Diseases of the inner ear treatment. Drug treatment of labyrinthitis. Video: labyrinthitis in the program "Live healthy"
Diseases of the ears can occur with a blurred symptoms and can not be expressed high fever or severe pain. Nevertheless, the consequences of such pathologies can be serious, because the matter concerns the organs responsible for hearing and located next to the brain. For example, inflammation inner ear, or labyrinthitis, can end with hearing loss and the need to install a hearing aid in the future, although its symptoms sometimes do not lead to serious disorders and disorders in the body.
General characteristics of the disease
Labyrinthitis (synonym - internal otitis) is an inflammatory lesion of the inner ear. This organ is not visible from the outside, as it is located in the region of the temporal bone, however, it performs the most important functions. The inner ear is a bone labyrinth that includes a cochlea, vestibule, semicircular canaliculi. The main part of the body - the cochlea, where the auditory analyzer is located, but the receptors of the tubules and the vestibule also play the necessary role for the person - are responsible for the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, that is, maintain the balance of the body. Inflammation of the inner ear, therefore, disrupts the activity of both the hearing organs and the vestibular receptors, from which the characteristic symptoms of labyrinthitis appear.
There are several classifications of labyrinthitis on various grounds. Because of its appearance, it can be bacterial, fungal, viral, and in terms of its coverage by the inflammatory process, it can be local and diffuse. Internal otitis is able to be non-purulent, purulent, necrotizing, and along the path of introduction of the pathogen:
- meningogenic (gets from the lining of the brain);
- hematogenous (penetrates with blood);
- tim pathogenic (infection spreads out of the middle ear);
- traumatic (is the result of direct damage to the inner ear when injured).
Acute labyrinthitis develops within 14-21 days, after which as a result of the treatment the disease subsides. Pathology tends to become chronic, especially with inadequate therapy. Chronic internal otitis often flows for many years without recurrence, but sometimes causes severe hearing loss of the ear. The severity of acute labyrinthitis can also be different: from a slight indisposition to disability.
Due to the structure of the inner ear, inflammation occurs more often in children than in adults, and necrotic type of labyrinthitis often develops in children.
Causes of Labyrinthitis
In most cases, internal otitis is caused by an infectious process that takes place in the body and somehow gets into the inner ear. Most often, the bacteria penetrate into the lesion from the middle ear in case of purulent otitis of non-specific nature, as well as in case of tuberculous inflammation of the ear. The causative agents of the disease are staphylococci, pneumococci, streptococci, mycobacterium tuberculosis. In weakened people with the presence of chronic diseases of the ear, in children the flu and ARVI, the virus of mumps, herpes can provoke a labyrinthitis.
With a bloodstream, the infection spreads to the region of the inner ear, in most cases, in children with mumps, scarlet fever, diphtheria, measles, and in adults with syphilis. Against the background of meningitis, infectious particles often penetrate into the inner ear, causing labyrinthitis. Ear injury - another possible reason development of the disease, because during the hit foreign body, chemicals, after burns, wounds with perforation of the eardrum or a fracture of the skull base bone, nonspecific flora can be easily inserted into the inner ear. Occasionally, pathology develops after surgery on the middle, inner ear, as well as after a stroke, when blood from a ruptured vessel leads to the formation of a hematoma, compression of the vessels of the inner ear and the gradual death of its tissues.
Some factors are considered provocative, increasing the risk of otitis media. These include:
- immunodeficiency;
- poor nutrition;
- frequent stress;
- regular supercooling of the head;
- chronic ear diseases;
- anomalies of the structure of the ears.
Usually, self-healing is characteristic of viral labyrinthitis, while the bacterial type of the disease must be urgently treated to avoid hazardous consequences. The pain inside the ear with internal otitis is caused by the appearance of hyperemia and edema of the ear structures, the formation of a large amount of edematous fluid, which increases pressure on the bone maze, irritation of the nerve receptors, and cell death during purulent inflammation or necrosis.

Symptoms of the disease
Viral labyrinthitis, which occurs on the background of a middle ear lesion in acute respiratory viral infections and other diseases, can lead to serous inflammation of the bone maze with minimal, blurred symptoms. Often, patients note a slight ear congestion, discomfort, which pass along with recovery from the underlying disease. But often, without treatment, the symptoms gradually increase, with the result that characteristic signs of pathology appear. Usually, the clinical picture of labyrinthitis occurs 7-10 days after the infection (after an injury, 1-2 days):
- dizziness, sense of rotation of objects (manifested by attacks of varying duration);
- increased dizziness with sharp head movements;
- nausea down to vomiting;
- immobility of the eyeball;
- imbalance, coordination;
- instability when walking (usually with a two-sided labyrinth);
- ear congestion, noise in the head;
- feeling that hurts inside the ear;
- decrease in auditory function;
- low-grade body temperature;
- pallor;
- palpitations.
If the main focus of inflammation is in the cochlea of the inner ear, then the patient will have slight pain, tinnitus, and changes in hearing, but when inflammatory process covers the vestibule and the semicircular canals, the main symptom is a violation of the vestibular function and dizziness. Attacks of nausea, vomiting, coupled with disruptions in balance and dizziness are called labyrinth attacks.
The most severe form of the disease is diffuse bacterial (purulent) labyrinthitis. With this pathology, the pus is formed directly in the bone maze. Pathology can be triggered by meningitis, or nonspecific bacteria against the background of long-term otitis media. In this case, labyrinthitis occurs suddenly and develops violently, with vivid symptoms, and auditory and vestibular receptors can quickly die off with complete hearing loss and other serious disorders.
Possible complications
Only when the serous form of otitis media does not cause symptoms of a serious violation in the patient's condition. Purulent forms of labyrinthitis are dangerous with a multitude of complications, the most serious of which are meningitis, brain abscess, cerebral thrombosis of the brain, sepsis, cerebral hemorrhage. Often purulent internal otitis causes the development of mastoiditis, neuritis of the auditory branch facial nerve, sensorineural hearing loss, complete deafness due to the presence of necrotic sequesters in the labyrinth. Children with an imperfect immune system are subject to the highest risk of complications, and only an early visit to a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease can prevent an unpleasant outcome of events. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment - components of success for complete recovery from labyrinthitis without consequences.
