Otitis effects in adults. What is the risk of otitis: consequences and complications
Such a disease as otitis is dangerous not so much by itself, as by the various consequences that may arise as a result of ignoring the need for treatment or failure to follow the doctor’s prescriptions. Also, quite often they develop against the background of excessive hobbies of traditional medicine.
Negative effects can develop equally, both in adults and children. In order to realize the full responsibility of the need to visit a specialist, we will talk about all sorts of complications after otitis and the characteristics of their manifestation in childhood and adulthood.
Malignant processes
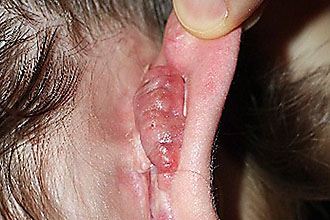
The location of cholesteatoma in the human ear
Malignant external otitis - perhaps the rarest and most dangerous complication otitis externa, first discovered in 1838.
At that time, the illness was characterized by a very aggressive course, an unfavorable prognosis and a high degree of mortality among the diseased. With the opening effective antibiotics cure projections have become more favorable.
Terrible name of the disease, even though he has nothing to do with oncology, remains to this day and can still be the cause of severe health effects. As striking outdoor auditory canalas well as the temporal bone.
- A pathology that develops as a result of a frivolous attitude to inflammatory processes in the organs of hearing. In most cases, due to chronic purulent otitis. Has pronounced symptoms and mainly requires surgical intervention.
Bone Inflammations: Mastoiditis and Petrositis
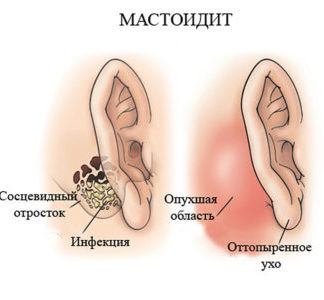
Characteristic features of mastoiditis
Mastoiditis develops as a complication of otitis and is characterized by a mass of specific symptoms.
It affects the mucous membrane and bone tissue of the mastoid process of the temporal bone and has the following developmental stages:
- exudative - The inflammatory process affects the membrane and periosteum of the mastoid cells. When this occurs, a significant thickening of the mucous;
- destructive - The process of destruction of bone tissue and necrosis.
Important! Without the necessary and timely treatment, the destructive process of bone tissue can reach the dura mater of the brain and provoke intracranial complications.
Petrosit (osteomyelitis) - inflammation of the top of the pyramid of the temporal bone. As a rule, it can develop along with acute otitis media or 3-4 days after mastoiditis. Much less likely to develop as a complication of chronic otitis.
Meningitis
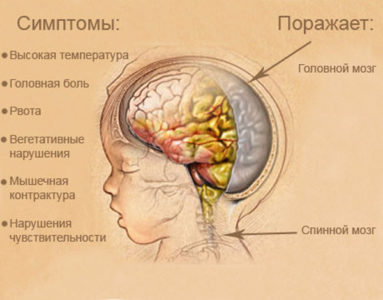
Symptoms of meningitis
Meningitis - one of the most dangerous possible consequences of otitis.
Under certain conditions, pathogenic microflora spreading during the inflammatory process of the ear can reach the lining of the brain and cause inflammatory processes in it.
If you do not see a doctor in time, this pathology can lead to death.
Important! In the case of meningitis, the expense of the patient’s life goes to the clock.
Therefore, in the manifestation of symptoms indicating meningitis, the patient should immediately call an ambulance.
Brain abscess
Brain abscess characterized by specific symptoms
Speaking about the various complications of otitis, it is worth to separately highlight brain abscess.
This pathology is a pathological process in which a limited focus of purulent inflammation forms in the cranial cavity.
This consequence of the disease is no less dangerous than meningitis and is characterized by numerous characteristic symptoms:
- Fever.
- Acute headache.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Swelling of the brain.
