Mixed hearing loss: its extent and effective treatment is the opinion of the Lore. Mixed hearing loss: its extent and effective treatment is the opinion of the Lore.
Hearing loss is hearing lossin which communication with people around is difficult. Hearing loss in a child as a rule leads to delayed psychoverbal developmentbecause he learns to speak, imitating what he heard, and the words “unheard of” lead to speech defects.
The more hearing is reduced, the rougher the psychoverbal development is.
The following figures show typical audiograms of a healthy person with hearing impairment and a person with a hearing impairment due to age. Why the rate of hearing loss is determined. The main reason for assessing the degree of hearing loss is the need for a clear classification of hearing impairment. A graphic representation of the state of hearing = audiogram = it can be more accurate, in many situations it is not suitable. There are many rules that require an accurate representation of a hearing in a simple symbol. This is necessary, for example, for driving permits, while working on the risk of military noise when applying for compensation, etc. in addition, there should also be the possibility of comparing the results between different workplaces or in individual patients over time.
Therefore, children with hearing loss for normal development is important:
- Identify the cause of hearing loss.
- Eliminate or have a therapeutic effect on the cause of hearing loss.
- If necessary, pick up a hearing aid.
- And also have a complex effect on the delay in the development of speech.
Diagnosis of hearing loss.
To identify hearing loss for children right in the hospital conduct a study- auditory evoked potentials.
However, in this case, only congenital hearing loss is detected. This type of hearing loss develops in a baby, if during pregnancy his mother suffered a disease like flu, rubella, herpes, toxoplasmosis. The degree of congenital hearing loss is usually severe, but in real life it is rare. Hereditary hearing loss is also rare.
In many children, hearing loss develops after birth and is diagnosed in the later stages. For example, in 3-4 years, when they begin to look for the cause of delay the development of speech in the baby, and it turns out that this is a reduced hearing.
To determine the degree of hearing loss, children at this age have an audiogram.
Hearing loss in children is divided into neurosensory hearing loss. (similar term - sensorineural hearing loss) and conductive hearing loss.
Evaluation of hearing is possible according to various criteria. In terms of communication: We evaluate the message in which the hearing loss is obvious. We evaluate whether we can negotiate without problems, whether we need to make some effort or we cannot agree. Limited communication = We gradually communicate with everyone, but this is a long process, the so-called heavy contract. Conceptual connection = again an example of an alien, knowledge and use of individual words, a small vocabulary. Senseless speech = no words, it only shows slides. Depending on the resolution of the words hearing impairment can be divided.
- This way of assessing communication skills and their failures is necessary for real communication.
- What can you imagine in terms of these concepts?
- Possible communication = an example of communication with an alien.
Causes of hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss in a child
Hearing loss is caused by impaired sound waves - by ear canaldamaged eardrum or sore auditory ossicles middle ear.
The most inoffensive cause of conductive hearing loss - sulfur plug (washed out with saline at the reception at the ENT doctor). But in children, much more often the cause of conductive hearing loss becomes chronic otitis (inflammation of the middle ear), and otitis can be caused by adenoids of grade 3-4, a chronic focus of infection in the nasopharynx and reduced immunity.
Hearing defect speech development 30 dB defective hearing loss speech is slow, but speech quality will not suffer 50 dB defect hearing loss will limit speech development, but you can talk to keep Hearing 80 dB defect using hearing aids will slow down or the development of speech restriction above 80 decibels using hearing aids is a development of speech. Endangered above 90 dB of hearing debris makes speech development impossible.
Fowler's hearing loss is calculated by the formula. The percentage corresponds to the coupling value of the corresponding frequency. Percentage values on one ear are added together. The calculation of total hearing loss as a percentage is carried out in such a way that the two values for each of the ears are mutually summed up, the difference is divided by four, and the value thus obtained is added to the better listening to the ear.