Diagnostics
Since the main complaints in labyrinthitis are dizziness, nausea and tinnitus, combined with the fact of infectious disease or injuries, this should arouse the suspicion of a specialist for the development of internal otitis. To confirm the diagnosis there are various methods of examination:
- CT, MRI of the brain - reflect the inflammatory process in the region of the inner ear;
- electronistagmography - allows you to differentiate the pathology of the eyeball, developing on the background of the destruction of the maze or arising from other reasons;
- audiometry - a test for the quality of hearing in humans;
- physical tests for hearing - express the activity of the auditory nerve;
- various studies of the vestibular function are necessary to control the state of the vestibular apparatus;
- otoscopy - detects signs of otitis media and pathology of the eardrum;
- x-ray of the temporal bone - more often recommended for head injuries;
- lumbar puncture - planned for suspected meningitis;
- differential diagnosis is made in comparison with the neuritis of the auditory nerve, brain tumors, otosclerosis, etc.
In the labyrinth, in addition to consulting an otolaryngologist, examinations may be needed from an infectious disease specialist, a neurologist, a traumatologist, a venereologist, depending on the cause of the disease. When a specific infection of the bone labyrinth is necessary to conduct blood tests for the presence of mycobacterium tuberculosis, pathogens of syphilis and other bacteria or viruses by ELISA, PCR and other research methods.
Treatment methods
In children and adults, serous pathology can occur independently and does not require admission. antibacterial drugs. But with severe course, as well as with any type of purulent labyrinthitis, the patient is urgently hospitalized. In early childhood placement in a hospital is mandatory for any form and type of internal otitis.
Treatment conservative should ensure the elimination of the pathogen and create conditions for the outflow and cessation of pus production. An integrated approach is also aimed at preventing hearing impairment, the activity of the vestibular apparatus and the blood supply to the inner ear. The following drugs and methods are used:
- antibiotics (drug use is determined by a detected pathogen, Azithromycin, Cephalexin is more commonly used);
- NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Nise);
- neuroprotectors (nootropil, cerebrolysin, lucetam);
- desensitizing drugs (Suprastin, Diazolin, calcium chloride);
- vestibulolitiki and sedatives (Betaserc, Betaver) along with diuretics (Lasix);
- antiemetics (Motilium, Metoclopramide);
- glucocorticosteroids (hydrocortisone, mometasone);
- b vitamins injections, magnesium sulfate;
- salt-free diet with limiting the amount of liquid to a liter per day.
If, against the background of inflammation of the inner ear, purulent foci of the middle ear have formed, they are opened and provided with drainage and regular antiseptic treatment. More serious surgery will be required when purulent accumulations or necrotic scars, strands formed in the area of the bone labyrinth. In addition to sanitizing interventions for a patient with heavy current pathology may require labyrinthomy, mastoidotomy, opening of the temporal bone, drainage of the cranial cavity. Acute and chronic labyrinthitis can lead to serious hearing impairment, and therefore hearing aids or cochlear implantation are performed.
Folk remedies when labyrinthism is permissible to use only in its serous form, and all of them must be agreed with the doctor. As a rule, experts do not mind if the patient independently takes herbal extracts to increase immunity, fortifying agents, for example, levzeyu, eleutherococcus, dogrose, hawthorn, echinacea. Abuse folk treatment and it is forbidden to drip into your ears when labyrinthite! In addition, it is impossible to warm the ears during the inflammatory process in the bone maze, since this can provoke the appearance of purulent foci, such as chronic suppurative otitis media.
Labyrinthitis prevention
The main measures to prevent pathology are timely treatment of diseases of the middle ear, especially, purulent otitis, prevention of injuries to the head and ears. You also need to carefully consider the health of acute respiratory viral infections, flu, all cold and infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract, do not overcool and observe the doctor's prescription for treatment.
In the next video, Elena Malysheva will talk about labyrinthite, a disease of instability. What is it and how to get rid of it.
) appears when pathogenic microorganisms appear in the internal cavity of the hearing aid, rarely afterwards are injuries. What causes middle ear inflammation? How dangerous is the inflammatory process in the middle ear?
Causes of inflammation in the inner ear
Infection
The middle ear is deep enough, so it becomes infected when other lesions are inflamed. When an infection is observed in the middle ear, the membranes begin to swell, through which microorganisms are inside. It is dangerous when outflow of pus is difficult and pressure rises inside the middle ear.
In some situations, pathogenic microflora in the middle ear multiplies with inflammation of the meninges (). An infection can affect two ears at once. In this case, the inflammatory process is dangerous because it leads to deafness.
Ear injury
The inflammatory process can be triggered by an injury to the ear, which is subsequently damaged by a pin, needle, or injury after a blow to the head.
Hematogenous inflammation
Very rarely observed hematogenous form of otitis media. It occurs if the pathogen from the blood is in the middle ear. This form develops later parotitis, syphilis. The causative agent in this case are staphylococci, streptococci, tuberculosis bacteria.
Symptoms of inner ear inflammation
- Constantly worried dizziness.
- Very noisy and sore in the ears.
- There are serious problems with hearing.
Unpleasant sensations are aggravated by moving the head. Attention! Dizziness accompanies different diseases, but in otitis, it appears 10 days after the person has had a bacterial infection. In chronic otitis media, dizziness is spontaneous, lasts several days. In some situations, dizziness increases when a person sneezes, goes to transport.
In the inflammatory process in the middle ear, there are problems with the reflex oscillation of the eyeballs. In severe cases, hearing may deteriorate permanently.
Caution! If the inflammatory process of the middle ear is purulent, it is urgently necessary to treat it, otherwise everything can result in complete deafness.
Do not start the inflammation, because it can affect the facial nerve, then the affected side can paralyze. In this case, you need to pay attention to the following signs:
- The crease on the forehead disappears when a person raises his eyebrows.
- The corners of the mouth become fixed.
- Salivation increases.
- Increased dryness in the eyeball.
- Unable to close your eyes.
- There are problems with taste.
Sometimes with labyrinth, sweating increases, the heartbeat is disturbed, nausea and vomiting are also observed. Person worried strong pain in heart.
Diagnosis of middle ear inflammation
The doctor must prescribe a patient a blood test. In order to find out why dizzy, the patient must pass a special test. Additionally assigned:
- Electrosystagmography.
- CT scan.
- Audiometry.
Ways to treat middle ear inflammation
At first, conservative treatment methods are used; if they do not help, surgical intervention is necessary. The patient must adhere to such a treatment plan. :
- Taking antibiotics. Antibiotics must be prescribed to affect the bacteria. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Penicillin, Cephalosporin. Do not take ototoxic antibiotics Gentamicin.
- Diet to cleanse the body, it is also necessary to reduce the amount of water. Drink no more than one liter.