Other complications
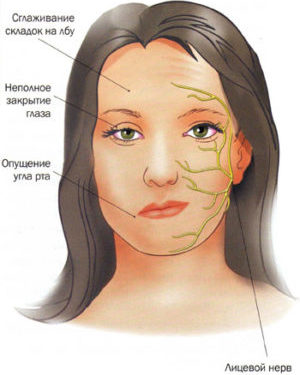
It looks like neuritis facial nerve
Neuritis of the facial nerve - can also be a consequence of otitis.
Pathology is characterized by inflammatory lesion of the nerve, which leads to a violation of the innervation of the facial muscles of a certain part of the face.
In the muscles affected by inflammation, weakness develops, which is the cause of paresis or paralysis of facial movements and manifestations of severe asymmetry of the face.
Otogenic sepsis - One of the possible negative consequences of this disease, in which pathogenic microorganisms constantly or periodically enter the blood from a nidus of purulent inflammation in the middle ear. The course of this disease is very severe and is characterized by very specific symptoms.
Complications of otitis media in children
The trouble is that in childhood, namely in the early, sometimes it is very difficult. From the moment of occurrence of inflammation in a baby to the moment of its determination by parents, it may take some time, which in this case is precious.
Since the inflammation of the ears in childhood develops rapidly, it is possible the development of various negative consequences for the children's body.
Another problem of the occurrence of consequences is the failure of the parents to follow the instructions of the doctor. Namely, the rejection of drugs, as soon as the small ears subside pain.
So many parents believe that they protect their children from the harmful effects of pharmaceuticals, while completely forgetting that otitis does not cure, and he will return again, and possibly with complications. And then with the help of this list of medicines can not cope.
To the most common possible complications Otitis in children include the following types:
- and hearing loss - usually this phenomenon does not last long. However, there are cases, the hearing is not restored or even lost completely. As medical practice shows, it is otitis that is a common factor that causes hearing loss in children;
- with relapses - requires frequent repetition of treatment, while the purulent masses in the ear periodically accumulate, then go away;
- meningitis - as well as in adults, it requires emergency hospitalization and treatment;
- mastoiditis - As previously noted, inflammation of the mastoid process. In this case, the child requires surgery to avoid blood poisoning.
In order to protect the child from the effects of the disease, parents must maintain constant vigilant control. This will protect the baby who suffered otitis media.

Only parents can save the child from the possible consequences of otitis
Inflammation of the ear can be treated quite well in children and adults, but subject to all the rules. This means that complications will not have the slightest possibility of harm to the patient's health.
Reference. Otitis in the non-running stage is cured in 100% of cases.
From the above, only one conclusion can be made: at the cost of neglect of the disease, in many cases it can be your own health or even life.
We take care of ourselves and our health, because it is much easier to prevent than to get tired from a long and complicated treatment.
The consequences of otitis, occurring in adults and children, are a greater threat to health than the disease itself. With timely treatment and a favorable outcome, they do not pose a particular danger and pass independently as the body recovers. In case of violation of the medium therapy, the risks of the development of irreversible destructive processes increase. It is important to know what can threaten similar situation and how to avoid problems.
Causes and further risks
Most often in adults there. Among all possible reasons should highlight infectious diseases. The ingestion of bacteria, tissue swelling and impaired immune protection are the first consequences of a cold. It is because of them and there is a complication in the ears, namely their inflammation.
In order to minimize the threat to the health of the hearing organs, it is necessary to start treatment as soon as possible, agreed with the doctor. Also, the patient is faced with the task of removing the root cause itself. Unfortunately, many people are not aware of the harm they do to themselves while ignoring these recommendations.
The situation is aggravated by such a popular self-medication, and this applies as an arbitrary reception drugsand the use of folk techniques.
As a result, the following consequences may occur:
- violation;
- the spread of infection to a healthy organ;
- the transition of the disease to the chronic form;
- distribution of destructive processes to adjacent organs and tissues.

Each situation should be considered in more detail.