Sensorineural (sensorineural) hearing loss in a child
Hearing loss caused by hearing loss nervous system: lesion of the cochlea (organ of hearing) or the auditory nerve, pathways and areas of hearing of the brain. Cause of sensorineural hearing loss most often lies in birth trauma, deep prematurity, hydrocephalus, perinatal pathology, ischemic damage to the central nervous system.
Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs. Conditions after traumatic brain injury with persistent disorders in neurological, psychiatric and psychological or sensory. The degree of disability%. Central autonomic disorders. Coordination and equilibrium disorders.
Personality disorders, behavioral disorders, and lack of intellectual communication caused by damage, illness, or dysfunction of the brain. Cerebral palsy and other paralytic perspectives syndromes-opinion: When determining the degree of disability, it is necessary to distinguish whether it affects the dominant limb, be it mild, moderate or severe paralysis and the inability to assess the effect on the overall performance of the body, agility, agility and mobility.
The cochlea (organ of hearing) often suffers when using ototoxic antibiotics - aminoglycosides (gentamicin, streptomycin, kanamycin, amikacin, monomitsin, etc.).
In children with hydrocephalus, conductive pathways (demyelination) are usually affected, and the snail “hears” sounds, but they “do not reach” the brain through damaged conductive pathways. In hydrocephalus, increased intracranial pressure also puts pressure on the auditory nerve, the pathways and on the hearing areas of the cerebral cortex, preventing their normal operation.
The lack of oxygen during pregnancy and childbirth leads to hypoxic-ischemic damage to the hearing areas in the cerebral cortex.
In a birth trauma of the cervical spine, the normal flow of blood through the vertebral arteries is disrupted, resulting in a lack of blood supply to the cochlea and the auditory nerve.
Many children have mixed hearing loss. That is, the birth affected the nervous system and there is for example chronic otitis media.
Epileptic seizures and other epilepsy. Narcolepsy, convulsions, drowsiness. Neuralgia of the face. Migraine-opinion aspect: The severity is determined by the frequency, duration of attacks and the occurrence of autonomic disorders. Facial nerve. Intracranial aneurysms, condition after subarachnoid hemorrhage, occlusion or stenosis of marginal arteries, condition after surgery, cerebrovascular diseases. Assessment aspect: the degree of disability is determined by persistent neurological, mental and psychological disorders.
Multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating diseases. Parkinson's disease and other extrapyramidal syndromes. Tumors of the cranial cavity and spinal canal point of view opinion: the degree of disability is determined by neurological, psychiatric, psychological diagnosis, and any sensory and other disorders and the result of surgical and oncological treatment.
Hearing loss 1, 2, 3, 4 degree.
Degree of sensorineural hearing loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss 1 degree (26-40 dB) the child does not hear quiet sounds, can not make out human speech in a noisy environment. It distinguishes spoken language at a distance of not more than 6 meters, and "whisper" - from a distance of 1-3 meters. In children with 1 degree of sensorineural hearing loss, pronunciation often suffers and they sometimes ask again.
Sensorineural hearing loss 2 degrees (40-55dB) is the reason for the "lack of hearing" of quiet and medium-loud sounds. Speaking is perceived at a distance of 4 meters, and whisper is captured only at the ear. In children with 2 degrees of hearing loss, speech development is delayed, the child reluctantly enters into voice contact, if it is, then it is usually poor "Inability to hear."
Sensorineural hearing loss 3 degrees (55-70 dB) is characterized by the inability to distinguish the majority of sounds, the child’s communication with other people is sharply hampered. "Whisper" speech is generally not perceived, and conversational only from a distance of 1 meter, if you speak loudly with it. In children with 3 degrees of hearing loss, as a rule, a gross delay of the psycho-speech development is formed; he does not understand and does not fulfill the request and does not try to talk.
Sensorineural hearing loss 4 degrees (70-90 dB) a child can only hear very loud sounds, the state borders on deafness. In children with 4 degrees of hearing loss - speech does not develop at all. If the hearing aid does not improve hearing, then at grade 4, complex surgical intervention, cochlear implantation, is resorted to.
