Kills microbes in the throat. Treatment of viral diseases of the throat
Viral infection is one of the main causes of a sore throat. Viral diseases of the throat should be distinguished from bacterial, primarily streptococcal angina. The fact is that a viral infection of the throat is not treatable with antibiotics. How to understand that the cause of the disease of the throat is a viral infection?
Viral infections throats can have a lung and severe course, trouble for 3 days or 2 weeks, cause pain when swallowing, loss of voice, cough and other symptoms. Such a variety of clinical manifestations is due to the heterogeneity of viral infections that can cause.
In this article we will take a closer look at the types of viral diseases of the throat, especially their symptoms, diagnostics, and also tell you how to properly treat them.
What is a viral infection?
Viral diseases - a group of disorders associated with the introduction into the body of very small, and at the same time highly contagious (ie, infectious) infectious agents. Indeed, viruses are hundreds of times smaller in size than the smallest bacteria and fungi. Viruses can penetrate into human cells and take control of all molecular processes occurring inside it. As a result, the cell ceases to perform its inherent function, and is engaged only in what helps the virus to divide, i.e. make thousands of your copies.
Fortunately, most viruses can only penetrate a certain type of cell. For example, respiratory viruses only disrupt the cells of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract.
Within 3-7 days, the human immune system forms immunity against the virus in the form of specific antibodies. Due to this, respiratory viral infections bother a person for no longer than a week.
The danger is that during a viral disease, a large amount of sputum is formed on the mucous membrane. It is a good breeding ground for other infectious agents - bacteria. Bacterial complications of viral infections can have a severe course and serious consequences. That is why it is so important to treat viral diseases of the throat in time.
What are viral diseases of the throat?
So, according to the localization of infection, viral diseases of the throat are divided into:
- Tonsillitis - the defeat of the tonsils. Symptoms similar to: patient complains of acute pain when swallowing, decreased appetite, weakness. When inspecting the throat noticeably significant increase and redness of the tonsils. Their surface may be covered with a transparent or muddy mucous coating.
- Pharyngitis - the defeat of the pharynx. If a virus has penetrated the cells of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, a sore throat, worries, dryness are disturbed.
- Laryngitis is a disease in which an infection affects the larynx and vocal cords. As a result of inflammation of the vocal cords, the voice of the patient changes - it becomes rough, hoarse or barely audible. When laryngitis may bother superficial wet cough (it is sometimes called "barking").
Laryngitis, pharyngitis and tonsillitis can be part of the clinical picture of various diseases caused by the introduction of the respiratory tract into the mucosa. different types viruses.
It is known that throat diseases can be associated with infections such as:
Symptoms
Depending on the type of pathogen virus, the symptoms of throat diseases will vary. We offer to get acquainted with the table, which presents the main symptoms, features and prognosis of viral diseases affecting the pharynx, tonsils or larynx (see Table 1).
| Symptom / Infection | Influenza Virus | ARVI viruses | Coxsackie virus (herpangina) | Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epidemiology | Often there are epidemics in the autumn-winter period. | Outbreaks of infection occur during the cold season. Adults tolerate the disease more easily than children. | It occurs mainly in childhood. There may be local outbreaks in children's groups. | Most often, children and teenagers are ill. In the summer-autumn period there are flashes in children's groups. |
| Body temperature | High from the first day of illness (38-41 ° C). | It can be high, especially in children (37-39 ° C). more often it does not reach 38 ° C. | Sharply rises in the first disease to 38-39 ° C. | The body temperature is low-grade (about 37 ° C). |
| Throat condition | Redness and swelling of the soft palate, pharynx. | Catarrhal form of tonsillitis, pharyngitis or laryngitis. The mucous is swollen, reddened. Mucus or mucopurulent plaque. | In the first days - swelling and redness of the pharynx, soft palate, tonsils. Next on the mucous are bursting sores. | Catarrhal tonsillitis - tonsils are enlarged, reddened, covered with a transparent or turbid coating. |
| Sore throat | Moderate. | Sore throat is usually mild, but can be severe. | Constant, aggravated by swallowing food. | Sore throat moderate. |
| Basic Symptomes | Symptoms of intoxication - headache, weakness, aches in muscles and joints. | Redness and sore throat, sneezing, runny nose. | Sores in the mouth, sore throat. | Edema swelling, coughing, increase and tenderness lymph nodes throughout the body. |
| Related symptoms | In addition to sore throat - cough, sometimes - a violation of digestion. Runny nose - rarely. | Weakness, drowsiness. conjunctivitis may occur (with adenovirus infection). | Poor appetite, indigestion, abdominal pain. | Severe fatigue for 2 weeks or more. Sometimes there is a red rash on the palate and then on the skin of the body. |
| Forecast | Deadly disease. When taking anti-flu drugs, the disease retreats within a week. | Orvi responds well to treatment. With improper treatment may be complicated by bacterial infections. | The disease is difficult, but has a favorable prognosis. Within a week, the patient forms immunity to the virus. | Complications are rare, mainly with improper treatment (taking antibiotics, aspirin). |
Table 1 Viral infections that can cause throat diseases.