Impaired ear function and hearing loss
The first thing that can be dangerous is ear otitis - a violation of its natural functions. There are three main ear functions:
- Protective.The epithelium, which covers the inner space of the middle ear, is capable of performing a bactericidal function, provided that there is sufficient oxygen supply to the tissues and control of partial pressure.
- Ventilation. At occurrence of tissue edema, air exchange in the organ cavity becomes difficult.
- Drainage. Exudate outflow is disturbed, as a result of which conditions are created that are optimally suitable for the reproduction of pathogenic microflora.
Similar complications in otitis media occur in the course of the disease in both adults and children. Similar phenomena are associated with tissue swelling and blocking.
![]()
The next symptom, which is a peculiar complication after otitis media in adults is a decrease in hearing acuity. This happens in several cases:
- fluid accumulation behind the eardrum;
- total membrane perforation;
- blocking auditory ossicles;
- ear cavity fouling by epithelium;
- impaired transmission of nerve impulses;
- dying off hairs.
Very often hearing loss and are the so-called residual effects. After removal of the swelling, fluid drainage and organ recovery, this symptom disappears on its own. To normalize the pressure and drainage of the middle ear, it is necessary to eliminate the problems associated with the auditory tube. If the cause of hearing loss is otherwise, there is a risk of continued hearing impairment.
Chronic form and serious complications
A rather serious consequence is the transition to the chronic form. In this case, the person is faced with the problem of increased propensity to in the event of circumstances favorable to the disease.
To provoke such a variant of events can running otitis media. Ignoring problems at the initial stage leads to the fact that irreversible processes are triggered in the body. The reproduction of bacteria and the destruction of tissues cause changes in the organs of hearing, which subsequently will cause frequent exacerbations of the disease.
The situation can be aggravated by bad habits in adults, the presence of anatomical abnormalities, other chronic diseases, especially those associated with the throat and nose. The slightest irritation, such as allergy or hypothermia, leads to suppression of the immune system and otitis returns again. To cure such a form of the disease is almost impossible, and the problem will torment a person for the rest of his life, not excluding other consequences.
Even more serious complications after otitis are associated with the destruction of healthy tissue and the spread of inflammation to other organs. These include intravascular and intracranial diseases:
- mastoiditis;
- paralysis of the facial nerve;
- meningitis;
- encephalitis;
- hydrocephalus.
Brain damage is especially dangerous for children. The risk of developing a similar phenomenon in adults is somewhat lower.
Inflammation can go beyond the middle ear due to the rapid progression of the disease or lack of effective treatment. With mastoiditis, bone damage occurs. The auditory ossicles first suffer, and then the carious process moves to the cranial structures.
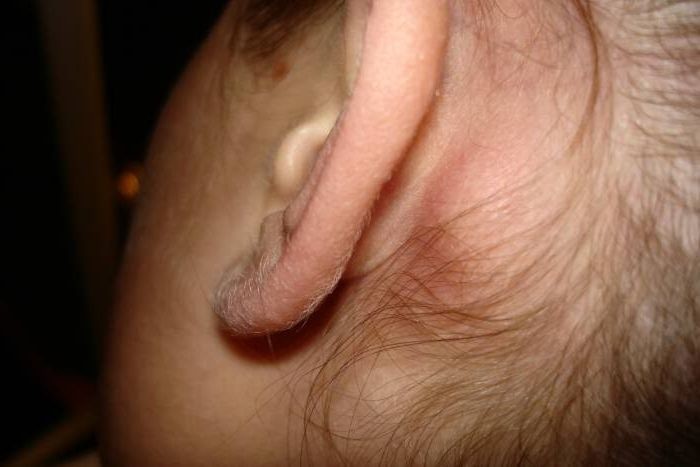
Mastoiditis is dangerous not only because it leads to the development of deafness. This disease is also a prerequisite for the transmission of infection to the brain. When meningitis occurs inflammation of the lining of the brain, encephalitis is a deeper pathology. In hydrocephalus, there is an accumulation of fluid in the cortex of the organ. Such complications lead to the development of irreversible processes, as a result of which an absolutely healthy person can become disabled. Deaths are also common. Such a terrible, irreversible consequences can lead to a banal inflammation of the ear, if it is not eliminated in a timely manner.