Assessment aspect: the degree of disability is determined by neurological, psychiatric and psychological diagnosis. Brain dysfunction in children. The severity was determined by functional attacks on the limbs and the severity of innervation of the bladder and rectum. It is necessary to differentiate whether the dominant limb is affected and whether it is mild, moderate or severe paresis or plegia.
Diseases of the neuromuscular junction. Other disorders of the nervous system. The degree of disability is determined by the degree and severity of disability, the frequency of attacks, disruption of social life, intelligence, behavior, memory, thinking, emotionality, emotionality, orientation, etc. The maximum value of the degree of disability is determined by the complete disintegration of the individual, the need for constant supervision, complete loss of social integration, regardless of the etiology of the disease.
Treatment for hearing loss in a child
It is important to identify and treat hearing loss in a child.The ENT doctor treats chronic otitis, laser can remove overgrown adenoids (laser reduction of adenoids).
If a child suffered a birth trauma at birth, treatment methods that improve the functioning of the central nervous system will improve hearing:
 Microcurrent reflex therapy for sensorineural hearing loss is carried out according to an individual program:
Microcurrent reflex therapy for sensorineural hearing loss is carried out according to an individual program:
1. Improving the blood supply of the cochlea and the auditory nerve
(due to the removal of the vertebral artery spasm).
2. Stimulation of the auditory nerve to improve the conduction of nerve impulses through it.
3. Activation of areas of hearing and understanding of speech of the cerebral cortex.
4. Activation of the speech areas of the brain responsible for
Organic mental disorders. Schizophrenia, schizotypal disorder and delusional disorder. Affective mood disorders. Neurotic, stress and somatoform disorders. Personality disorders and behavioral disorders. Disorders of the psychological development of children in compulsory school attendance.
Mental, behavioral disorders and organ damage caused by excessive psychoactive substances, alcoholism, drug addiction. Dependence with severe organ damage, organic, psychological and somatic changes, determined by the prevailing type of organ or mental impairment mentioned in this Appendix.
- speech understanding
- desire to make voice contact,
- vocabulary,
- skill building sentences.
6. The decrease in excitability in neurotic, disinhibited and aggressive children improves their adaptation to kindergarten and increases the effectiveness of classes with a speech therapist.
Vitamins of group B and preparations containing phospholipids (lecithin, ceraxon, gliatilin, etc.) are necessary for restoring affected pathways of the nervous system and the auditory nerve.
- Vascular preparations - improve the blood supply of the cochlea, the auditory nerve.
- Nootropics (Cortexin, Mexidol, Ceraxon, Actovegin, etc.) - nourish and restore the affected nervous system.
- To stabilize the intracranial pressure in children, it is preferable to use not diacarb, but diuretic herbs (horsetail, fennel, lingonberry leaf). As well as "horse chestnut" (eskuzan), which strengthens the vessels of the venous plexuses that produce cerebrospinal fluid and thus reduces intracranial pressure.
Emotional and behavioral disorders in children as part of compulsory school attendance. The degree of severity was determined in accordance with the achieved visual acuity with correction, which can be used on an ongoing basis, the field of view and their effect on orientation in everyday life. next to the visual function of the body, it is necessary to consider the obvious irritating phenomenon, lacrimation, sensitivity to external influences, as well as its associated disease.
Enucleation of the eye for a malignant tumor. Incurable forms of tumors 90. Loss of lens without disability in artifakia. Loss of one eye lens in blindness or loss of a second eye 30. Ptosis of the upper eyelid closure from the palpebral fissure 20. Polyvascular eye muscle in one eye, if the eye should be excluded from seeing 20.
Drug therapy each child is selected strictly individually, depending on the causes of sensorineural hearing loss after the course of the main treatment - Microcurrent reflexology.