 As we already know, the throat can ache for various reasons. Depending on what kind of viral throat disease occurs, appropriate therapy is selected.
As we already know, the throat can ache for various reasons. Depending on what kind of viral throat disease occurs, appropriate therapy is selected.
Thus, the treatment of the throat should begin from the exact determination of the causes of the disease, i.e. making a diagnosis.
It is worth noting that the symptoms of streptococcal angina are in many ways similar to viral tonsillitis.
It is very difficult to say exactly which infection develops in the throat, based only on pharyngoscopy data. That is why the doctor who examined the patient, can send him to pass the refinement tests. First of all, such analyzes as a general clinical blood test and bacteriological seeding of a pharyngeal swab are resorted to. These two tests are enough to find out what kind of infection the patient develops (fungal, viral or bacterial), how severe the inflammation is, whether there is streptococcus in the pharynx, whether there is any reason to believe that the patient develops mononucleosis, etc.
In many cases, testing is not required. If the patient has all the symptoms of ARVI (runny nose, sore throat, sneezing), treatment is started immediately.
Additional tests may be required if the patient has a deterioration of health, or the disease does not go away within 7 days. In this case, the attending physician may suspect the development of bacterial infection against a viral background.
Treatment
Treating viral infections in the throat is similar to treating a cold.
If a patient develops flu symptoms - heat body, sore throat, cough, aching muscles and joints, you must call a doctor. Treatment of influenza is based on taking antiviral drugs.
With SARS, antivirals are not always used. They affect the course of the disease only if treatment is started on the first or second day of the disease. With herpangina and infectious mononucleosis, antiviral drugs are ineffective.
The human body rather quickly, within 3-5 days, produces antibodies to the virus, and from that moment the patient is recovering. Thus, the main thing is to support the body during the acute period (in the first 3 days of the disease). The acute period is the most dangerous; it is at this time that the patient may have a fever, strong pain throat sneezing, runny nose, indigestion. In the acute period, body temperature should be controlled and dehydration should be controlled. Symptomatic medication plays a secondary role. local action. It is very important to adhere to bed rest during the acute period, as the body spends a lot of energy on fighting the virus.
Thus, in the acute period of the disease the following treatments can be used:
- antiviral drugs;
- antipyretic drugs (when the temperature rises to 38.5 ° C and more);
- drink plenty of water (give preference to warm herbal teas, mineral water);
- sleep and rest;
- food light fortified food, should not overeat;
- local treatment - instillation of the nose, gargling, tonsil irrigation drugs etc.;
- when laryngitis should be as little as possible to talk, including a whisper.