How to avoid negative consequences
To prevent a negative scenario, it is important to take appropriate measures. First of all, you can not ignore the alarming symptoms, even if you suffer from a common cold or allergies. For pain in the middle ear, hearing loss and general well-being, consult a doctor immediately. Cure acute otitis with timely treatment can be just a week. But with the development of the chronic stage there is always the risk of serious consequences.
To prevent disease in adults should stop smoking, as the smoke is an irritant of the nasopharynx and causes swelling. auditory tube. Also take care to strengthen the immune system. If you have a tendency to otitis, visit an otolaryngologist from time to time and avoid hypothermia.

If there is already inflammation, treatment should be carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the doctor. Various popular approaches are not only ineffective in the fight against pathogen microorganisms, but sometimes they can only aggravate the situation. In addition, it should be borne in mind that in some cases even conservative therapy is not enough and surgery is required.
If you do not delay the treatment and take your health responsibly, you can avoid many negative consequences not only of otitis, but also other diseases.
The disease lasts at least 4 weeks. But after a couple of days, not without the help of drugs, ear ache may weaken or go altogether, so many people discontinue further treatment. It is this action that most often is the mistake that ends in sad consequences.
Why complications arise
After adequate antibiotic therapy in the ear cavity and the focus of inflammation, pus and other changes will be absent. But when hearing is restored after otitis, it is quite difficult to predict.
To speed up rehabilitation periodThe doctor may additionally prescribe a physiotherapy treatment and preventive examination. Conscientious fulfillment of all appointments of the treating doctor for a certain period of time (about 4 weeks) guarantees success, and such a problem, like a buried ear after otitis, soon recedes.
Forecasts
In most cases, hearing loss after otitis is fully cured in both small and adult patients. Complications of an intracranial nature are rare, and the prognosis for them with timely therapy will also be favorable.
The transition of the acute form of the disease to the chronic one is observed mainly in childhood. Treatment chronic disease should be carried out in a hospital and as soon as possible, so that the disease could not progress, and the restoration of hearing after otitis passed with minimal consequences.
Reduced immunity and the presence of somatic diseases ( chronic tonsillitis, diabetes, etc.) interfere with the favorable prognosis for recovery. If the body has low resistance to infectious agents, then treat accompanying illnesses complicated. It is important for such people to take care of their own health and, when the slightest signs of pathology appear, for example, if there is noise in the ear after otitis, immediately go to the doctor.
How to avoid complications after otitis?
Any disease is easier to prevent, this also applies to its complications. Therefore, initially it is necessary to remember about the prevention of infections, which is based on hardening, increasing the body's defenses, vitamin therapy, balanced nutrition and moderate exercise in the fresh air.
If it was not possible to avoid otitis, it is necessary to treat the disease under the control of an otolaryngologist. In this case, you should follow all the recommendations of the doctor and in no case should not interrupt the prescribed treatment. ahead of time. After recovery, a conscientious patient will not have a question about how to restore hearing after otitis, because the treated infection does not cause complications in time.
Possible consequences
Of course, the complications of otitis media are serious. For example, hearing loss. If there is a congestion of the ear after otitis, it means that the disease is not cured until the end, and medical help is needed. Fortunately, in most cases this condition is temporary and reversible, and the doctor knows how to return the hearing after otitis, unless, of course, the condition is neglected.
In addition to hearing loss, there may be consequences such as mastoiditis and meningitis. Both conditions are dangerous, as they are characterized by serious inflammatory disorders. Mastoiditis is accompanied by severe pain, hyperemia and swelling of the skin pinnawhich changes its shape. Meningitis occurs with convulsions, vomiting, changes in consciousness, impaired motor activity.
Both pathologies can be fatal. If ear congestion after otitis does not pass, and the first signs of mastoiditis or meningitis appeared, emergency care is needed.