The goal of hearing loss treatment is: Not only improve hearing but most importantly run n proper speech development and learning skills.
Lunging field of view by half full or quad view. Lunging perspectives: While an incomplete half or a quarter of a lap is necessary to assess the degree of disability should be reduced accordingly. Concentric constriction at 5 ° from the center of the normal field of view of the other eye 20.
Concentric constriction in the absence of the other eye. Irregular attacks of the field of view, large scotoma in the binocular field of view 50 ° 30. Glaucoma is determined by the degree of visual impairment. Other eye diseases and visual impairment, inflammation, cataracts, degenerative changes, vascular occlusion, retinal detachment and fissures, etc. - opinion point of view: the degree of disability is determined in connection with the restriction of vision, vision, orientation ability.
Children with neurosensory hearing loss are also needed - Classes with speech therapist and pediatric psychologist:
Educational activities are aimed at expanding the horizons, the development of fine motor skills, thinking, the study of such concepts as color, size, the formation of skills of counting, reading and writing.
Some of the children in the classroom can do without a hearing aid, others without a hearing aid do not hear well enough to develop properly.
In this case, wearing a hearing aid is necessary.
But the improvement of hearing and speech on the background of complex treatment will still be.
Severity is determined by the degree of hearing loss for speech, the presence of tinnitus, pain, imbalance, dizziness or speech disorder. The estimate is carried out in percent Fowler. Complete deafness means that hearing impaired with any sound reinforcement perceive sound only vibration.
Practical deafness means that hearing impaired with aural perception of benefits speech sounds, but does not understand. Loss of hearing means that hearing impaired hearing aids in a quiet room in which the alarm sound level does not exceed 50 dB, the lips of the reader, without meaning is expressed in simple sentences, by at least, by 90%.
If a child has 4 degree of hearing loss and he has already been operated on cochlear implantation, but the speech has not developed to the age norm, the child is excitable and poorly assimilates the educational material microcurrent reflexotherapy can also help him.
TREATMENT OF CHILDREN WITH A COCHLEAR IMPLANT IS TAKEN ONLY IN THE CENTRAL DEPARTMENT OF THE REACENTER IN SAMARA.
In objective shakosti. Loss of one auricle 10. Loss of both ears 30. Malignant tumors head and neck. Section A - oral cavity and upper airways. Extensive defect of the sky with a well-fitting prosthesis, covering defect 30. Relapse paralysis, unilateral with voice impairment 30.
Patent respiratory and respiratory disorders affecting overall performance by reducing the body 50. The degree of severity is determined by the restriction of lung function, the effect on the general condition and the subsequent manifestations of other organ systems.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO TIMELY PURPOSE TO THE TREATMENT OF DEADLY
More information about hearing loss treatment you can get
by phone 8-800-22-22-602
(free call within RUSSIA)
Microcurrent reflexology for the treatment of hearing loss 1, 2, 3, 4 degrees,as well as other problems with hearing are carried out only in divisions of the Reatsentr in the cities: Samara, Kazan, Volgograd, Orenburg, Tolyatti, Saratov, Ulyanovsk, Naberezhnye Chelny, Izhevsk, Ufa, Astrakhan, Yekaterinburg, St. Petersburg, Kemerovo, Kaliningrad, Barnaul, Chelyabinsk.
Protracted bronchitis ventilation without failure or recurrent pneumonia without ventilation failure 10. Bronchial asthma or asthmatic syndrome in children until the end of compulsory school. Tuberculosis point of view: the degree of disability is determined by persistent functional deficiency under the guidance and the general condition of the body.
Tuberculosis of the respiratory system. Inactive, without organ dysfunction 10. Tuberculosis of other organs and systems. The severity is determined by the degree and severity of the cardiovascular system limits the performance of the system. Congenital or acquired heart defects and major cardiovascular diseases, coronary heart disease, after a heart attack, chronic rheumatic heart disease, postoperative conditions, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, angina pectoris.