Starting from 3-4 days the patient's condition should improve significantly. Common symptoms, such as headache and fever, recede into the background and gradually disappear; only local symptoms remain - pain when swallowing, runny nose, cough. During this period, the main task of treatment is to clear the respiratory tract from mucus and prevent the development of bacterial complications. For this purpose, the following procedures are recommended:
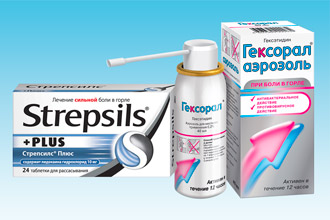
- gargling with saline water or soda solution;
- rinsing with decoctions of medicinal plants (if you are sure that you are not allergic);
- irrigation of the throat with antiseptic preparations in the form of a spray (any antiseptic will be suitable for treating the tonsils and pharynx - Ingalipt, Hepilor, Hexoral);
- the resorption of medicinal candies (Strepsils, Faringosept, Lizobact) - not only has an antiseptic effect, but also reduces pain;
- plentiful drink continues to be relevant, you can enter the usual dishes in the diet.
Viral diseases such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis and laryngitis respond well to treatment and have a favorable prognosis. If a home treatment does not have an effect during the week, consult your doctor. Perhaps the treatment regimen will have to be revised.
About antiviral drugs
Influencing the course of a viral infection is not as easy as it may seem. Many viruses have not yet developed drugs, the effectiveness of which would be confirmed by research.
For example, the Epstein-Barr virus and the Coxsackie virus are practically unaffected by any antiviral drugs. Best medicine against these viruses - antibodies produced by the patient’s own immune system.
Thus, the treatment of mononucleosis and herpangina mainly symptomatic (rest, antiseptic treatment of the throat, excessive drinking, etc.).
However, there are drugs that are effective against certain viruses, for example, the influenza virus. Since it is the flu that poses a serious threat to a person’s life, his treatment should begin with an antiviral drug.
Drugs that are actively used in the treatment of influenza can be divided into 3 groups:
- Substances that violate the reproduction of the virus by blocking the enzyme neuramidase (drugs such as Zanamivir, Oseltamivir).
- Drugs that affect the metabolism of the M2 protein, necessary for the division of the virus (Amantadin, Rimantadine).
- Means stimulating the production of its own antiviral substance - interferon (drugs Arbidol, Amixin, Groprinosin, Cycloferon).
Antiviral drugs, like any other medication, may have contraindications and side effectstherefore, before applying them, you must carefully read the instructions and consult with a specialist.
Our immune system is daily exposed to infection. It surrounds us everywhere, constantly attacking the body. Due to the persistence of immunity, a person is able to resist pathogens, as a result of which the disease does not develop.
Throat infections in otolaryngology are quite common, because in the oropharynx are the tonsils - the first defensive formations that take an attack on themselves.
Tonsils are lymphoid accumulations in which infection is controlled. In normal tonsils can increase, indicating an acute course of infectious diseases. However, after the death of microbes, they return to their previous size.
Mostly from infectious diseases Children suffer from throats, as their immune system is not so strong, and they are much more likely to come into contact with their peers.
This is associated with an increase in glands and the development of adenoids in children, because the tonsils with frequent attacks of pathogens or the presence of chronic infections hypertrophy, disrupting breathing through the nose.
Often it is the hypertrophied lymphoid formations that become the source of chronic infection in the oropharynx.
When an infection in the throat is suspected, the symptoms depend on the type of pathogenic microorganisms whose reproduction has led to the development of the disease. These can be bacteria, fungi, and viruses. They affect the mucous membrane of the throat, causing inflammation and the appearance of clinical signs.
Bacterial infection
Infectious diseases of the throat, caused by bacteria, have more severe symptoms than viral pathology. Most often, the disease develops as a result of the activation of staphylococci, streptococci, hemophilus bacilli, or pneumococci.
Streptococci normally live in the human body without causing the development of diseases. However, with a decrease in immune protection during hypothermia, exacerbation of chronic pathology or allergy, conditionally pathogenic flora is activated and begins to multiply.
Pathogens can cause scarlet fever, rubella, measles, whooping cough, sore throat, or erysipelas. If not treated in time, such complications appear as:
- otitis media (with affection of the middle ear department);
- sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses);
- (as complications of advanced angina);
- bronchitis, pneumonia;
- lymphadenitis;
- endocarditis, myocarditis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- polyarthritis;
- meningitis;
- sepsis;
- osteomyelitis.