In children, otitis may be periodically repeated until the child grows up. Less common is the chronic form of the disease. In any case, if the parents do not know what to do, if after otitis, the ear does not hear well, and they ignore this condition (and this often happens), the consequences can be dire.
In adult patients, the picture is almost the same. Intracranial (meningitis) and extracranial changes, for example, fluid in the ear after otitis and hearing loss, appear infrequently. The main consequence of the disease is partial or complete deafness after otitis, which should be treated immediately.
All of the above otitis effects mainly lead to a temporary loss of the human hearing ability. But sometimes they may be irreversible. Thus, deafness is the hardest consequence of the disease, so complaints that he cannot hear the ear after otitis can occur in children and adults.
Useful video about the complications of otitis
Otitis is one of the most common otolaryngological diseases resulting from ear inflammation. Late diagnosis and therapy ear pathology provokes complications. The most serious consequences of otitis occur during the development inflammatory processes in the middle ear and the labyrinth.
The cavities of the inner and middle ear are separated from the environment by the eardrum, which prevents the penetration of the pathogenic flora. Infection most often occurs in a tubular way, i.e. through the Eustachian tube, which connects the nasopharynx with the tympanic cavity in the middle ear. Rapidly developing catarrhal processes lead to the destruction of epithelial and bone tissue, which is fraught with complications.
Statistics
What is dangerous otitis? In the analysis of more than a hundred cases of development of ear pathology requiring surgical intervention, the specialists recorded the frequency of serious complications:
- perforation (perforation) of the ear membrane - 47%;
- cholesteatoma (benign neoplasm) - 36%;
- mastoiditis (defeat of the mastoid process) - 10%;
- meringitis (degenerative changes in the ear membrane) - 7%.
The most common consequence of the ENT disease is a violation of the integrity eardrum. Membrane perforation is among the simplest and reversible complications, but only in the case of proper and timely treatment. In the chronic course of the inflammatory process, persistent perforation is observed, which is fraught with the occurrence of conductive hearing loss, i.e. hearing loss.
There is at least 10 more severe complications otitis media, many of which lead not only to the development of auditory dysfunction, but also disability or death. That is why the detection of alarming symptoms should seek help from the otolaryngologist.
Cholesteatoma is a cyst-like neoplasm in the ear cavity that occurs when otorrhea, i.e. discharge from the ear of hemorrhagic or purulent contents.
 The tumor consists of epithelial cells, which eventually begin to secrete fluid secretion, destroying soft and bone tissue. The destruction of the auditory ossicles responsible for carrying out the sound signals causes a decrease in hearing.
The tumor consists of epithelial cells, which eventually begin to secrete fluid secretion, destroying soft and bone tissue. The destruction of the auditory ossicles responsible for carrying out the sound signals causes a decrease in hearing.
Overgrowth of the tumor leads to damage to the ear maze, resulting in damage semicircular canalsresponsible for spatial orientation. Spontaneous rupture of cystic neoplasms leads to the evacuation of pathogenic exudate, which is fraught with generalization of inflammatory processes. When cholesteatoma rupture, the following complications of otitis media occur in adults:
- meningitis;
- brain abscess;
- otogenic sepsis;
- paresis of the facial nerve;
- mastoiditis.
Important! Cholesteatoma almost not amenable to conservative treatment. When new growths are found in the ear, surgery is required.
Otogenic sepsis is called generalization of inflammatory processes in which the lesions are located in the ear cavity. Pathology occurs as a complication of labyrinthitis, external or secondary purulent otitis. Due to a decrease in the reactivity of the organism, the aggressive pathogenic flora prevails over immunity, as a result of which an intensive spread of infection in the blood occurs.
Often the disease-causing flora spreads through the venous sinuses located inside the skull. Sigmoid and stony sinuses are connected to the borders of the maze and middle ear. In the presence of catarrhal or purulent processes, large veins are damaged, as a result of which phlebitis develops.
The development of phlebitis is fraught with the formation of blood clots in the vessels, which further leads to tissue necrosis and the development of gangrene.
