not pose a particular danger, which cannot be said about newborn babies. They may be infected by the mother, an asymptomatic carrier of the infection, during the birth process. The result is often sad enough: pneumonia, respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, or even sepsis. Mortality in newborn babies from this infection despite the achievements of modern medicine is very high and amounts to 15-30%. Therefore, any pregnant woman in whom a hemolytic streptococcus B group is detected during urine testing should be sanitized, that is, treated with antibacterial drugs until the corresponding microbes in the analysis have completely disappeared.
Other beta hemolytic streptococci
There are many more rare beta hemolytic streptococci that are dangerous to humans: enterococci, fecalis, fezum, bovis streptococcus, etc. life is almost impossible to meet with them. Detect these dangerous streptococci in a smear of pharynx, nose, blood and urine.
A distinctive feature of Streptococcus pneumonia, or, as it is commonly called, pneumococcus, is that the two bacteria combine in pairs and move in this way. However, even within this narrow group of microbes, there are more than 90 different subspecies. The peculiarity of the streptococcus pneumonia bacterium is that, unlike others, it is not a conditional pathogen. Infection with this microbe occurs through direct contact with a sick person: an airborne droplet (with exhaled air) or a contact-household route (when using only household utensils).
Pneumococcus can cause quite serious diseases that require mandatory medical participation: otitis media, pneumonia, meningitis. If a person in the analysis revealed streptococcus pneumonia in combination with various dangerous symptoms: fever, cough, pains in the chest, ears, head, etc., then he must receive anti-bacterial treatments for which he is sensitive. Lack of timely treatment can lead to serious consequences and even death.
The best prevention of diseases that Streptococcus pneumonia causes is the vaccine from the corresponding pathogen. Since January 1, 2014, it has been entered into the National Calendar of Vaccinations for Children in our country, but this vaccine will also be useful for adults at risk.
Streptococcus: symptoms of infection

Streptococcus is a common inhabitant of the oral cavity of the vast majority of people. It is a conditional pathogen, that is, it is on the mucous membrane and does not cause any harm to the host. Therefore, if a streptococcus is found in a perfectly healthy person in the throat, then this is not a reason for active treatment. This microorganism is so widespread in the environment that several hours after its complete elimination from oral cavity, they appear there again.
However, strep throat is not dangerous for humans, provided that the strength of local immunity is sufficient to resist it. If for some reason they are reduced, the bacterium can penetrate the oral mucosa, tissue and cause a serious infectious process. Inflammation of the tonsils caused by streptococcus (most often it is hemolytic streptococcus group A) is called acute tonsillitis or tonsillitis. Its symptoms are as follows:
- extreme sore throat, which is aggravated by swallowing or talking,
- periodic cough
- fever to febrile numbers 39-40 ° C,
- symptoms of general intoxication (weakness, aches, pains in muscles, joints, bones, headache).
The first sore throat in a person’s life occurs under the guise of an infectious disease called scarlet fever. In addition to the above symptoms, a spotted rash appears in a person (usually a child) for 2-3 days, which begins on the skin of the scalp and then goes down. After a few days a peeling appears on the palms. If untreated with antibiotics, streptococcus in the throat of the tonsil tissue is carried with the bloodstream throughout the body and causes a complication of the kidneys (glomerulonephritis), heart (endocarditis or myocarditis) or joints (rheumatism).
Therefore, it can be said that streptococcus in the throat is not dangerous for most people, but in some cases it can cause serious health problems.
Streptococcus in the nose
Streptococcus in the nose is conditionally pathogenic flora, that is, it can be found in most people who do not experience any unpleasant symptoms. However, by reducing the strength of local immunity, bacteria can be activated and cause a rather pronounced inflammatory process.
Most often, streptococcus in the nose can penetrate into the sinuses (maxillary and frontal) and cause bacterial sinusitis. This disease is characterized by pain in the projections of the sinuses, aggravated by bending and pressure on the corresponding area, nasal congestion, fever and very poor health (headaches, aches, weakness, dizziness). The diagnosis is confirmed by x-ray and nose smear. Sometimes streptococci in the nose can spread with a current of inhaled air in the upper and lower respiratory tract, causing pharyngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis or pneumonia.

Streptococcus in the urine usually occurs as a result of getting it there from the intestine. Most often it is streptococcus agalactia (beta hemolytic streptococcus group B). Also, this result is often false-positive, that is, the presence of a microbe in it indicates a violation of the technique during the analysis: the patient forgot about the rules of personal hygiene before the analysis, or he was collected on an emergency basis when he did not have the physical ability to wash off.
For an adult healthy person, this microorganism is not so dangerous, although under unfavorable circumstances it can cause the development of cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis or vulvovaginitis. The high content of streptococcus agalactia in the urine of a pregnant woman can cause infection of the fetus during the passage of the birth canal, which is extremely dangerous for him. Therefore, all future mothers pass this analysis to identify this microorganism, because if they have streptococcus in their urine analysis, they need to be treated before the onset of labor.
Streptococcus in the blood
Normally, a healthy person should not have streptococcus in the blood. Its presence in the bloodstream indicates a serious pathological process in which this microorganism from the primary focus (nose, throat, intestines or skin) spread throughout the body. This condition is called sepsis and is one of the most severe in medicine, as it requires active treatment in the intensive care unit and is the cause of high mortality.

Often you can find this situation: a young mother who feeds a baby breast, complains about the presence of various skin rashes and problems with the intestines. She is sent for research on the sterility of breast milk and reveal streptococcus in it. Some experts explain this by the presence of a rash and advise her to wean the child away, or to drink a course of antibiotics. However, these recommendations are fundamentally wrong.
When expressing breast milk, it partially flows down the skin of the breast, comes into contact with the hands of a woman, who certainly has this microorganism, because it is a conditional pathogen. Therefore, this result can be called false-positive, because it is simply impossible to assemble this analysis in compliance with the ideal sterility technique.