Complications of the disease develop if throat infections turn into a generalized form. Pathogens spread with blood flow, forming infectious foci in the internal organs. The excreted toxins affect the heart muscle, the kidney tissue, the articular structures, the blood cells and the skin.
Streptococcus is transmitted through the air, through everyday objects, dirty hands and when coughing from a sick person. Bacterial disease of the throat is often manifested by angina, which is characterized by:
- febrile hyperthermia;
- severe pain when swallowing;
- tonsil raids;
- suppurating follicles in the tonsils;
- purulent discharge in lacunae;
- malaise;
- loss of appetite.
With the development of complications may appear:
- earache, hearing loss as a sign of otitis;
- heaviness behind the sternum, disruption of the heart - with myocarditis, endocarditis;
- joint pain, limiting their mobility - with polyarthritis;
- pain in the lumbar area, with urination - with kidney damage;
- neck pain, pus or spilled cavity formation purulent inflammation - with abscesses, phlegmon.
Infection in the throat is diagnosed using a pharyngeal smear test. Under the microscope or by bacteriological analysis, the type of pathogenic microorganisms and their resistance to antibacterial drugs is established.
Staphylococcus has several species (golden, epidermal, and saprophytic). It belongs to the conditionally pathogenic flora of the body, which only under certain conditions leads to the development of the disease. Infection occurs from a sick person through air, dust or household items.
The pathogen can cause sore throat, tonsillitis, skin pathology (furunculosis, pyoderma), inflammation of the bronchopulmonary system, intestines, brain abscess, sepsis or affect internal organs, forming infectious foci in them.
Symptoms include pain in the throat when swallowing, fever, cough and symptoms of intoxication.
For the diagnosis, it is enough to carry out an ELISA, examine the swabs of the pharynx and perform backwater, during which the culture of staphylococci grows.
Fungal diseases
Fungal infection of the throat often leads to the development of pharyngomycosis. It refers to chronic pathology, as it is difficult to treat. Fungi can also cause rhinomycosis, otomycosis or laryngomycosis.
In most cases, Candida fungi are the cause of the disease, but mold damage is not excluded. Some types of fungi belong to the conditionally pathogenic flora, so they may normally be present on the mucous membranes.
Long-term antibiotic therapy, dental caries, chronic and pharynx, diabetes and a temporary decrease in immunity after hypothermia or exacerbation of a chronic disease can be triggers for their activation.
Fungal infections in the throat are manifested:
- cheesy plaque on the mucosa of the oropharynx;
- dry mouth;
- burning sensation.
In the diagnosis used microscopic examination.
Viral pathology
Infectious lesions of the throat can be caused by viral pathogens. When a virus enters the body, its reproduction begins, and typical symptoms appear:
- nasal congestion, rhinorrhea;
- body aches;
- fever (less persistent compared to bacterial diseases);
- sore throat;
- lacrimation;
- sneezing;
- malaise.
Pathogens are transmitted through the air, when sneezing or kissing. It is possible infection through household objects.
Significantly increases the likelihood of infection with viruses in closed, poorly ventilated areas when in contact with a sick person.
To distinguish bacterial disease from viral, it is enough to conduct a study of smears from the throat or nose.
Separately, I want to say about herpes infection, often diagnosed in children. It causes stomatitis or sore throat. In adults, the infection is manifested by rashes on the lips, nose, or eyes.
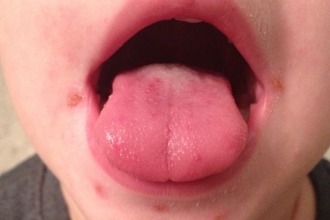 Symptoms develop after the activation of the herpes virus of the first type during the initial infection or its exacerbation against the background of reduced immunity. Children have:
Symptoms develop after the activation of the herpes virus of the first type during the initial infection or its exacerbation against the background of reduced immunity. Children have:
- muscle pain;
- low-grade fever;
- sore throat, ears, or eyes;
A child’s weak immune system defeats a viral infection after 10–14 days, while bacterial illnesses may bother with residual manifestations (coughing, some nasal voices) for another week.