- Reception of glucocorticoids and diuretic drugs.
- Intravenous solution of glucose, magnesium sulfate, calcium chloride.
- Reception of vitamins K, B, C, R.
- Atropine preparations are injected intramuscularly.
To relieve the symptoms of the patient, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Against vomiting to eliminate nausea and vomiting that worries when dizzy - Zerukal, Fenegran.
- Antihistamines - Dimedrol, Suprastin, Fenistil.
- Steroid drugs help stop the inflammatory process.
- Scopolamine as a patch, you can get rid of nausea and vomiting.
- Sedation drugs - Lorazepam, Diazepam.
Surgical intervention for middle ear inflammation
If the disease proceeds in a purulent form, a sanitized trephination is necessary, in which it completely removes pus. Before the operation, you should take antibiotics for about a week. In advanced cases with necrotic or a complete maze removal is required.
Traditional methods of treating middle ear inflammation
- Broth with burnet root. You must take 2 tablespoons of the plant and pour 400 ml of boiling water. Keep everything for about half an hour. Broth drink three times a day at least a tablespoon.
- Onion juice should be mixed with vegetable oil, then it is necessary to prepare a cotton swab and with a moistened mixture, hold in the ear for up to two hours.
Prohibited!A hot or warm heating pad can cause a pus to break through to the head, so this procedure is strictly prohibited.
Prevention of inflammation in the inner ear
To prevent complications, it is necessary to diagnose the disease in a timely manner. It is especially important to treat in time the purulent form of otitis media. If you start the inflammatory process, everything can result in hearing loss or brain damage.
So, do you want to get rid of middle ear inflammation? Urgently go to an otolaryngologist. That he will be able to find out the cause of your pathology and prescribe treatment. No need to endure pain, dizziness and other unpleasant symptomsit is better to undergo a comprehensive course of therapy.
If the labyrinthitis was caused by a traumatic brain injury, the symptoms may be different. With the defeat of the inner and middle ear is often observed accumulation of inflammatory fluid mixed with blood ( hemorrhagic exudate), which appears through the eardrum. Also, damage to the temporal bone can lead to paresis of the facial nerve. This complication is manifested by the inability to arbitrarily control the muscles of the face ( half of the face on the affected side remains immobile). Paresis of the facial nerve occurs in case of damage to the facial nerve canal located in the temporal bone.
Symptoms of labyrinthitis
| Symptom | Mechanism of occurrence | External manifestation |
| Involuntary oscillatory eye movements (nystagmus) | Arise due to dysfunction of one of the labyrinths. Subcortical and cortical regions of the brain, which process signals from the semicircular canals, in response to dysfunction of the maze lead to nystagmus. At the beginning of the disease, nystagmus is directed toward the affected ear, and then within a few hours changes its direction in the opposite direction. In the context of damage to the cavity of the inner ear, this symptom is the most important. |  |
| Nausea and vomiting | Appear as a result of the transition of nerve impulses from the vestibular nerve to the nearby nerve fibers of the vagus nerve. In turn, this nerve is able to irritate the upper section. gastrointestinal tract, which leads to nausea, and with excessive stimulation of the soft muscles of these departments - to vomiting. |  |
| Increased sweating (hyperhidrosis) | Appears at the initial stage of the labyrinth damage or during exacerbation of chronic labyrinthitis. Increased sweating occurs due to excessive stimulation of the vagus nerve. |  |
| Dizziness | Caused by lesions of the semicircular canals. Information about the position of the head and body reaches the brain only from a healthy maze. As a result, the vestibular center is not able to assess the current position, which leads to a violation in spatial orientation. Dizziness may subjectively manifest itself as a feeling of rotation of surrounding objects, a feeling of uncertainty in determining its current position in space, or as the withdrawal of soil from under its feet. Attacks of dizziness may be brief ( 3 - 5 minutes) or last for several hours. |  |
| Hearing loss down to deafness | Hearing loss occurs when the cochlea of the inner ear and / or the auditory nerve is damaged. Deafness, as a rule, occurs as a result of purulent damage to the cavity of the inner ear or after acute acoustic trauma of the ear. It should be noted that hearing loss is more pronounced in the high frequency range. |  |
| Movement coordination disorders | Observed with pathological changes in the semicircular canals and in the pre-door-cochlear nerve. These disturbances lead to a change in gait ( uncertain and shaky), as well as to the deviation of the trunk and head in a healthy way. |  |
| Tinnitus (tinnitus) | Occurs with the defeat of the auditory nerve. Tinnitus in the absolute majority of cases appears along with a decrease in hearing. Subjectively, tinnitus is perceived as hum, buzzing, hissing, ringing or squeaking. |  |
| Heart rate change | With labyrinth, a decrease in heart rate is most often observed. This is due to the excessive activation of the vagus nerve, which also supplies the nerve fibers and the heart. The vagus nerve is able to alter the conductivity of the heart and lead to a slower rhythm. |  |
Diagnosis of labyrinthitis
 The labyrinthitis is diagnosed by an otorhinolaryngologist ( ENT doctor). In some cases, for proper diagnosis, consult a neurologist, as well as an infectious disease specialist. For labyrinthitis is characterized by the presence of complaints such as dizziness, impaired coordination of movements, hearing loss, noise in one or both ears. One of the main symptoms of labyrinthitis is the presence of involuntary oscillatory eye movements ( nystagmus). By carefully collecting all the necessary information about the disease, the ENT doctor can use a variety of different instrumental diagnostic methods.
The labyrinthitis is diagnosed by an otorhinolaryngologist ( ENT doctor). In some cases, for proper diagnosis, consult a neurologist, as well as an infectious disease specialist. For labyrinthitis is characterized by the presence of complaints such as dizziness, impaired coordination of movements, hearing loss, noise in one or both ears. One of the main symptoms of labyrinthitis is the presence of involuntary oscillatory eye movements ( nystagmus). By carefully collecting all the necessary information about the disease, the ENT doctor can use a variety of different instrumental diagnostic methods. There are the following methods of diagnosis of labyrinthitis:
- otoscopy;
- vestibulometry;
- fistula test;
- audiometry;
- electronistagmography.
Otoscopy
Otoscopy is used to examine the auricle, the ear area auditory canal (together with mastoid process) and the eardrum. Also, the doctor must probe for all nearby lymph nodes for the presence of their increase.Examination always start with a healthy ear. For a more convenient examination of the external auditory canal, the doctor delays the auricle posteriorly and upwards. Using a special otoscope tool, you can visually identify defects in eardrum. If the eardrum is partially or completely destroyed, using this method, you can inspect the middle ear cavity. Otoscopy is used if the labyrinthitis was caused by acute acoustic trauma of the inner ear or when the inflammatory process spreads from the middle ear cavity to the inner one.