Hearing loss is a violation of the perception of sounds, which occurs as a result of pathological changes in the functioning of the human hearing aid. People suffering from this disease, lose their ability to perceive the sounds of low frequencies, which is carried out throughout the process of communicating with each other. Over time, depending on the degree of hearing loss, their hearing threshold rises more and more, which can lead to complete hearing loss.
Depending on the location of disorders in the ear, there are three types of disease: neurosensory, conductive and mixed.
Sensor type
The neurosensory type of the disease, or as it is often called - sensorineural hearing loss, is characterized by impaired perception of sounds directly inner earwhere the transmission of sound vibrations to the nerve.
Often, with this type of disease, not only the sound-perceptive apparatus is exposed to pathological changes, but also the hearing centers in the temporal lobes of the brain, which further impair the audibility of the patient.
All three ears can be affected
There are many reasons for the development of sensorineural pathological changes both in adulthood and in young children. Usually they are all associated with impaired blood supply or an increase in pressure in the inner ear.
Conductive type
Conductive hearing loss is associated with impaired functioning of the human conductive apparatus, as a result of which not all sound waves reach the inner ear, from which sensory information is sent for processing to the large hemispheres of the brain.

The doctor must first determine the localization of pathology in the ear canal
The causes of this type of disease are considered neoplasms and developmental pathologies in the external ear or in the tympanic cavity.
Mixed type
Usually, a person has only a sensor-type or conductive type of the disease, however, it also happens that violations are observed at once in all parts of the ear, then we can talk about mixed hearing loss.
If the first two types are characterized by the presence of at least one reason for the occurrence of hearing impairment, then with a mixed type, there are usually several of them at once.
Stages of development of the disease
If children most often distinguish the acute stage of the disease, over the years it tends to progress slowly and turn into chronic hearing loss.

Children undergo hearing impairment at least adults
Depending on the hearing threshold (the minimum level of sound that is capable of picking up a person’s hearing aid), it is customary in a patient to distinguish 4 degrees (stages) of a chronic disease.
1st degree
Hearing loss 1 degree is characterized by a relatively small decrease in hearing. From the norm of 20 Dz, the hearing threshold rises only to 40 Dz.
At a distance of several meters, provided there is no extraneous sounds, the person does not have any problems with audibility, distinguishes all the words in the conversation. However, in a noisy environment, the ability to hear the interlocutors' speech is clearly deteriorating. It also becomes hard to hear whispers at a distance of more than 2 meters.
The problem of the early stage of the disease is that a person rarely notices that he began to hear worse, since the changes at the beginning are minor. Therefore, visits to a doctor are very rarely observed, and it is at the beginning that it is easiest to slow the progression of the disease with the help of drug treatment.
It is especially difficult to determine the first degree in a child, since complaints are almost always absent.
2nd degree
Grade 2 is distinguished by a progressive loss of the ability to hear normally and by changing the threshold to 55 Dz inclusive.
In people at this stage, the hearing begins to fall rapidly, they can no longer hear normally, even in the absence of extraneous noise. They cannot distinguish whispers at a distance of more than a meter, and ordinary speech - at a distance of more than 4 meters.
At this stage, the symptoms of the disease are more pronounced, because a person often begins to ask again during a conversation, especially by telephone. It also becomes necessary to listen to music or watch TV at a higher volume than before. Children also begin to appear complaints that they have become worse to hear.
At stage 2, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. Medicines are still effective, so timely treatment can protect against complete deafness in the future.
3rd degree
If at the first two stages the patient did not undergo treatment, or the intended effect did not occur, then the disease develops into a severe 3 degree. The threshold reaches the value of 70 Dz, a person does not fully hear at a distance of more than two meters and does not distinguish between whispers.
This stage is considered a severe form of the disease, because it becomes extremely difficult for a person to communicate with others, to study and work comfortably. If start drug treatment so late, then, unfortunately, it may not bring an expected result.