The presence of a positive analysis for streptococcus can be taken into account only when a woman has signs of mastitis, and even then, in the overwhelming case, it causes staphylococcus.
Diagnosis of Streptococcal Infection
Streptococcus in pharyngeal swab
The direction to detect streptococcus in a pharyngeal smear is usually given by doctors when a person has certain symptoms: sore throat, redness of the oral mucosa, tonsils, presence of purulent plaque on them, an increase in the submandibular lymph nodes, fever and symptoms of general intoxication. What is important is not the very presence of this microorganism in the analysis, but its quantitative content.
Streptococcus in a pharyngeal smear in healthy people is defined as 10 3 -10 4 CFU / ml, this result can be seen in the analysis. However, if it is 10 5 -10 6 CFU / ml and higher - this may indicate an infectious process that is caused by these microorganisms. And yet, active treatment required by a person only if there are clinical symptoms. Streptococci that live in the mouth are usually well sensitive to antibacterial drugs.
Before taking a smear on streptococcus from the pharynx you need:
- don't drink or eat in the morning
- don't brush your teeth,
- do not use any local antiseptic agents (candies, sprays).
A smear is taken from the surface of the pharyngeal mucosa with a cotton swab. The procedure is almost painless. The degree of streptococcal infection is determined by the number of microorganisms found in it:
The doctor directs the patient to smear for streptococcus in the nose with certain indications. They can be: severe nasal congestion, purulent and offensive discharge, pain in the projection of the maxillary or frontal sinuses, fever and symptoms of general intoxication. After all, sometimes it can cause development inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract. However, it is worth knowing that this microorganism lives in the nasal cavity of almost any person, and only one presence in the absence of specific symptoms of streptococcus does not require mandatory treatment with antibiotics.
A smear on streptococcus from the nose is taken similarly to this analysis from the pharynx. The doctor holds a cotton swab on the mucous membrane of the anterior part of the nasal cavity. The procedure is completely painless and does not cause negative symptoms in the patient.
Before researching for streptococcus in the nose, you must follow certain rules:
- do not use any antiseptic drops and sprays
- do not rinse nose with saline solutions.
The extent of streptococcal infection is determined for a nasal smear similar to that for the study of the microbial landscape of the oral cavity.
- 10 1 -10 2 CFU / ml - the microorganism is in the oral cavity in the minimum amount and is not capable of causing an infectious disease,
- 10 3 -10 4 CFU / ml - the microorganism is in the oral cavity in a normal amount and in the absence of clinical manifestations it is safe,
- 10 5 -10 7 CFU / ml - the content of the microorganism in the oral cavity is high and it can cause an infectious disease, corresponds to the average degree of streptococcal infection,
- “Confluent growth” - this phrase means that the content of a microorganism in a smear is so high that it simply cannot be counted, corresponds to a high degree of streptococcal infection and requires immediate treatment.
Blood test for streptococcus
If a septic process is suspected, the doctor sends the patient's blood for bacteriological testing to the laboratory. The positive growth of streptococci on blood agar suggests that human life is in grave danger, because in normal blood must be sterile. After a positive test for the presence of streptococcus in the blood is obtained, the laboratory diagnostic doctor continues an in-depth study to determine whether it belongs to a particular species.
In addition, there is another type of research: serological, in which it is not the microorganisms themselves that are detected, but antibodies to it.
Urinalysis for Streptococcus
The analysis for streptococcus in the urine must be collected very carefully. Elementary failure to comply with the collection rules may lead to false positive analysis. Often streptococci, which normally live in the rectum with improper leaching (or even in the absence of it) fall on the surface of the urethra. As a result, the analysis of urine for streptococcus gives a false positive result, which causes particular concerns during pregnancy.
Therefore, in order for the study to reflect the true picture, you must follow certain rules:
- before collecting urine, it is necessary to wash the vulva with ordinary running water without the use of special hygiene products,
- before the beginning of urine collection it is necessary to widely dilute the labia minora,
- the first portion of urine needs to be drained into the toilet, because microorganisms from the surface of the urethra are present in it,
- the average portion is suitable for analysis, the latter should also be flushed down the toilet.
The presence of streptococcus in the urine is not affected by the time of day, the phase of the menstrual cycle and other factors.

If an externally healthy person, in the absence of complaints and specific symptoms, a streptococcus is found in a smear of the pharynx, nose, and breast milk, treatment is not required. The presence of streptococcus in the analysis of urine in a pregnant woman requires therapy. Human blood is normally sterile; therefore, the appearance of streptococci in it indicates a septic process, which is treated in the intensive care unit of hospitals.
If a person with obvious signs of an infectious disease reveals a high content of streptococci, treatment should be carried out with antibacterial drugs. All other aspects (washing, rinsing, inhalation, taking candy) are auxiliary.
Streptococci are sensitive to penicillin antibiotics, cephalosporins, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, etc. However, the sensitivity to them is most accurately determined in the process of special microbiological analysis. In each case, the doctor chooses an antibacterial drug with maximum efficiency and in most cases there are no special problems with therapy. Some species (enterococci, penicillin resistant pneumococci) sometimes require more careful selection of treatment and cause certain difficulties.
A large amount of streptococcus in children found in a smear from a nose, throat, or urinalysis also requires antibiotic treatment, but the list of approved drugs in pediatrics is very limited.
Strep throat infection is a group of pathologies that develop under the influence. From birth, a person interacts with the world around him, so streptococcus in the throat is considered to be commonplace.
When creating optimal conditions and the confluence of certain circumstances, such bacteria provoke the progression of inflammatory processes in the human body. The pathologies of such a group differ from each other according to the type of localization and may be accompanied by the appearance of certain symptoms.
Streptococci can provoke the development of such dangerous pathologies in humans as pharyngitis and tonsillitis. The main cause of diseases in childhood is considered the primary infection in the body or a strong decrease in protective functions as a consequence of acute respiratory viral infections. The consequence of this is an increase in the number of bacteria that inhabit the mucous throat.
