The use of semi-synthetic penicillins. Penicillin antibiotics, penicillin use.
Today, no medical institution can do without antibiotics. Successful treatment of various diseases is possible only through the appointment of effective antibiotic therapy. The antibiotic today is represented by a wide range of various drugs aimed at the death of a pathogenic bacterial environment.
The first antibiotic created was penicillin, which defeated some epidemics and fatal diseases in the 20th century. To date, antibiotics penicillin group rarely used in medical practice due to the high sensitivity of patients and the risk of allergies.
Antibacterial therapy without the use of penicillin components involves the appointment of alternative drugs of other pharmacological groups. Antibiotics without penicillin in a large assortment are available for the treatment of various diseases in hospital and outpatient practice in children or adults.
Cephalosporins group
Cephalosporins are antibiotics. wide spectrum effects, which is caused by adverse effects on many groups of microorganisms, strains and other pathogenic environments. Cephalosporin group drugs are available as intramuscular or intravenous injections. Antibiotics of this group are prescribed in the following conditions:
Known cephalosporins include Ceforal, Supraks, Pancef. All antibiotics of this series have similar side effects, for example, dyspepsia (stool disorder, skin rash, nausea). The main advantage of antibiotics is not only a detrimental effect on many strains, but also the possibility of treating children (including the neonatal period). Cephalosporin antibiotics are classified into the following groups:
I generation
Cefaloxorine antibiotics include Cefadroxil and Cefalexin, Cefazolin, Cefuroxime.
They are used in inflammatory diseases caused by many anaerobic bacteria, staphylococcal infection, streptococci and others.
Forms of release of the drug are diverse: from tablets to solutions for parenteral administration.
2nd generation
Known drugs of this group: Cefuroxime (injection), Cefaclor, Cefuroxime Axetil. Drugs are particularly active against many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Preparations are available both in the form of solutions and in tablet form.
III generation
 Antibiotics of this series are just related to a wide spectrum of action. The drugs affect almost all microorganisms and are known by the following names:
Antibiotics of this series are just related to a wide spectrum of action. The drugs affect almost all microorganisms and are known by the following names:
- Ceftriaxone;
- Ceftazidime;
- Cefoperazone;
- Cefixime and Ceftibuten.
Forms of release - injections for intravenous or intramuscular administration. With the introduction of the drug is often mixed with saline or lidocaine solution to reduce pain. The drug and additional components are mixed in one syringe.
IV generation
The group is represented by only one drug - Cefepim. The pharmacological industry produces the drug in powder form, which is diluted just prior to administration via the parenteral or intramuscular route.
The destructive effect of the antibiotic is a violation of the synthesis of the body wall of the microbial unit at the cellular level. The main advantages include the possibility of treatment on an outpatient basis, ease of use, use in children early age, minimal risk of side effects and complications.
Macrolide group
 Macrolide antibiotics are a new generation of drugs, the structure of which is a full macrocyclic lactone ring. According to the type of molecular-atomic structure, this group received such a name. Several types of macrolides are distinguished from the number of carbon atoms in the molecular composition:
Macrolide antibiotics are a new generation of drugs, the structure of which is a full macrocyclic lactone ring. According to the type of molecular-atomic structure, this group received such a name. Several types of macrolides are distinguished from the number of carbon atoms in the molecular composition:
- 14, 15 members;
- 15-member.
Macrolides are particularly active against many gram-positive coccal bacteria, as well as to pathogens acting at the cellular level (for example, mycoplasmas, legionelles, campylobacter). Macrolides have the lowest toxicity, suitable for the treatment of inflammatory diseases ENT organs (sinusitis, whooping cough, otitis of various classifications). The list of macrolide drugs is as follows:
Numerous medical studies have confirmed a small chance of side effects. The main disadvantage is the rapid development of resistance of various groups of microorganisms, which explains the lack of therapeutic results in some patients.
Fluoroquinolone group
Fluorquinol antibiotics do not contain penicillin and its constituents, but are used to treat the most acute and severe inflammatory diseases.
These include purulent bilateral otitis, severe bilateral pneumonia, pyelonephritis (including chronic forms), salmonellosis, cystitis, dysentery, and others.
To fluoroquinol include the following drugs:
- Ofloxacin;
- Levofloxacin;
- Ciprofloxacin.
The very first development of this group of antibiotics belong to the XX century. The most famous fluoroquinols can belong to different generations and solve individual clinical problems.
I generation
Known drugs from this group are Negram and Nevigremon. The basis of antibiotics is nalidixic acid. Preparations detrimentally affect the following types of bacteria: 
- proteas and Klebsiella;
- shigella and salmonella.
For antibiotics of this group is characterized by strong permeability, a sufficient amount of negative effects of admission. According to the results of clinical and laboratory research, the antibiotic confirmed the absolute uselessness in the treatment of gram-positive cocci, some anaerobic microorganisms, Pseudomonas bacillus (including nosocomial type).