Treatment of infection
When an infection in the throat is confirmed, the treatment is prescribed based on the type of pathogen. With bacterial disease the bacterial material taken from the oropharynx is carried out, which makes it possible to determine the resistance of the pathogen to antibacterial agents. Considering the results of the antibiotic, antibiotics are prescribed:
- penicillin series - Augmentin, Flemoklav, Amoxicillin;
- cephalosporin group - Cefepim, Cefuroxime, Cefataxim;
- macrolides - Sumamed, Azitroks, Klacid.
Antibacterial drugs are used in pill form, in powder form - for intramuscular administration or solution - for intravenous. The choice is made exclusively by the doctor based on the severity of the disease.
In the case of a viral disease, antibiotics should not be taken, as many of us do, as soon as we see 38 degrees on the thermometer. Firstly, antibacterial agents are not effective in viral infection, and secondly, while indulging in antibiotics, resistance to them can be developed.
As a result, in the more severe case of a bacterial disease, they will not have a detrimental effect on bacteria.
In case of viral pathology of the throat, treatment should include taking antiviral drugs (Tsitovir-3, Remantadin, Amiksin, Arbidol, Aflubin). Some antiviral medications have an immunomodulatory effect, which is also necessary in case of illness. Fluconazole, Intraconazole or Pimafucin are prescribed for fungal infections of the mucous membranes. The duration of the course is determined by the doctor based on the results of the examination.
Local therapeutic effects are provided by:
- solutions for rinsing the oropharynx - Miramistin, Furacilin, Chlorhexidine;
- spray for irrigation of the throat and tonsils - Bioparox, Givalex, Kameton, Ingalipt, Chlorophyllipt, Tantum Verde;
- lozenges - Falimint, Faringosept, Dekatilen, Strepsils.
In addition, for therapeutic purposes, you can use decoctions of herbs (chamomile, oak bark, sage) for the preparation of solutions for rinsing or inhalation. Do not forget about vitamin therapy, regular ventilation, wet cleaning in the room, good nutrition and enhanced drinking regime.
The infection of the throat is very common, therefore, it is necessary to immediately begin treating the disease, avoiding the chronicity of the infectious-inflammatory process. It is especially important for parents to completely cure the child in order to avoid surgery to remove the tonsils or adenoids in the child.
Throat diseases are often diagnosed rather late, because their symptoms initially resemble colds and are ignored by patients.
In some cases, common symptoms such as hoarseness and sore throat can be signs of other illnesses. Often viruses, bacteria, or infections cause the disease.
The throat due to its location, structure and functions is an ideal place for the development of microbes. Located immediately after the nose, it is the first line of defense with microbes that fall outside.
In most cases, microorganisms do not enter the body, however, when their attack is the most effective and massive, they penetrate into the tissues of the mucous membranes, multiply and destroy epithelial cells, which leads to various diseases.
Diseases of the throat include various benign and malignant tumors, contact ulcers, granulomas, laryngitis, ligamentous paralysis, polyps and nodules, as well as croup and cancer.
Most disorders cause dysphonia, which is characterized by loss of voice. Although it changes with age, becoming more hoarse and aperiodic, sharp and visible changes should not be left without examination. Throat diseases in children are often associated with ENT infections and are characterized by symptoms such as pain, dry mouth, sensitivity to hot or cold foods, or drinks.
What are the diseases of the throat and larynx? They are quite different and depend on the cause and pathogens:
- throat diseases without fever;
- viral diseases;
- chronic diseases;
- infectious diseases.
Symptoms of diseases of the throat and larynx
Signs of throat disorders are dependent on the causative agent.
- Viral diseases of the throat
The most common cause of diseases that produce two types of viruses is adenovirus and enterovirus. Viral infections attack most often in the autumn-winter period and in early spring, especially when the immune system is weakened. They develop as a result of penetration into the body along with inhaled air. Viruses are small organisms that easily pass through biological filters, immediately after which they attack the mucous membrane that covers the upper respiratory tract.