In adults, the main cause of streptococcal infection can become unhealthy habits, which severely injure the oral mucosa and make it susceptible to the disease.
There are some factors that increase the likelihood of streptococcal sore throats:
- the penetration of juice from the stomach into the esophagus and pharynx, that is, heartburn
- long-term treatment with glucocorticosteroids
- chemotherapy
- immunodeficiency states
Hemolytic streptococcus group B is a component component of the organs of the reproductive system of the female body, and its number can significantly increase during pregnancy.It is for this reason that bacteria can manifest themselves in a newborn immediately after birth, because they will get an infection while passing through the sexual way.
From the video you can learn how to distinguish viral infection from bacterial:
The risk of infection increases with protracted labor, with premature rupture of the fetal membranes and when other adverse factors affect the female body.Medical practice shows that if a streptococcal infection is present in the maternal organism, then in half of the cases it is transmitted to the baby.
In childhood, the infection can enter the body upon contact with the mucous membranes of adults who are carriers of bacteria. In most cases, children born with a streptococcal infection become infected. ahead of timethat violate the mechanism of obtaining antibodies of the mother. Infection of children at any age can occur airborne when coughing or sneezing, as well as prolonged contact with a sick person.
Symptomatology

The incubation period for streptococcal infection is several days, and the severity of symptoms is determined by the age of the patient. In childhood, the progression of pathology is much faster and is accompanied by the appearance of bright signs of illness.
AT early age You may notice the following symptoms in a child:
- nausea and vomiting;
- mucus from the nasal cavity yellow-green color;
- rise in body temperature;
- loss of appetite or lack of it;
- irritability and moodiness;
- constant crying
An older child can already answer what it hurts and what discomfort bother. The patient becomes sluggish, constantly asleep and refuses to eat, and his lymph nodes are noticeably increasing on the neck. The child has such signs of illness as headache, pain, scratchy and increased dryness in the throat. With streptococcal infection, the body temperature rises significantly and can be 40 degrees.
On examination of the patient, the doctor notices strongly reddened tonsils and the appearance of pustules on the mucous membrane.
With further progression of inflammatory processes, there is an even greater deterioration in the patient's well-being and the manifestation of symptoms of intoxication of the whole organism. When streptococcal pharyngitis, the patient complains of a dry cough, which in the absence of the necessary treatment turns into tracheitis. When a rash appears on the body, experts say that scarlet fever has developed in a child.
In adults, streptococcal tonsillitis can be severe and is accompanied by the appearance of these symptoms. The main complaints of patients is nausea, weakness and low-grade fever. In addition, worried pain sensations throat on both sides, swelling of the face and swollen lymph nodes.
Possible complications

Mostly complications develop with streptococcal tonsillitis and, especially, in people with reduced immunity.
The early complications that appear several days after the onset of infection are:
- pneumonia
- bronchitis
- sinusitis
- otitis
- lymphadenitis
A few weeks after an imaginary recovery, late complications may develop, which are associated with the absence of antibiotic therapy or failure to follow the course of treatment prescribed. Possible development in patients:
- meningitis
- osteomyelitis
- endocarditis
- myocarditis
- acute rheumatism
With the development of streptococcal bronchopneumonia in childhood, the centers of inflammation grow and merge with each other. The development of pleurisy, severe necrotic lesions of the lungs and empyema of the pleura can become a consequence of this pathology. Most severe complication streptococcal infection, the progression of which may be supplemented, is its generalization with the development of sepsis.
Diagnosis and methods of eliminating infection

It is easiest to diagnose the presence of streptococcus in the throat when performing special bacteriological seeding. To identify bacteria in humans, a smear is taken from the throat, which is applied to a special nutrient medium. When conducting such a study, a grown colony of microorganisms can be immediately tested for sensitivity to various antibiotics, which will subsequently make it possible to select the most effective treatment.
Another way to identify a streptococcal infection is to detect it in a person’s blood. Such a study is resorted to only if the streptococcal infection does not affect the symptoms, but it is necessary to determine the carrier state and select an effective treatment.
The treatment of streptococcal infection is the responsibility of the doctor who is responsible for the focus of the inflammatory process.
Medical practice shows that in most cases, treatment is carried out using antibacterial drugs from the group semi-synthetic penicillins. In the event that the patient is allergic to them, then they resort to taking macrolides, lincosamides and cephalosporins.
Treatment of streptococcal infection can be carried out using the following antibacterial drugs:
- Ceftazidime
- Cefotaxime
- Augmentin
- Amoxicillin
- Erythromycin
- Josamycin
Usually course drug treatment Streptococcal infection with antibiotics is 7-10 days, and it is not allowed to stop taking them while improving the condition of the patient. In addition to the selected antibacterial treatment, the use of local preparations in the form of aerosols, sucking tablets and mouthwash is prescribed.
The most effective drugs local action It is considered:
- Ingalipt
- Bioparox
- Tonsilgon N
- Chlorhexidine
- Hexoral
- Lizobact
In the event that the treatment of streptococcal infection was carried out with the help of antibiotics, then medication is necessary to restore the normal microflora of the internal organs. The most effective drug among all their diversity is:
- Bifiform
- Atsipol
- Linex
Treatment of streptococcal infections in children is carried out with the use of antihistamines such as Zodak, Cetrin and Claritin. In addition, prophylactic intake of vitamin C, which helps strengthen the walls of blood vessels, and improves immunity.
It is important to stay in bed during an illness and to rest in bed as much as possible. For acute pharyngitis or tonsillitis, it is not allowed to eat too hot and rough foods. To remove toxins from the body should consume up to 3 liters of fluid per day in the form of tea, juice, fruit drink or water.
Traditional methods of treatment

For a speedy recovery, the patient is recommended to combine the main therapy of streptococcal infection with prescriptions. traditional medicine.