4th degree
The most severe form of hearing impairment is hearing loss 4 degrees. Unfortunately, it often develops into complete deafness. According to audiometry, the hearing threshold reaches disappointing values of 70 C, and even the loudest sounds become extremely difficult to hear.
The patient does not hear the whisper at this stage at all, and the spoken language can hardly be distinguished only at a distance of no more than 1 meter. The main task of doctors in this period is considered not to allow the threshold to rise to values above 90 Dz, because in this case, the ear will not be able to perceive sounds of any frequency and volume. Deafness will come.
Disability and army service
In accordance with the laws of the Ministry of Health, third degree disability can be obtained by a person with a hearing loss of 3–4 degrees on a better hearing ear. Patients with bilateral hearing loss in the last stage usually fall into this category.
Older people often get disabilities because of hearing loss
However, for young men with a severe stage of the disease, even in the event of a single ear loss, the army is contraindicated in most cases. More detail can be judged only by the audiogram.
Often in children, the acute form of the disease progresses very quickly, and they get a disability at a rather young age. Usually they attend specialized schools for hearing impaired children, where they are helped to learn the language of the deaf and dumb.
Modern methods of treatment
Treatment always depends on the severity of the disease. Unfortunately, in most cases, patients with severe medical treatment do not help, they can not do without installing a hearing aid.
However, if you go to a doctor in time and start taking medicines, hearing loss can be significantly slowed down even at the initial stage.
Medications
In modern medicine, the use of nootropic drugs is often practiced. They have a pronounced antihypoxic property, that is, they reduce insufficient blood saturation with oxygen. As a result, the blood supply to the inner ear improves and increases the flow of nutrients to the acoustic nerve.
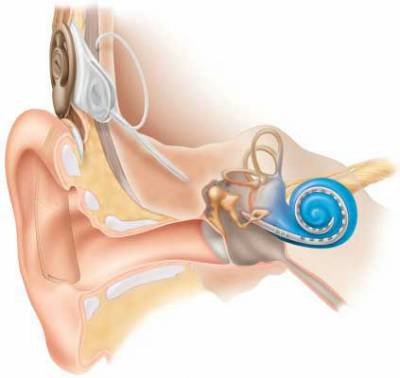
Installing a cochlear implant has changed the lives of millions of people.
Nootropics are also considered excellent neuroprotectors, they protect the myelin sheath of nerves, thereby strengthening the nervous tissue as a whole.
For severe hearing impairment, such drugs are prescribed intravenously for 2 weeks, then the treatment continues for several months, but the drugs are already injected intramuscularly.
In second place in popularity are antihistamines. The thing is that often hearing problems are accompanied by disturbances in the labyrinth of the inner ear, which is the main part of the vestibular apparatus. Antihistamines help reduce the pressure in the maze, thereby improving blood flow.
When medications no longer help
Indeed, in the later stages of the disease, drug treatment often loses its effectiveness. Many patients, in order to be able to return the joy of communication with others, are beginning to use artificial hearing aids.
Fortunately, modern designs are small, so they are almost invisible to others, and the quality of new devices are far superior to their predecessors.
For those who do not use the device, doctors offer a quick solution to the problem - the installation of a cochlear implant. This operation is suitable for those whose disorders are caused by pathological changes in the inner ear, namely in the organ of Corti, which perceives and transmits sound vibrations to the auditory nerve. The implant completely takes all of its functions on itself, thereby once and for all solving the problems with the audibility of the patient.
Popular
- Blood disorders in children
- What can not drink a pill
- Blood disorders in children
- Blood disorders in children
- Bones: structure, composition, types of bones, types of connections and their characteristics
- How many live with lung cancer
- Influenza in children: how to treat, what can and cannot be done to parents, what medicines will help?
- "They are people too ..." - you say
- What helps "Prednisolone"
- How are menstruation for endometriosis?