The main symptom of sepsis is hyperthermia, characterized by a sharp increase in temperature. When the mechanism of thermoregulation is triggered, strong perspiration occurs, which very quickly leads to dehydration. At occurrence of characteristic signs immediate hospitalization of the patient with the subsequent surgical and medical treatment is required.
Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is called inflammation of the antrum and cellular structures, which are located behind the auricle (mastoid process). The penetration of the infection into the porous structure of the bone leads to its softening and the development of osteomyelitis. As a rule, provocateurs of pathological changes in the bone tissue are Pseudomonas aeruginosa, anaerobic microbes, mycobacteria and aerobic bacilli.
The following clinical manifestations most often indicate the development of complications after otitis in adults:
- hyperthermia;
- swelling behind the ear;
- shooting pains in the ear;
- hearing loss;
- noise in ears.
Severe illness requires urgent medical intervention. In the early stages of the development of pathology, therapy is carried out with the help of antibiotics. Components however antibacterial drugs hard to penetrate the cavernous structures of the mastoid process. To prevent abscess Bezolda, characterized by the formation of large abscesses under the neck muscles, carry out a sanitizing operation. This allows you to clean the cells of the bone process from purulent foci.
Paresis of the facial nerve
Among the most terrible consequences of otitis in adults include paresis of the facial nerve, in which there is impotence of mimic muscles. The development of neuropathology is characterized by contractures of muscle tissue. This is manifested in the inability to close the right or left eye, smile or speak clearly.
Late therapy may cause muscle atrophy. In this case, even after regeneration of the inflamed nerves, absolute restoration of facial movements is impossible.
Inflammatory processes in the ear cavity lead to the defeat of the processes of the facial nerve, which are located in the pyramid of the temporal bone, stapes, mastoid bone etc. Destruction of the nerve sheath provokes severe pain, which radiate to the teeth, temple, neck, neck and other parts of the body.
In the transition from otitis media to the chronic form, the development of persistent conductive hearing loss, which occurs as a result of mechanical impairment of the sound-conducting function of the auditory analyzer, is possible.  Tinnitus after otitis is due to the impossibility of the smooth passage of the sound signal through the ear canal, ear membrane and auditory ossicles.
Tinnitus after otitis is due to the impossibility of the smooth passage of the sound signal through the ear canal, ear membrane and auditory ossicles.
Sound barriers most often appear at the level of the eardrum, in which large perforated holes are formed. This helps to reduce its working area and, consequently, reduce hearing acuity. Pathologies may appear at the level of the auditory ossicles. With purulent inflammation Fibrin filaments are formed in the tympanic cavity, which during solidification limits the amplitude of oscillations of the auditory ossicles.
Conservative treatment of deafness after otitis is ineffective. Complete immobilization of the stirrup on the ear membrane can be eliminated only during stapedectomy.
Surgical intervention prevents further mineralization of the stirrup, which leads to the regeneration of elastic tissues and the restoration of its sound-conducting function.
Prevention of complications
The first step towards preventing serious complications is an adequate and timely response to the appearance of alarming symptoms. It should be understood that even SARS and allergies can cause swelling of the Eustachian tube, which will lead to a violation of its drainage function. As a result, serous effusions will begin to accumulate in the ear cavity, leading to the development of an ENT disease.
You can not postpone the visit to the otolaryngologist in the presence of the following symptoms:
- ear congestion;
- shooting pains in the ear;
- hearing impairment;
- temperature rise;
- serous or purulent discharge from the ear canal.
If you start the course of treatment in time, you can stop local and general manifestations of otitis within a week.
Popular
- Breast cancer is curable at any stage.
- The remedy for the cold Sinupret
- Azitrox - official instructions for use
- Chicken-bjaka: allowed antibiotics were found in Russian chicken
- Oral Cancer: Symptoms and Treatment
- Dark and thick blood during menstruation.
- Modern analogues of doxycycline tablets
- Is it possible to die from pneumonia
- What earwax will tell all about your health
- Tussin: instructions for use