- Effective preparation is propolis, which is recommended to cut into small pieces and chew them for several minutes several times a day.
- When streptococcal infection should gargle with broth broth prepared from a series of willow bark. Besides, effective remedy for rinsing sore throat is beet porridge with the addition of apple cider vinegar.
- To alleviate the patient's condition with the help of a drink made from cranberries, raspberries and rosehips. You can chop the pulp of apricot and take it in the morning and evening, which will speed up the recovery of the patient.
It is important to remember that eliminating streptococcal infection with the help of some traditional medicine is unlikely to work out, so you should not refuse the prescribed antibacterial treatment. It is possible to get rid of the pathology only with an integrated approach to treatment and with the obligatory observance of all the recommendations of a specialist.
Streptococcal infection is a group of diseases caused by beta - hemolytic streptococcus, which has the ability to destroy blood cells, enter the blood, brain, respiratory tract, urinary system or ENT organs and cause many diseases, including tonsillitis (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, scarlet fever). There are several types of streptococcus, but in 70% of cases, beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A causes inflammatory processes in the throat and pharynx.
What is streptococcal infection?
Streptococcal infection of the throat is a disease of an acute or chronic course in which inflammatory processes occur in the throat and pharynx, with lesions of the tonsils and upper respiratory tract. The causative agent of the disease is considered - group A streptococcus, which is present in the body of almost every person, but shows its activation only under certain conditions.
Gamma - hemolytic streptococcus refers to the bacteria that are present in the oral cavity, intestines, respiratory system, but they do not cause harm to our body. Beta streptococci, which, after penetrating the cells, provoke the development of inflammatory processes with a high risk of complications are considered dangerous for the human body. Pathogenic streptococcus secretes toxic enzymes that penetrate the blood stream, lymph and spread throughout the body, affecting internal organs and systems. It is streptococcus toxins that cause pronounced symptoms and symptoms of intoxication that are present during the development of angina or scarlet fever.
The immune system after the introduction of streptococcal infection is unstable, which can cause repeated inflammatory processes or the development of complications.
How does strep throat infection develop?
Diseases of the throat and larynx of infectious origin in 70% of cases are caused by streptococci, which are in a safe amount on the mucous membranes of the mouth. However, under certain conditions, when there is a shift in the immune system or a person has direct contact with a sick person, or a carrier of streptococcus, pathogenic bacteria are activated, which ultimately leads to the development of angina (tonsillitis), pharyngitis or scarlet fever.
Infection with streptococcal infection of the throat can occur in several ways: by airborne droplets, by contact - domestic or by close contact with a sick person. However, not all people suffer from infectious diseases of the throat. The fact is that the probability of morbidity depends on the state of the local immunity of the tonsils. The weaker the local immunity, the greater the chance of getting streptococcal infection of the throat. In cases when the general immunity is reduced, streptococcal infection of the throat can manifest itself against the background of predisposing factors: hypothermia, allergic reactions or adverse environmental conditions.
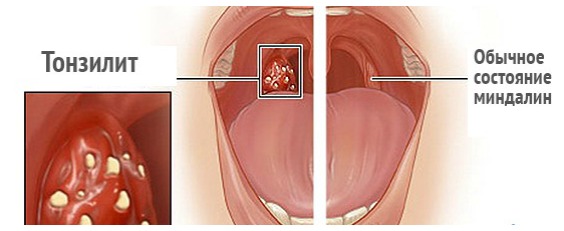
After penetration of streptococcus into the mucous throats, it begins to multiply actively, which leads to the impossibility of local immunity of the tonsils to overcome the bacterium. When streptococcus overcomes the barriers of local immunity, it penetrates the bloodstream, releases toxins, and, together with the blood flow, spreads throughout the whole body, causing inflammation and general intoxication. The inflammatory process in streptococcal infections of the throat, by its nature and course, can cause catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, or necrotic inflammation, which explains the appearance of angina, its shape and severity. Indeed, it is known that a sore throat happens: catarrhal, lacunar, necrotic or purulent and follicular, it can also occur in an acute or chronic form. With the development of one type of angina, streptococcal infection penetrates not only into the blood stream, but also the lymph nodeswhere causes their acute inflammation.
Strep throat infection of the throat: causes
The main cause of strep throat infection is a decrease in local or general immunity, which is not able to withstand pathogenic microbes. The provoking factors for the development of streptococcal infection of the throat include:
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Reduced immunity compared to other internal diseases;
- Mechanical injuries of the mouth, throat, larynx;
- Dental diseases;
- Diseases of the nasal mucosa: sinusitis, sinusitis, chronic rhinitis.
There are other causes that can cause inflammation in the throat, but in any case of strep throat infection requires immediate treatment under the supervision of a physician.
Symptoms of strep throat infection
The causative agent of streptococcal infection (streptococcus) releases toxins that poison the human body, which causes intoxication and severe symptoms. The main clinical signs of streptococcal infection of the throat are:
- temperature increase up to 38 С and above;
- headache, muscle weakness, body aches;
- plaque on tongue and tonsils;
- sore throat;
- dry cough;
- redness, hyperemia of the tonsils and posterior sky;
- appearance purulent plugs - characteristic of follicular or necrotic angina;
- small-point, itchy rash - characteristic of scarlet fever;
- lower blood pressure;
- increase submandibular lymph nodes;
- general intoxication of the body.

Strep throat infection of the throat (sore throat or scarlet fever) require immediate treatment. Late or poor treatment of streptococcal infections in the throat often leads to complications: glomerulonephritis, myocarditis, rheumatism, brain damage, pneumonia, and other severe pathologies that are difficult to treat and can often lead to disability or death.
Diagnosis of Streptococcal Infection
Identify the causative agent and the cause of the disease is possible only after the results of the survey. The attending physician should exclude other diseases that have similar symptoms with streptococcal infection: diphtheria, measles, rubella, infectious munocleosis, and only then make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. The following examinations will help determine the type and stamp of the pathogen:
- blood chemistry;
- analysis of urine;
- bacteriological seeding;
- electrocardiography.