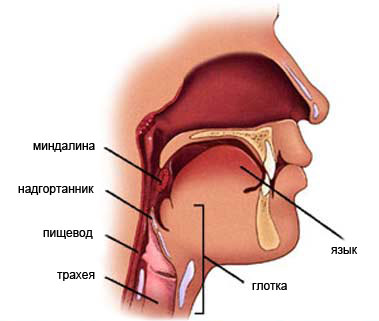
There are several diseases that are caused by a viral infection:
- Pharyngitis.
It usually occurs with other diseases such as the flu, the common cold, measles, chicken pox. The area of its distribution includes the mucous membrane of the throat. Before the onset of the disease, runny nose and cold symptoms appear. The main symptom is swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, which leads to sore throat and difficulty in swallowing. Treatment of pharyngitis depends on the etiological agent. If a sore throat is caused by viruses, then measures are taken to minimize the symptoms, painkillers and anti-inflammatories are prescribed to the patient.
- Acute laryngitis.
Usually caused by viruses, rarely bacteria, often accompanied by infections of the upper respiratory tract. Inflammatory changes may include the defeat of the vocal cords and other parts of the larynx. Symptoms are hoarseness, a sense of presence. foreign body throat, nasal congestion, cough, fever body. The treatment consists of retaining the voice, humidifying the air, inhaling and consuming enough liquid, painkillers and syrups.
- Throat infections
Bacterial infections usually cause streptococci and less commonly other bacteria, such as staphylococcus. These infections most often occur during winter or early spring, but it often happens that bacteria attack an organism already weakened by viruses. In adults, such diseases rarely occur, and children and adolescents between the ages of 5 and 15 are more likely to get sick. Bacterial sore throat and tonsillitis are a highly contagious disease.
Symptoms of infectious diseases are more severe and usually appear without prior warning. It may be:

In case of infection, antibiotic penicillin and second-generation cephalosporin are prescribed.
- Chronic throat diseases
- Chronic laryngitis.
The disease can occur with repeated inflammation of the larynx, abuse of the voice, for example, among teachers, excessive drinking of alcohol, and also being in polluted or overheated air. The risk increases when several factors coincide.
As a result of irritation, the larynx comes to changes in vocal cords - hyperplasia (thickening) or endometrial atrophy. If you ignore the problem, chronic laryngitis sometimes leads to precancerous lesions.
In the initial stage, the disease can be seen on the Internet with a photo, and the symptoms appear in the form of hoarseness, which increases with speaking, dry cough, burning sensation in the larynx, and sometimes loss of voice.
Treatment primarily consists of changing lifestyles and getting rid of bad habits, such as smoking, consuming expectorants, preventing dry larynx.
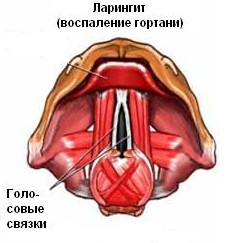 You should gargle with a mixture of vitamins A and E or a decoction of chamomile and sage. Good results are given by inhalation with soda or with the addition of essential oils (for example, eucalyptus or pine), as well as recovery in mountainous areas or by the sea.
You should gargle with a mixture of vitamins A and E or a decoction of chamomile and sage. Good results are given by inhalation with soda or with the addition of essential oils (for example, eucalyptus or pine), as well as recovery in mountainous areas or by the sea. - Throat disease without fever
- Throat swelling.
As a rule, it develops in the presence of an allergic contact reaction, and can also be the result of injury or inflammation of the larynx.
- Polyps of the larynx.
The most common benign laryngeal nodules. It is usually the result of voice overvoltage and smoking.
They are small growths that appear in the vocal cords. They are formed as a result of chronic inflammation, most often due to voice overload - with singers, teachers, speakers.
- Papillomas.
Most often occur due to viruses, appear on the vocal cords, but can also cover the trachea.