Vestibulometry
Vestibulometry implies the use of different tests to detect pathological changes in the vestibular apparatus. Evaluation of these methods is based on the duration and type of nystagmus. It should be noted that vestibulometry is only an auxiliary method and is used in combination with other methods of labyrinthitis diagnostics.Vestibulometry implies the use of the following functional samples:
- caloric test;
- rotational test;
- pressor test;
- otolithic reaction;
- fingertip test;
- pointing test.
Rotational sampleit is made on a special chair with a rotating seat. To do this, they ask to sit in a chair, keep your head straight, and close your eyes completely. Next, spend 10 rotations in right sideand then 10 more spins to the left. In this case, the rotation speed should be 1 revolution in 2 seconds. After this test is completed, the doctor monitors the appearance of nystagmus. Normally, nystagmus lasts about half a minute. The shortening of the duration of nystagmus speaks in favor of the defeat of labyrinthitis.
Pressor testcarried out with a special balloon Politzer. Air is forced into the external auditory canal by means of this balloon. If nystagmus occurs, this speaks in favor of a fistula ( pathological canal) in the lateral semicircular canal.
Voyachek otolith reaction,as well as the rotational test, it is produced on a special rotating chair. The studied patient closes his eyes and lowers his head down so that his chin touches the sternum. The chair rotates 5 times within 10 seconds. Then wait 5 seconds, after which the subject must lift his head and open his eyes. The function of the vestibular apparatus is assessed by various symptoms (nausea, vomiting, cold sweat, facial blanching, fainting).
Paltsenosovaya sample It is a simple test for detecting impaired motor coordination. The patient is asked to close his eyes and take one of the hands, and then slowly touch the tip of the nose with the index finger of this hand. When labyrinth, this test helps to identify vestibular ataxia. Ataxia is a violation of gait and coordination of movements and may occur due to the defeat of the vestibular apparatus. Most often, vestibular ataxia is one-sided.
Indicative test Barani held in a sitting position. The patient is asked to hit the forefinger of the hand on the finger of the doctor's outstretched hand alternately with the eyes open and then with the eyes closed. When labyrinthite, the person under study, with eyes closed, misses with both hands.
Audiometry
Audiometry is a method for studying hearing acuity and determining auditory sensitivity to sound waves. This method is carried out using special equipment - an audiometer. It should be noted that to perform audiometry, you need a special soundproof room.The following types of audiometry are distinguished:
- tonal audiometry;
- speech audiometry;
- audiometry using a tuning fork.
Speech Audiometrynecessary to determine the quality of word recognition at different levels of sound. Through aerial telephones, the person being investigated is offered to listen to a recording of 25 or 50 words spoken at various intensities. At the end of speech audiometry, count the number of words that have been heard. Any word change ( use singular instead of plural and vice versa) is considered an incorrect answer.
Audiometry using a tuning forkused in the absence of tonal audiometry. As a rule, use the test of Weber or Rinne. To do this, the leg of the sounding tuning fork is applied to the crown ( weber's test). With an unaffected hearing analyzer, the sound is felt in both ears with the same intensity. With a one-sided labyrinth, the patient will hear better the affected ear. For the Rinne test, a leg of a sounding tuning fork is applied to the mastoid process of the temporal bone. After the subject says that the sound of the tuning fork has ceased to be felt, it is removed and brought to the auricle. With a labyrinth, the sound of a tuning fork is not felt when approaching the ear, while normally a person begins to hear the sound of a tuning fork again.
Electrostagmography
Electronistagmography is a method that allows quantitative and qualitative assessment of the nystagmus that occurs during labyrinthitis. This method is based on recording the electric potential difference between the cornea of the eye and the retina ( corneoretinal potential). The obtained data is recorded on a magnetic tape and further processed by a computer, which allows determining various parameters of nystagmus ( quantity, amplitude, frequency, speed of the fast and slow component). The result of electronistagometry allows us to distinguish nystagmus caused by a violation of the vestibular apparatus from other types of nystagmus.In addition to the above methods, other highly informative diagnostic methods that can detect damage to the inner ear can be used.
The following instrumental methods of labyrinthitis diagnostics are distinguished:
- radiography;
Computed tomography of the temporal boneis one of the preferred methods in the labyrinthitis diagnosis. This method allows you to visualize not only the bone structures of the temporal bone, but also various soft tissue structures in their natural arrangement. Computed tomography allows not only to identify the nature and extent of damage, but also allows you to visualize the state blood vessels and nerve tissue in this segment. As with radiography, the only contraindication of this method is the presence of pregnancy.
Magnetic Resonance Imagingis the "gold standard" in the diagnosis of various lesions of the inner ear. Magnetic resonance imaging is the most informative diagnostic method and allows you to study in detail the structure of the bone and membranous labyrinth. The only drawback of this method is the inability to obtain information about the cavity of the middle ear.
If the labyrinthitis is a consequence of a viral or bacterial infection, it is necessary to perform a complete blood count. If the labyrinthitis is caused by a bacterial infection entering the cavity of the inner ear, an increased number of white blood cells will be detected in the blood ( white blood cells that protect the body from bacteria), and viral disease - increased lymphocyte count ( immune cells). Also, the infectious process leads to an increase in ESR ( erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
If the labyrinthitis is caused by otitis media, then in this case it is necessary to conduct a bacteriological examination of the discharge from the ear ( method to identify the type of pathogen).
Labyrinthitis Treatment with Medicines
 Treatment of labyrinthitis is most often performed in a hospital setting ( hospital). The treatment regimen is selected depending on the cause of the labyrinthitis, as well as on the basis of the symptoms of the disease.
Treatment of labyrinthitis is most often performed in a hospital setting ( hospital). The treatment regimen is selected depending on the cause of the labyrinthitis, as well as on the basis of the symptoms of the disease. Drug treatment includes use drugs different groups. Antibiotics are prescribed for the treatment of a bacterial infection, taking into account the sensitivity of microorganisms ( antibiogram). Also prescribed drugs that have anti-inflammatory effects, as well as normalize metabolic processes in the cavity of the inner ear and brain.