The results of laboratory examinations, the patient’s history, as well as the examination of the nasopharynx, will help the doctor to get a complete picture of the disease, make a correct diagnosis and prescribe an appropriate treatment for streptococcal infection of the throat.
Treatment of streptococcal infection
Treatment of streptococcal infections of the throat is carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis, it depends on the extent of the disease, the diagnosis made, the patient's age, the risk of complications and other features of the human body. The main treatment is antibiotic therapy, which is aimed at destroying the pathogenic pathogen, eliminating the inflammatory process. From antibacterial drugs, doctors most often prescribe antibiotics. wide spectrum actions: erythromycin, drugs of penicillin group, erythromycin, cephalosporins. Such drugs include: Augmentin, Ampicillin, Penicillin, Sumamed, Fromilid, Makropen. Such drugs are available in different pharmacological forms: tablets, capsules, suspension for children or ampoules. If you suspect complications or in severe cases, the doctor may prescribe penicillin antibiotics: benzylpenicillin, bicillin-3, bicilli-5 in the form of ampoules for intramuscular or intravenous. Antibiotics are taken on the 3rd - 4th day after the treatment of streptococcal infection in the throat is carried out with penicillin preparations. The course of treatment is 5-7 days. The dose of drugs prescribed depending on the patient's age, body weight and other features of the body. 
Together with antibiotics, you need to take probiotics that will protect the intestinal microflora from the development of dysbiosis: Linex, Laktovit, Beefy - forms and others.
In addition to receiving antibacterial therapy, other patients are prescribed medications:
- Antipyretic and anti-inflammatory: Paracetamol, Ibuprofen;
- Antihistamines: Suprastin, Tavegil, Loratadin.
- Throat spray - relieves inflammation, has anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, analgesic properties: Orasept, Ingalipt, Kameton, Protosol.
- for sucking - they have the same effect as a throat spray: Faringosept, Dekatilen, Trachisan, Strepsils, Lysobact.
- Vitamin therapy, immunotherapy - allow you to provide the body with essential substances, improve immunity, speed up the healing process.
- Mucolytic, antitussive drugs - prescribed for dry cough, which is often a companion of angina and scarlet fever: Ambroxol, Lasolvan, Sinekod and others.
All drugs should be prescribed by the attending physician and only after the results of the examination and diagnosis. In addition to drug treatment, patients are prescribed bed rest, heavy drinking, and lack of physical exertion. Efficacy in treating streptococcal infections are considered gargling with antiseptic solutions (Furacilin, Dekasan) or herbal decoctions with anti-inflammatory effect: chamomile, calendula, oak bark. Some herbal plants used in the treatment of throat infections can cause allergic reactiontherefore, they should be consulted with a physician before using them.
In cases when conservative treatment does not give positive results, and exacerbations appear more often, then the tonsils, which should protect us from infection, become its source. In such cases, the doctor recommends an operation to remove the tonsils.
It is important to note that streptococcal throat infection cannot be treated without antibiotics. The absence of antibiotic therapy in the treatment of streptococcus in 90% of cases will lead to complications. Treatment of infectious diseases of the throat caused by pathogenic streptococcus should be carried out at the first symptoms of the disease and only under the supervision of a physician. Self-treatment can not only not bring the desired results, but also provoke the development of complications. The earlier the treatment is carried out, the greater the chances for a successful recovery.
Prevention of strep throat infection
To reduce the risk of infection of streptococcal throat infection is possible in cases of compliance with certain rules:
- Enhance immunity.
- Lack of contact with a sore throat.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Proper and balanced nutrition.
- Treatment of other diseases of infectious or non-infectious origin.
Compliance with basic preventive measures can not fully protect against the disease, but can reduce the risk of infection.
Streptococcus is one of those pathogens that are normally found in the microflora of any person. The bacterium stays on the mucous membrane of the nose and pharynx, in the respiratory tract, colon and urinary organs, and for the time being does not cause any harm to its owner. Streptococcal infections occur only in conditions of weakened immunity, hypothermia or ingestion of a large number of unfamiliar strains of pathogens.
Not all types of streptococci are dangerous to human health, moreover - in this group there are even microbes that are beneficial. The very fact of a bacteriocarrier should not become a cause for alarm, because to avoid it is almost impossible, just as it is impossible to completely eradicate streptococcus from your body. A strong immunity and compliance with the elementary rules of personal hygiene give every reason to expect that the disease will bypass you.
Nevertheless, everyone is concerned about the question of what to do if you or your relatives still get sick: what medicines to take and what complications to worry about. Today we will tell you absolutely everything about streptococcus and the diseases that it causes, as well as methods of diagnosing and treating streptococcal infections.
What is Streptococcus?
From a scientific point of view, streptococcus is a member of the family Streptococcaceae, spherical or ovoid asporogenic gram-positive elective anaerobic bacterium. Let's understand these difficult terms and “translate” them into simple human language: streptococci are in the form of a regular or slightly elongated ball, do not form a spore, do not have flagella, are not able to move, but can live in complete absence of oxygen.
If you look at streptococci through a microscope, you can see that they are never found alone - only in pairs or in the form of regular chains. In nature, these bacteria are very widespread: they exist in the soil, on the surface of plants, and on the body of animals and humans. Streptococci are very resistant to heat and freezing, and even lying in the roadside dust, they retain the ability to reproduce for years. However, they are easy to defeat with penicillin antibiotics, macrolides or sulfonamides.
To streptococcal colony began to actively develop, she needs a nutrient medium in the form of serum, sweet solution or blood. In laboratories, bacteria are artificially created favorable conditions in order to observe how they multiply, ferment carbohydrates, secrete acid and toxins. A colony of streptococci forms a translucent or greenish film on the surface of a liquid or solid nutrient material. Her research chemical composition and properties allowed scientists to determine the pathogenicity factors of streptococcus and establish the causes of streptococcal infections in humans.