- Cancer of the larynx.
Mainly affects men aged 55-65 years, especially smokers. The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chance of successful treatment.
The disease begins with a gradual increase in hoarseness, the timbre of the voice changes over time, the patient begins to feel obstruction in the throat, pain when swallowing, in the later stages shortness of breath, coughing, hemoptysis, and an increase in the lymph nodes in the neck appear. The type of treatment depends on the location and severity of the disease. The doctor may use radiation or surgery.
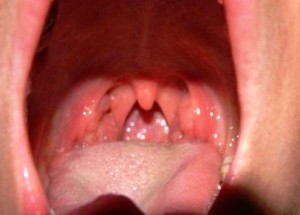 The most common diseases of the throat in children:
The most common diseases of the throat in children:
- angina;
- tonsillitis;
- pharyngitis;
- laryngitis.
Sometimes the symptoms are not associated with diseases of the larynx:
- Pain and burning in the throat, a sensation that seems to prevent swallowing, can be caused by gastroesophageal reflux. The content of the stomach enters the upper part of the esophagus and throat, irritating the mucous membranes of the larynx, which is the cause of this disease - in this case it is necessary to contact a gastroenterologist.
- Hoarseness, coughing, or sudden loss of voice can be the result of severe stress or neurological disorders — sometimes a neuropathologist will require help or.
- Deposition of the voice or hoarseness is also sometimes caused by hormonal disorders, for example, the work of the thyroid gland, estrogen deficiency in women after menopause - in this case it is necessary to consult with an endocrinologist or gynecologist.
Fungal diseases of the throat - symptoms and treatment
Fungal infections of the throat are quite similar to lore - diseases. The conditions for their development is a decrease in the resistance of the organism to various microorganisms. They can be acute or chronic, characterized by sore throat and redness of the tonsils.
Fungal diseases are most often caused by different species fungi - Candida. Most often accompanied by all types of fungal diseases of the oral cavity, namely:
- Pseudomembranous candidiasis - mainly children and the elderly are ill.
- Candidiasis is most common in diabetic patients and patients taking antibiotics.
- Erythematous chronic itching.
Symptoms of the disease are sore throat, fever, weakness, fatigue, dry cough, lack of appetite, an increase in the neck and submandibular lymph nodes and their soreness.

Treatment relies mainly on maintaining good oral hygiene and rinsing. oral cavity antifungal agents. Such drugs have antiseptic, disinfectant and fungicidal properties, and contain chlorhexidine. Often, doctors are attributed to individual oral antifungal and antibacterial drugs.
Treatment of diseases of the throat and larynx
Regardless of the cause of the disease, it is first necessary to alleviate the symptoms that will help stop the spread of the infection. To reduce fever use antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs. You can rinse your throat with a solution of salt or baking soda, as well as use disinfecting aerosols.
At the first signs of illness, it is necessary to consult a doctor, because some diseases will cure only antibiotics (for example, angina or bacterial pharyngitis). This is especially true of the younger age group, because children often have quite serious complications that can result in deafness.
Along with the prescription of a doctor in the fight against infections, treatment should not be neglected. folk remedies. It includes an abundant warm drink, the use of natural vitamin C, often ventilate the room and avoid infections of the upper respiratory tract, because they precede diseases of the throat.
Diseases of the larynx, as a rule, have common symptoms. This includes dry mouth, a change in voice, difficulty swallowing, and finally a sore throat and hoarseness. However, not all the blame for all are signs of a cold, in some cases, such manifestations may have a completely different background.
Therefore, when the first alarming symptom you must immediately consult a doctor to determine the cause of the disease.
Popular
- Breast cancer is curable at any stage.
- The remedy for the cold Sinupret
- Azitrox - official instructions for use
- Chicken-bjaka: allowed antibiotics were found in Russian chicken
- Oral Cancer: Symptoms and Treatment
- Dark and thick blood during menstruation.
- Modern analogues of doxycycline tablets
- Is it possible to die from pneumonia
- What earwax will tell all about your health
- Tussin: instructions for use