Antibiotics for treating labyrinthitis
| Antibiotic group | Representatives | Mechanism of action | Application |
| Penicillins | Amoxicillin | Joining the bacterial cell wall destroys one of its components. Able to inhibit growth and reproduction different kinds microorganisms ( possesses wide spectrum actions). | Inside Adults and children weighing over 40 kg, 0.5 g three times a day. In severe infectious process, the dose may be increased by 2 times ( up to 1 g). Children from 5 to 10 years on 250 mg ( 1 teaspoon or 1 capsule), from 2 to 5 years old - 125 mg. Children up to 2 years old are served in liquid form ( suspensions) 20 mg / kg also three times a day. |
| Piperacillin | Blocks the components of the cell wall of bacteria, as well as some bacterial enzymes. Suppresses the growth and reproduction of various microbes ( has a wide range of action). | Intravenous droppers. The drug is administered drip, for half an hour or a jet, for 4 to 5 minutes. From the age of 15, the drug can be administered intramuscularly. In the treatment of moderate infection, the drug is prescribed in a daily dose of 100-200 mg / kg, three times a day. The maximum daily dose is 24 grams. | |
| Oxacillin | Blocks the component of the cell wall of microorganisms. Active against staphylococci and streptococci. | Inside for 1 hour before meals or 2 to 3 hours after meals. The single dose for adults is 1 g, and the daily dose is 3 g. It is also possible to apply intramuscularly or intravenously. Adults and children whose weight exceeds 40 kg - 250-1000 mg every 5-6 hours or 1.5-2 g every 4 hours. For children weighing less than 40 kg, 12.5 to 25 mg / kg, and for newborns, 6.25 mg / kg, every 6 hours. The maximum daily dose is 6 g. | |
| Macrolides | Erythromycin | According to the spectrum of action is close to penicillins. Blocks the growth of bacteria due to the violation of the formation of protein bonds. | Inside Adults and children over 15 years old 0.25 g every 5-6 hours. The drug is taken one and a half hours before meals. The maximum daily dose is 2 g. For children under the age of 14, 20-40 mg / kg four times a day. |
| Clarithromycin | Blocks the synthesis of proteins of microorganisms. It affects both intracellular and extracellular pathogens. | Inside Children over 12 years old and adults 0.25 - 0.5 g twice a day. The duration of treatment is 7-14 days. The maximum daily dose is 0.5 g. For children under 12 years old, 7.5 mg / kg twice a day. |
With sudden symptoms of dysfunction of the inner ear ( labyrinth attack) or during exacerbation of chronic labyrinthitis, vestibulolytics are shown. This group of drugs improves blood supply in the labyrinthitis and helps to reduce the severity of various vestibular symptoms ( dizziness, nausea, bradycardia, lack of coordination).
Drug treatment of labyrinthitis
| Group of drugs | Representatives | Mechanism of action | Application |
| Histamine preparations | Betahistine | Improve blood supply in the cavity of the inner ear. Able to reduce the degree of excitation of the vestibular nuclei and thereby reduce the severity of vestibular symptoms. Accelerate the process of recovery of the vestibular organ after lesions of the semicircular canals. | Inside, during the meal, 8 - 16 mg three times a day. The duration of treatment should be selected individually. The effect is observed 2 weeks after taking the drug. |
| Bellatamininal | |||
| Alfaserk | |||
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | Diclofenac | They have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects. Inhibit biologically active substances that further support the inflammatory process. | Inside Adults on 25 - 50 mg three times a day. With the improvement of the state, the dose is gradually reduced to 50 mg / day. The maximum daily dose is 150 mg. |
| Naklofen | |||
| Dicloran | |||
| Preparations blocking histamine receptors | Bonin | Have a pronounced antiemetic effect. Impact mainly in the labyrinth structures and lead to a decrease in vertigo. These drugs are valid for 24 hours. | Children over 12 years old and adults 25 to 100 mg per day. The drug must be taken three times a day. |
| Dramina | |||
| Dedalon |
Labyrinth operation
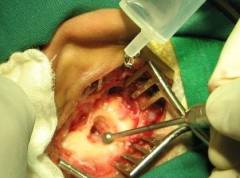 In some cases, surgical treatment is the only possible, since the effect of drug treatment is absent. Surgery is carried out only according to indications.
In some cases, surgical treatment is the only possible, since the effect of drug treatment is absent. Surgery is carried out only according to indications. The following important points concerning the operation at labyrinth should be mentioned:
- indications;
- method;
- anesthesia;
- hearing forecast;
- rehabilitation.
Indications
 An indication for the operation in labyrinth is a number of different pathologies and complications.
An indication for the operation in labyrinth is a number of different pathologies and complications. There are the following indications for surgery:
- irreversible hearing loss;
- purulent labyrinthitis;
- the combination of labyrinthitis with inflammation of other bone structures of the temporal bone;
- penetration of infection from the cavity of the inner ear to the brain.
Purulent labyrinthitiscaused by falling into the cavity of the inner ear staphylococci or streptococci. This form of labyrinthitis leads to a complete lesion of the organ of Corti. Further purulent inflammation of the inner ear can lead to necrotic labyrinthitis, which is manifested by the alternation of dead ( necrotic) plots of soft tissue and the bony part of the labyrinth, along with foci of purulent inflammation.
The combination of labyrinthitis with inflammation of other bone structures of the temporal bone.In some cases, the inflammatory process in addition to the labyrinth can affect the adjacent bone segments of the temporal bone. Inflammation of the mastoid process ( mastoiditis) or the top of the pyramid bone ( petrosite) is usually treated surgically ( operation to remove purulent foci).
Penetration of infection from the cavity of the inner ear to the brain.One of the complications of labyrinthitis is the spread of the inflammatory process along the acoustic nerve to the brain. In this case, meningitis, meningoencephalitis ( inflammation of the brain and membranes) or an abscess of the brain ( accumulation of pus in the brain).
Technique
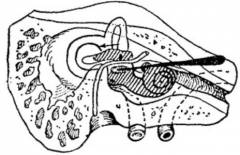 At the moment there are a large number of different techniques and variations on the surgical opening of the cavity of the inner ear. In each case, the surgeon ( otosurgeon) the most suitable technique is selected.
At the moment there are a large number of different techniques and variations on the surgical opening of the cavity of the inner ear. In each case, the surgeon ( otosurgeon) the most suitable technique is selected. To access the maze you can use the following techniques:
- Ginsberg way;
- Neumann's way.