Causes of Streptococcal Infections

The cause of almost all streptococcal infections is beta-hemolytic streptococcus, since it is he who is able to destroy red blood cells - red blood cells. In the process of life streptococci secrete a number of toxins and poisons that have a detrimental effect on the human body. This explains unpleasant symptoms diseases caused by streptococcus: pain, fever, weakness, nausea.
The pathogenicity factors of streptococcus are as follows:
Streptolysin - the main poison that violates the integrity of blood cells and heart;
Scarlatinal erythrogenin - a toxin, due to which the capillaries dilate, and a skin rash occurs during;
Leukocidin is an enzyme that destroys the immune cells of the blood - leukocytes, and thereby suppresses our natural defense against infections;
Necrotoxin and lethal toxin - poisons that cause tissue necrosis;
Hyaluronidase, amylase, streptokinase and proteinase - enzymes with which streptococci devour healthy tissue and spread throughout the body.
In the place of introduction and growth of the streptococcal colony, a focus of inflammation occurs, which worries a person severe pain and swelling. As the disease progresses, the toxins and poisons secreted by the bacteria spread through the bloodstream throughout the body, so streptococcal infections are always accompanied by general malaise, and in severe cases, large-scale intoxication, including vomiting, dehydration and clouding of consciousness. Lymphatic system reacts to the disease by engulfing the lymph nodes located next to the inflammatory focus.
Since streptococci themselves and their metabolic products are foreign to our body, immunity reacts to them as a powerful allergen, and tries to produce antibodies. The most dangerous consequence This process is an autoimmune disease, when our body ceases to recognize the modified tissue streptococcus and begins to attack them. Examples of terrible complications: glomerulonephritis, (endocarditis,).
Streptococcus groups
Streptococci are divided into three groups according to the type of erythrocyte hemolysis:
Alpha hemolytic or green - Streptococcus viridans, Streptococcus pneumoniae;
Beta-hemolytic - Streptococcus pyogenes;
Non-hemolytic - Streptococcus anhaemolyticus.
For medicine, it is the second type of streptococcus that matters, beta-hemolytic:
Streptococcus pyogenes - the so-called pyogenic streptococci, which cause in adults and scarlet fever in children, and give serious complications in the form of glomerulonephritis, and endocarditis;
Streptococcus pneumoniae - pneumococci, which are the main culprits and;
Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecies - enterococci, the most survivable bacteria of this family, causing purulent inflammations in the abdominal cavity and heart;
Streptococcus agalactiae are the bacteria responsible for the majority of streptococcal lesions of the urogenital organs and postnatal inflammations of the uterine endometrium in new mothers.
As for the first and third types of streptococci, green and non-hemolytic, they are simply saprophytic bacteria that feed on humans, but almost never cause serious diseases because they do not have the ability to destroy red blood cells.
In fairness it is worth mentioning the good bacteria from this family - lactic streptococcus. With its help, dairy products are made by dairy products at all at dairies: kefir, yogurt, ryazhenka, sour cream. The same microbe helps people with lactase deficiency - this is a rare disease, manifested in a deficiency of lactase - an enzyme necessary for the absorption of lactose, that is, milk sugar. Sometimes thermophilic streptococcus is given to babies for the prevention of strong regurgitation.
Streptococcus in adults
Pharyngitis
The receiving physician quickly diagnoses pharyngitis by visual inspection of the pharynx: the mucous membrane is swollen, bright red, covered with a grayish bloom, the tonsils are swollen, here and there scarlet bagel-shaped follicles are visible. Streptococcal pharyngitis is almost always combined with, moreover, the mucus is transparent and so abundant that it can cause maceration (soaking) of the skin under the nose. The patient is prescribed local antiseptics for the throat in the form of a spray or lozenges, there is no need to take antibiotics inside.
Usually, this disease passes as suddenly as it began, and does not last long - 3-6 days. The victims of pharyngitis are mostly young, or vice versa, elderly people with weakened immunity, who have been in contact with a sick person, using his dishes or a toothbrush. Although pharyngitis is considered to be a widespread and not serious disease, it can give very unpleasant complications.
The consequences of pharyngitis can be:
Angina
Streptococcal sore throat (acute) can turn into a real disaster for an adult patient, especially an elderly one, because late and poor-quality treatment of this disease often causes serious complications in the heart, kidneys and joints.
Factors contributing to the development of acute streptococcal tonsillitis:
Weakening of general and local immunity;
Hypothermia;
Recently suffered another bacterial or viral infection;
The negative impact of external factors;
Long contact with the sick person and subjects of his use.
A sore throat begins as suddenly as pharyngitis — the night before it becomes painful for the patient to swallow, and the next morning the throat is completely covered by the infection. Toxins are carried through the bloodstream throughout the body, causing an increase in lymph nodes, high fever, chills, weakness, anxiety, and sometimes confusion and even seizures.
Symptoms of tonsillitis:
Severe sore throat;
Febrile temperature;
Submandibular lymphadenitis;
Swelling and redness of the pharyngeal mucosa;
Enlarged tonsils;
The appearance on the mucous throat of loose grayish or yellowish plaque, and sometimes purulent plugs;
In young children - dyspeptic disorders (nausea,);
In blood tests, strong leukocytosis, C-reactive protein, accelerated ESR.
Streptococcal angina has two types of complications:
Purulent - otitis, sinusitis, flux;
Non-purulent - rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, syndrome, myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis.
Treatment of angina is carried out with the help of local antiseptics, but if the inflammation cannot be stopped for 3-5 days, and the body is covered by total intoxication, it is necessary to resort to antibiotics to prevent complications.
Streptococcus in children
Streptococci are very dangerous for newborn babies: if intrauterine infection occurs, the child is born with high fever, subcutaneous bruises, bleeding from the mouth, difficulty breathing, and sometimes with inflammation of the lining of the brain. Despite the high level of development of modern perinatal medicine, it is not always possible to save such children.