Ginsberg way.Labyrinth open in the area of the cochlea and the vestibule from the side ( horizontal) semicircular canal. An autopsy is performed with a special surgical chisel in a place that corresponds to the main curl of the cochlea. It is necessary to precisely perform surgical manipulations, since if the chisel under the blow of the hammer jumps to the oval window, this will lead to damage to the facial nerve. Also located near the branch of the internal carotid artery, which can also be easily damaged. At the second stage, the horizontal semicircular canal is opened. Next, through this channel, a special spoon is used for scraping ( destructiona) the vestibule and snail moves.
Neumann's way.This method is more radical, since not one, but two semicircular canals are opened ( top and side). After these channels have been opened, the snail is scraped. This type of operation is much more complicated than the Ginsberg method, but allows for a better drainage of the maze ( outflow of pathological secretion from the cavity of the inner ear).
Anesthesia
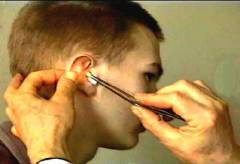 During surgery on the inner ear, as a rule, local anesthesia is used. 30 minutes before the start of the operation, 2 sandwiches are placed in the middle ear cavity and moistened in anesthetic medicines local action (3% solution dikaina or 5% solution of cocaine). General anesthesia is performed in rare cases. An indication is the increased pain sensitivity of the patient.
During surgery on the inner ear, as a rule, local anesthesia is used. 30 minutes before the start of the operation, 2 sandwiches are placed in the middle ear cavity and moistened in anesthetic medicines local action (3% solution dikaina or 5% solution of cocaine). General anesthesia is performed in rare cases. An indication is the increased pain sensitivity of the patient. Forecast hearing
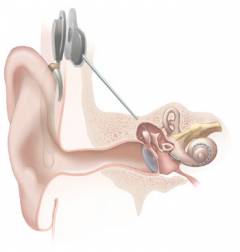 As a rule, an uncomplicated inflammatory process that occurs in a maze, which is promptly diagnosed and treated, does not lead to persistent hearing loss. Hearing loss can be observed with acoustic trauma of the ear, when the hair sensory cells of the organ of Corti undergo irreversible degenerative processes. Also, neurosensory hearing loss is observed with the defeat of the auditory nerve on the background of meningitis, tuberculosis or syphilis.
As a rule, an uncomplicated inflammatory process that occurs in a maze, which is promptly diagnosed and treated, does not lead to persistent hearing loss. Hearing loss can be observed with acoustic trauma of the ear, when the hair sensory cells of the organ of Corti undergo irreversible degenerative processes. Also, neurosensory hearing loss is observed with the defeat of the auditory nerve on the background of meningitis, tuberculosis or syphilis. A separate examination needs hearing aid. This method is effective in case of damage to the cochlea of the inner ear and is based on the installation in the human body of a special device that can convert sound signals into nervous ones. A cochlear implant is used as a prosthesis ( implant that performs the function of the cochlea), which consists of several parts. In the temporal bone, the implant body is implanted under the skin, which is able to perceive sound signals. A special electrode array is conducted into the snail ladder. Having received sound signals, a special processor in the implant body processes them and transmits them to the cochlea and then to the electrode array, in which the sound is transformed into electrical impulses recognized by the auditory area of the brain.
Rehabilitation
 The rehabilitation period after a maze operation, on average, ranges from 3 weeks to 3 months. Long recovery times are associated with slow recovery of the function of the vestibular apparatus. Also, the period of rehabilitation depends on the general condition of the patient and the associated diseases.
The rehabilitation period after a maze operation, on average, ranges from 3 weeks to 3 months. Long recovery times are associated with slow recovery of the function of the vestibular apparatus. Also, the period of rehabilitation depends on the general condition of the patient and the associated diseases. Rehabilitation after hearing aids can last for quite a long period of time. This is due to the fact that within a few months the adaptation process takes place, and the patient is taught to re-hear through this cochlear implant.
Labyrinthitis prevention
 Prevention of labyrinthitis is reduced to the timely and correct detection of inflammation of the middle ear ( otitis media
). Often it is otitis media in children that causes inflammation of the inner ear. It is also necessary to carry out a rehabilitation of the nose, mouth and nose of the pharynx.
Prevention of labyrinthitis is reduced to the timely and correct detection of inflammation of the middle ear ( otitis media
). Often it is otitis media in children that causes inflammation of the inner ear. It is also necessary to carry out a rehabilitation of the nose, mouth and nose of the pharynx. Sanitation is a method of healing the body. During the rehabilitation of the upper respiratory tract ( nasal cavities, nasal sinuses, pharynx, larynx, ears) there is the destruction of microorganisms that live there and can lead to various diseases with a decrease in immunity.
There are the following indications for the rehabilitation of the ENT organs:
- increase in body temperature above 37ºС;
- the appearance of pain in the nasal region or in the sinuses;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- deterioration of smell;
- painful sensationstickling or burning in the throat;
- increase in gland size ( tonsils) and the presence of films on them.
For rehabilitation use the following medicinal substances:
- furatsilin;
- chlorhexidine;
- chlorophyllipt;
- tomitsid.
Chlorhexidineis an antiseptic substance that neutralizes not only various bacteria, but also viruses and microscopic fungi. Chlorhexidine can be used in various dilutions ( 0.05 and 0.2% solution) for rinsing the mouth.
Chlorophylliptis an oil or alcohol solution that is effective against staphylococcus. In diseases of the nasal sinuses ( sinusitis) the drug is instilled 5-10 drops 3 times a day during the week.
Tomitsidis a drug that inhibits the growth of gram-positive microorganisms ( staphylococci, streptococci). For rinsing, you must use 10 to 15 ml of a pre-warmed thicicide solution 4 to 6 times a day. When rinsing the throat, contact with this drug should not exceed 5 minutes.
It should be noted that the rehabilitation should be used together with other methods of treatment of diseases of the upper respiratory tract ( antibiotic therapy). Surgical sanitation is resorted to only when drug therapy has no effect.
The inflammatory process in the tissues of the inner ear is called labyrinthitis or internal otitis. The disease usually develops when various pathogenic bacteria enter the inner ear.
The development of the inflammatory process in the inner ear can be caused by various factors.
The main causes of internal otitis:
- Average
- Bacterial or viral infections
- Injury
- Meningitis
- Infections such as syphilis, mumps, a virus or tuberculosis can cause labyrinthitis.
Usually, inflammation of the inner ear occurs against the background of infectious processes occurring in the body.
In most cases, labyrinthitis develops as a complication of otitis media.
When this disease accumulates purulent masses, thereby increasing the pressure in the tympanic cavity. As a result, the purulent process spreads from the inside.Injury of the ear can be obtained when injured by various sharp objects: knitting needles, hairpins, etc. The lesion of the inner ear can be associated with a head injury.
More information about the maze can be found in the video.
The cause of labyrinthitis can be meningitis. Infection from the meninges enters the inner ear and causes inflammation. For meningogenic labyrinthitis is characterized by bilateral lesion.Infection in the inner ear can spread through the bloodstream without being damaged by the meninges. This is observed in syphilis, parotiditis and other diseases.
Symptomatology
Depending on the speed with which the inflammatory process spreads, symptoms are manifested.
When inflammation of the middle ear can be observed the following symptoms:
- Dizziness
- Movement Coordination
- Hearing loss
- Noise and pain in the ears
With the development of internal otitis in a patient, involuntary oscillatory eye movements are observed.
Dizziness occurs due to lesions of the semicircular canals.
Such attacks are short and usually do not exceed 5 minutes. In some cases, dizziness may last for several hours.There may also be complaints of sweating, rapid heartbeat.If the labyrinthitis has passed into a purulent or necrotic stage, then the patient's hearing is completely lost from the side of the lesion.
Diagnostics
To diagnose inflammation of the inner ear, an otolaryngologist will prescribe a number of studies.The doctor will examine the auricle, and ear region external auditory canal using a special device - otoscope.
Other instrumental methods for the diagnosis of labyrinthitis:
- Audiometry. With the help of audiometry, it is possible to determine the auditory sensitivity and sharpness of hearing. The procedure is performed using an audiometer.
- Vestibulometry - allows you to identify the state of the vestibular apparatus.
- Electrosystagmography.Thanks to electronistagmography, nystagmus, which occurs when the inner ear is inflamed, is examined.
To clarify the diagnosis using high-informative methods: magnetic resonance and computed tomography, x-rays.In addition, the patient must pass a blood test and discharge from the ear. This will help determine the viral or bacterial nature.
Drug treatment

With conservative treatment, if the disease is caused bacterial infectionthen nominate.
The treatment scheme for each is chosen individually, depending on the cause and clinical manifestations of the disease:
- Oxacillin, Amoxicillin, Piperacillin are prescribed from the penicillins group; Erythromycin or Clarithromycin is used for treatment of the disease from macrolides.
- To improve blood supply in the inner ear, histamine preparations are prescribed: Alfaserk, Betahistin, etc.
- To reduce dizziness, nausea and vomiting, prescribe Diazolin, Suprastin, Dimedrol, etc.
- Also prescribed drugs that have antipyretic and analgesic effect: Diclofenac, Dicloran, Naklofen, etc.
- To normalize the trophic disorders in the cavity of the inner ear, take vitamins C, P, K, as well as drugs Cocarboxylase, Preductal.
If the treatment is started on time, then the prognosis is favorable. After therapy or surgery, vestibular functions and hearing are restored.In order to avoid re-development of the disease, it is necessary to promptly identify and treat diseases, infectious processes in the body. It is also important at the first sign not to delay a visit to the doctor.
Folk treatment
To reduce the symptoms, you can use the methods of alternative medicine.
- AT sore ear drip solution based on honey. In equal proportion to dissolve the honey in warm water and bury 2 drops in the ear. Instead of honey, you can use tincture.
- When maze can be done ear tampon. Take onions, squeeze the juice and mix with vegetable oil in equal amounts. Then soak the swab with the prepared solution and insert it into the sore ear overnight.
- Pretty effective remedy is an infusion of rhizome burnet. 2 tablespoons of rhizome pour 400 ml of hot water, put on water bath for half an hour and strain. Inside take a tablespoon 3 times a day.
- It is useful to wash the ear with a decoction of chamomile, lemon balm, strong tea from the flowers of wild rose.
Before you apply folk methods treatment, you need to consult a doctor. It is forbidden to self-medicate, as the flow can be aggravated.
It is forbidden to use a heating pad in the treatment of labyrinthitis - the heat generated by the heating pad may cause pus to spread to healthy areas.
Traditional methods will help get rid of the symptoms of the disease, but can not eliminate the true cause of the development of labyrinthitis. If you do not take action and do not consult a doctor, then the background of the disease is a high probability of development.
The labyrinthitis operation is indicated if the disease has passed into a purulent form and has arisen against the background acute otitis middle ear. Surgical treatment is carried out only according to indications, in severe cases, when there is no effect from drug treatment.
An otosurgeon performs an anthromastoidotomy, labyrintotomy or abdominal surgery, depending on the evidence. The main purpose of surgery is to remove a purulent focus from the cavity of the middle and inner ear. A few days before surgery, conservative therapy is prescribed.
Labyrintotomy is an operation that is performed when purulent inflammations, to eliminate pus and prevent infection in the cranial cavity. Antibiotics and dehydration therapy are prescribed to the patient after surgery. This takes into account the condition of the patient.
Antromastoidotomy is performed in case of complications of purulent internal otitis - mastoiditis.
During the operation, the mastoid process is opened and pus is removed.The operation uses local anesthesia. Half an hour before the start of the manipulation, two sandwiches are moistened in a solution of cocaine or dikain. The operation under general anesthesia is performed in rare cases.The recovery period after surgery can last up to 3 months.
Possible consequences

Against the background of labyrinthitis occur when the middle ear is inflamed to other organs. It develops in advanced cases and delayed treatment.
Purulent otitis media of the inner ear can lead to meningitis, cerebral thrombosis, brain abscess, sepsis. Also purulent otitis can cause the development of mastoiditis, petrositis, and in more serious cases, can lead to hearing loss.Complications are dangerous in both adults and children.
Labyrinthitis is an inflammatory process that is localized in the inner ear, in which nerve receptors are affected, which perceive sounds and regulate balance. Accordingly, the main symptoms of labyrinthitis are hearing loss and dizziness (cochleovestibular disorders).
Little anatomy
The ear is not only auriclewhich we see and can touch. The ear is the most complex apparatus, the organ of hearing and balance, whose function is the perception of sounds and signals of the position of the body in space, their conduction, transformation into nervous impulses, which later pass to the brain. The ear is divided into 3 parts:
- Outer ear (auricle and external auditory canal).
- Middle ear (drum cavity, in which there are 3 smallest bones of our body, conducting sound vibrations).
- Inner ear.