All streptococcal infections in children are conventionally divided into two groups:
Primary - angina, scarlet fever, otitis media, pharyngitis, laryngitis,;
Secondary - rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, glomerulonephritis, endocarditis, sepsis.
Unconditional leaders in the incidence of incidence in children are angina and scarlet fever. Some parents consider these diseases completely different, and some, on the contrary, confuse them with each other. In fact, scarlet fever is a severe form of streptococcal sore throat, accompanied by a skin rash.
Scarlet fever
The disease is very contagious, and is distributed among pupils of preschool institutions and schools with the speed of a forest fire. Scarlet fever usually affects children between the ages of two and ten years, moreover, only once, because a strong immunity is formed to the disease. It is important to understand that the cause of scarlet fever is not Streptococcus itself, but its erythrogenic toxin, which causes severe poisoning of the body, up to clouding of consciousness, and a pinpoint red rash, according to which the pediatrician can unmistakably distinguish scarlet fever from normal angina.
It is customary to distinguish three forms of scarlet fever:
Easy - the disease lasts 3-5 days and is not accompanied by large-scale intoxication;
Medium - lasts a week, is characterized by a strong poisoning of the body and a large area of eruptions;
Severe - may take several weeks and go into one of the pathological forms: toxic or septic. Toxic scarlet fever is manifested by loss of consciousness, dehydration and, and septic - by strong lymphadenitis and necrotic tonsillitis.
Scarlet fever, like all streptococcal infections, has a short incubation period and affects the child suddenly, and lasts an average of 10 days.
Symptoms of scarlet fever:
General weakness, lethargy, drowsiness;
Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, dehydration, loss of appetite;
Characteristic puffy face and unhealthy luster of the conjunctiva;
Very strong increase and soreness of the submandibular lymph nodes, up to the inability to open the mouth and swallow food;
Redness of the skin and the appearance of small roseol or papules on them, first on the upper part of the body, and after a few days on the extremities. It looks like goose bumps, moreover, on the cheeks rash merges and forms a scarlet crust;
Blanching of the nasolabial triangle in combination with cherry lips;
The tongue is covered with a gray bloom that passes three days later, starting from the tip, and the entire surface becomes scarlet with prominent papillae. The tongue resembles a raspberry berry;
Pastia syndrome - a collection of skin rashes in the folds and a strong judgment;
Clouding of consciousness up to fainting, at least - nonsense, hallucinations and convulsions.
Painful symptoms increase during the first three days since the onset of the disease, and then gradually subside. The number and severity of the rash is reduced, the skin becomes whitish and dry, sometimes the child on the palms and feet, it comes off in whole layers. In the body, antibodies to erytotoxin are produced, so if children who have had scarlet fever again encounter the pathogen, this only leads to sore throat.
Scarlet fever is very dangerous for its complications: , inflammation of the heart muscle, chronic lymphadenitis.
The average and severe form of this disease requires adequate and timely antibiotic therapy, as well as careful care of the child and follow-up measures to strengthen his immunity, for example, rest in a sanatorium and a course of multivitamins.
Streptococcus in pregnant women

One of the reasons why future mothers need to be very scrupulous in matters of personal hygiene is streptococcus and staphylococcus, which can easily penetrate the genital tract with improper wiping, long wearing underwear, using non-sterile means of intimate hygiene, touching the genitals with dirty hands and unprotected sex. Of course, streptococcus is normally present in the vaginal microflora, but the body of a pregnant woman is weakened, and the natural protective mechanisms may not be enough to contain the infection.
The following streptococci are most important in the development of pregnancy pathology:
Streptococcus pyogenes causes sore throat, pyoderma, cystitis, endometritis, glomerulonephritis, postpartum, as well as fetal infection with all the ensuing consequences;
Streptococcus agalactiae can also cause endometritis and inflammatory diseases urinary organs in the mother, and in the newborn cause, sepsis, pneumonia and neurological disorders.
If a smear in a pregnant woman reveals a dangerous concentration of streptococci, carry out a local reorganization with the help of antibacterial suppositories. And with full-scale streptococcal infections, for example, angina, the situation is much worse, since most antibiotics, to which streptococcus is sensitive, are strictly contraindicated during pregnancy. The conclusion is banal: future mothers need to carefully protect their health.
Complications and consequences of streptococcus
Streptococcal infections can produce the following complications:
Purulent otitis media;
Rheumatoid arthritis;
Chronic lymphadenitis;
Inflammation of the heart membranes - endocarditis, myocarditis, pericarditis;
Concomitant viral and anaerobic infections: ARVI,;
Sexually transmitted infection.
If there are very few streptococci in a smear, and there are a lot of Doderlein sticks, on the contrary, there are many, then we are talking about the first variant. If there are more streptococci than Doderlein sticks, but the number of leukocytes in the field of view does not exceed 50 pieces, we are talking about the second variant, that is, vaginal dysbacteriosis. Well, if there are a lot of leukocytes, then the diagnosis is “bacterial vaginosis”, which is specified depending on the type of main pathogen. They can be not only streptococcus, but also staphylococcus, gerdnerella (gardnerellosis), trichomonas (), candida (), mycoplasma (mycoplasmosis), (), chlamydia () and many other microorganisms.
Thus, the treatment of streptococcus in the vagina, as well as the eradication of any other pathogen, is carried out only if its amount in the smear is disproportionately large and is accompanied by marked leukocytosis. All such genital infections have very bright symptoms, and a smear test is necessary in order to identify the culprit and select the appropriate antibiotic.
Streptococcus treatment

The treatment of streptococcal infections is carried out by the specialist who is responsible for the focus of inflammation: therapist cures colds, the pediatrician scarlet fever, dermatitis and erysipelas - the gynecologist and urologist, and so on. In most cases, the patient is prescribed antibiotics from the group of semi-synthetic penicillins, but if they are allergic, they resort to macrolides, cephalosporins, or linkosamides.