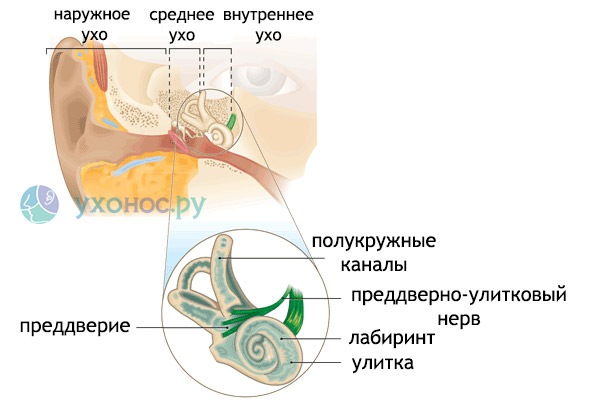
The inner ear is located in the thickness of the temporal bone. This is a system of intraosseous spaces communicating with each other. The following sections of the inner ear are distinguished: the cochlea, the vestibule, and 3 semicircular tubules. Because of its intricate form, this system is called the bone labyrinth. The diameter of the lumen of each channel - up to 0.5 mm. Inside the bone there is a webbed labyrinth. It is located in it receptors - sensitive cells that perceive signals from the external environment. In the cochlea there are sound-perceiving receptors, on the threshold and of the tubule - the structures of the vestibular apparatus, that is, the organ of balance.
Causes of Labyrinthitis
The main cause of labyrinthitis is infection. The penetration of the infection into the inner ear occurs in different ways. Accordingly, the paths of distribution distinguish labyrinthitis:
The course of labyrinthitis is acute and chronic, the prevalence of inflammation - limited and diffuse, the nature of the inflammatory exudate - serous, purulent or necrotizing.
The most common serous tympanogenic labyrinthitis. When the purulent membrane separates the middle ear from the inner, it becomes permeable to the inflammatory exudate - serous inflammation occurs in the inner ear. Sometimes, due to the accumulation of exudate, the pressure increases very much, which leads to rupture of the membrane, breakthrough of pus and then purulent labyrinthitis develops.
In chronic otitis media, the pathological process affects the bone labyrinth, with the formation of a fistula (fistula) in the semicircular canal, the infection from the bone wall passes to the internal structures of the labyrinth.
Symptoms of Labyrinthitis
Accordingly, the physiology of the inner ear also manifests the symptoms of its defeat. This is a hearing loss and dizziness. The severity and rapidity of increase of symptoms depend on the severity of the process and the nature of the inflammation.
In acute currents, a so-called labyrinth attack occurs: the hearing suddenly decreases or disappears, there is a sharp dizziness, the balance is disturbed. The slightest head movement worsens the condition, the patient is forced to lie motionless on his side on the side of the healthy ear.

Labyrinth dizziness is defined by the patient as an illusion of rotation of the surrounding objects or the rotation of the person himself. There may be nausea and vomiting. Such dizziness is called systemic. There is also non-systemic vertigo with lesions of the cortical (brain) parts of the vestibular analyzer. It manifests a sense of instability, falling through while walking.
The duration of a labyrinth attack is from several minutes to several hours, sometimes - days. During the purulent process, then the stage of inhibition of the affected labyrinth begins, and signs of asymmetry of the labyrinths appear, which are detected during normal neurological examination.
A sharp labyrinthitis can manifest itself in a single labyrinth attack. In the chronic course of the disease, bouts of dizziness periodically recur.
Other less specific symptoms of inner ear inflammation: , headache, sweating, palpitations. Perhaps a complication in the form of neuritis of the facial nerve, the trunk of which passes between the vestibule and the cochlea of the inner ear. Also, when the infection spreads to the mastoid process of the skull, mastoiditis can develop. And the most terrible complication of purulent labyrinthitis is meningitis, encephalitis or abscess of the brain.
Diagnosis of labyrinthitis
In the presence of typical complaints of paroxysmal systemic dizziness, hearing loss and an indication of 1-2 weeks before the disease, it is not difficult to suspect a diagnosis of labyrinthitis. With a limited process and a chronic course, clinical manifestations can be erased. Assist in the diagnosis of vestibular tests, the identification of latent nystagmus.
Nystagmus is the involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyeballs.. This is the main objective syndrome in the defeat of the maze (although there are many other causes of nystagmus). It is detected during a routine inspection or during a fistula test.

They also help in the diagnosis of labyrinthitis:
- Otoscopy (inspection of the ear canal and eardrum).
- Audiometry.
- Electrosystagmography.
- X-ray of the temporal bone.
- CT of the temporal bone.
Labyrinthitis Treatment
In cases of acutely developed labyrinthitis, emergency hospitalization is indicated. Such a patient must be provided with bed rest and complete rest.
Basic principles of conservative treatment of inner ear inflammation:
If labyrinthitis has arisen as a complication of purulent otitis media and there is no improvement from conservative treatment within 4-5 days, surgical treatment is indicated.  The purpose of the operation is the rehabilitation of a purulent focus in the tympanic cavity, a revision of its medial wall, which borders on inner ear. In the presence of a fistula of the semicircular canal - plastic its periosteum section. The operation is performed using a special operating microscope.
The purpose of the operation is the rehabilitation of a purulent focus in the tympanic cavity, a revision of its medial wall, which borders on inner ear. In the presence of a fistula of the semicircular canal - plastic its periosteum section. The operation is performed using a special operating microscope.
Emergency surgery is indicated in the presence of intracranial complications. And a very rarely performed operation in our time is a labyrintectomy. Conducted with purulent or necrotic labyrinth.
Outcomes of Labyrinthitis
Basically, the outcome of maze is favorable. All symptoms (hearing loss, bouts of dizziness) are reversible and stop rather quickly with the treatment started on time.
Only with purulent forms (which are, fortunately, extremely rare) can partial or complete irreversible hearing loss, which requires further hearing aid or cochlear implantation. The function of maintaining balance even after complete destruction of the maze is restored with time.
Prevention
The primary prevention of labyrinthitis is the timely treatment of otitis. Any earaches are the reason for immediate treatment to an ENT specialist. In turn, mv middle ear infection gets through auditory tube from the nasopharynx. Therefore, it is necessary to take more seriously the treatment of any cold.
Video: labyrinthitis in the program "Live healthy"
Popular
- Breast cancer is curable at any stage.
- The remedy for the cold Sinupret
- Azitrox - official instructions for use
- Chicken-bjaka: allowed antibiotics were found in Russian chicken
- Oral Cancer: Symptoms and Treatment
- Dark and thick blood during menstruation.
- Modern analogues of doxycycline tablets
- Is it possible to die from pneumonia
- What earwax will tell all about your health
- Tussin: instructions for use