The following antibiotics are used to treat streptococcal infections:
Benzylpenicillin - injection, 4-6 times a day;
Phenoxymethylpenicillin - adults, 750 mg, and children, 375 mg twice a day;
Amoxicillin (Flemoksin Solutab) and Augumentin (Amoxiclav) - in the same dosage;
Azithromycin (Sumamed, Azitral) - adults 500 mg once a day, then 250 mg every day, children the dosage is calculated based on 12 mg per kg of body weight;
Cefuroxime - 30 mg injection per kg of body weight twice a day, 250-500 mg orally twice a day;
Ceftazidime (Fortum) - injection once a day, 100-150 mg per kg of weight;
Ceftriaxone - injectable once daily for 20–80 mg per kg of body weight;
Cefotaxime - once daily for injection 50 to 100 mg per kg of body weight, only if there is no effect from other antibiotics;
Cefixime (Supraks) - orally 400 mg once a day;
Josamycin - orally once a day, 40-50 mg per kg of body weight;
Midecamycin (Macropen) - orally once a day, 40-50 mg per kg of weight;
Clarithromycin - orally once a day, 6-8 mg per kg of weight;
Roxithromycin - 6–8 mg orally per kg of weight;
Spiramycin (Rovamycin) - orally twice a day, 100 U for each kg of weight;
Erythromycin - Per oral four times a day, 50 mg per kg of weight.
A standard course of treatment for streptococcal infection takes 7-10 days. It is very important not to stop taking the drug immediately after feeling better, not to allow skips and not to change the dosage. All this causes multiple recurrences of the disease and significantly increases the risk of complications. In addition to intramuscular, intravenous or oral antibiotics for the treatment of streptococcus using local antibacterial agents in the form of aerosols, solutions for gargling and sucking tablets. These drugs significantly accelerate recovery and facilitate the course of the disease.
Most effective drugs for local treatment streptococcal infections of the oropharynx are as follows:
Bioparox - an aerosol based on the latest-generation antibiotic Fuzafunjin, sprayed into the throat and nasal passages;
Inhalipt - sulfanilamide antibacterial aerosol for the throat;
Tonsilgon N - a local immunostimulant and antibiotic of plant origin in the form of drops and dragees;
Geksoral - antiseptic spray and solution for gargling;
Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic, sold separately as a solution, and is also included in many pills for sore throat (Anti-Angina, Sebidine, Faringosept);
Cetylpyridine, an antiseptic, is contained in Septolet tablets;
Dichlorobenzene alcohol - antiseptic, contained in many aerosols and lozenges (Strepsils, Ajisept, Rinza, Lorsept, Suprima-LOR, Astracept, Terasil);
Iodine - contained in aerosols and solutions for gargling (Iodinol, Vokadin, Yoks, Povidone-Iodine).
Lizobakt, Immunal, IRS-19, Imunorix, Imudon- local and general immunostimulants.
If antibiotics were taken orally for the treatment of streptococcal infections, drugs will be needed to restore the normal microflora of the internal organs:
Bifidumabacterin;
Bifiform
Treatment of streptococcus in young children is carried out with the addition of antihistamine drugs:
Claritin;
It will not be superfluous to take vitamin C, which strengthens the walls of blood vessels, improves the immune status and detoxifies the body. In difficult situations, doctors use a special streptococcal bacteriophage for treatment - it is an artificially created virus devouring streptococci. Prior to use, the bacteriophage is tested, injecting it into a flask with the patient’s blood and observing its effectiveness. The virus does not cope with all strains, sometimes it is necessary to resort to a combined pyobacteriophage. In any case, this measure is justified only when the infection cannot be stopped by using antibiotics, or the patient is allergic to all current types of antibacterial drugs.
It is very important to observe the correct regimen during the treatment of streptococcal infections. A serious illness with severe intoxication of the body requires staying in bed. It is active movements and work during the period of illness that are the main prerequisites for the development of serious complications in the heart, kidneys and joints. To eliminate toxins you need a lot of water - up to three liters daily, both in pure form and in the form of warm medicinal tea, juices and fruit drinks. Warming compresses on the neck and ears can be put only if the patient does not have a high body temperature.
With streptococcal sore throat it is absolutely impossible to try to speed up recovery, tearing off purulent plaque and plugs from the mucous membrane of the throat with a bandage dipped in iodine or lugol. This will lead to the penetration of the pathogen even deeper and aggravate the disease.
With acute tonsillitis and pharyngitis can not irritate the throat is too hot, or vice versa, ice food. Rough food is also unacceptable - it injures the inflamed mucous membrane. It is best to eat cereals, soups, mashed potatoes, yogurt, soft curds. If the patient has no appetite at all, you do not need to stuff him with food, it will only result in nausea and vomiting. Digestion is a process on which our body spends a lot of energy. Therefore, during the treatment of streptococcal infections, when the digestive organs so poorly and the body is poisoned by toxins, fasting with abundant drinking may be more beneficial than good nutrition.
Of course, children with streptococcal sore throat or scarlet fever need the most thorough care. Every one and a half hours a child is given warm lime or chamomile tea, cool lotions are applied to the sore eyes and hot forehead, and itchiness and scaly skin are smeared with baby cream. If the kid is able to gargle, you need to do it as often as possible using infusion or. After recovering from a severe form of scarlet fever, young patients are recommended to rest in a sanatorium, preventive intake of multivitamins, immunostimulants, pro-and prebiotics.
Popular
- What is useful mineral water
- What is the name of the Scottish skirt
- What women like a man archer
- Dosage and use of doxycycline when tick bite
- Sinupret - complete instructions
- Number of antennae in arachnid and insect crustaceans
- Help for enterobiasis for the pool, how much is valid
- Ceftriaxone suspension. What is ceftriaxone?
- Third degree breast cancer: prognosis and treatment
- Salt Scrub for the scalp