2nd generation
Second generation antibiotics are derived from a combination of chlorine atoms and quinoline molecules. Hence the name - a group of fluoroquinolones. The list of antibiotics of this group is represented by the following drugs:

Second-generation antibiotics are prescribed for serious surgical situations and are used in patients of any age group. Here the main factor is risk deathand not the appearance of any side effects.
III, IV generation
Levofloxacin (otherwise, Tavanic), used for chronic bronchitis, severe bronchial obstruction in other pathologies, anthrax, and diseases of the upper respiratory tract, should be attributed to the main pharmacological drugs of the 3rd generation.
![]() Moxifloxacin (pharmacol. Avelox), known for its inhibitory effect on staphylococcal microorganisms, is reasonably attributed to the 4th generation. Avelox is the only drug that is effective against non-spore-forming anaerobic microorganisms.
Moxifloxacin (pharmacol. Avelox), known for its inhibitory effect on staphylococcal microorganisms, is reasonably attributed to the 4th generation. Avelox is the only drug that is effective against non-spore-forming anaerobic microorganisms.
Antibiotics of various groups have special indications, indications, and also, contraindications to use. In connection with the uncontrolled use of antibiotics without penicillin and others, a law was passed on prescription drugs from pharmacy chains.
Such an introduction is very necessary medicine because of the resistance of many pathogenic environments to modern antibiotics. Penicillins are not widely used in medical practice for more than 25 years, so it can be assumed that this group of drugs will effectively affect new types of bacterial microflora.
Penicillins - The oldest group of antibiotics. Some types of penicillins have lost their relevance in infectious therapy, since the bacteria have developed resistance to them, but their important advantages over other antibiotic groups induces the scientists to search for new modifications of penicillins and actively apply them.
If we talk about the benefits, then their low toxicity, wide spectrum of action, and high antibacterial activity are important. Side effects, as a rule, appear much less frequently than when treated with other drugs. Most of the side effects occur allergic reactions, dysbacteriosis, occasionally inflammatory reaction at the injection site. They are not recommended for people with hypersensitivity to other antibiotics, with a tendency to allergies, patients bronchial asthma, urticaria and other allergies. Many penicillins can only be used as an injection, as they are destroyed in the acidic environment of the stomach. This applies particularly to biosynthetic drugs (obtained by biosynthesis), with the exception of phenoxypenicillin - it is acid resistant, it is used orally in the form of tablets.
Penicillins are not advisable to combine with other drugs, especially antibiotics, especially bacteriostatic. Penicillins are prescribed mainly for infections caused by gram-positive bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci), spirochetes. They are not prescribed because of low efficacy in viral, fungal diseases, tuberculosis, amebiasis. Broad-spectrum penicillins are often prescribed for mixed infections.
Obtained by biosynthesis:
Benzylpenicillin salts
For injection, destroyed in the acidic environment of the stomach. Available in powder form in vials, dissolve just before the introduction, because their solutions are very unstable. Usually injected intramuscularly, less often under the skin. Quickly destroyed, you often have to enter to maintain the desired concentration in the blood. The course of treatment is at least 5-7 days. If there is no positive effect for 3-5 days, replace it with another antibiotic or combine it.
- Benzylpenicillin sodium salt powder for solution for injection (for serious diseases, sometimes administered intravenously drip)
- Benzylpenicillin potassium salt powder for solution for injection (not injected intravenously)
- Procaine Penicillin G3 mega powder for solution for injection ("Biochemie", Austria)
Salts slowly dissolve, so-called "depot" medication, because the therapeutic concentration in the blood is maintained for a long time (up to 4 weeks). Introduced only intramuscularly. Often used to treat syphilis and rheumatism and its relapses.
Benzathine Benzylpenicillin
- Bicillin-3 powder for solution for injection
- Bicillin-5 powder for solution for injection
- Retarpen powder for solution for injection ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Extensillin powder for solution for injection ("RhonePoulencRorer")
Acid-resistant, apply inside
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin tab.250mg №30 taken for 30 minutes. - 1 hour before meals 4-6 times a day
Import analogue - smallpox. Produced in the form of granules for the preparation of suspensions and in the form of tablets. There is evidence that smallpox can weaken the effect of hormonal contraceptives. Excretion of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - indomethacin, salicylates) worsens. Usually taken 3 times a day, regardless of the meal. Often used in pediatrics.
- Osp-400 granules for the preparation of suspensions for oral administration ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Osp-750 granules for the preparation of suspensions for oral administration ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Ospin tab. 1g №10 ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Ospin tab. 250mg №20 ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Ospin tab. 500mg # 10 ("Biochemie", Austria)
Semisynthetic (chemically modified biosynthetic penicillins) Broad spectrum of action
Ampicillin salts
It acts on gram-negative (like benzylpenicillin) and some gram-positive bacteria, therefore they are considered to be a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Gram-positive bacteria act weaker than benzylpenicillin, but stronger than oxacillin. Usually well tolerated. It is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract slowly.
Apply inside, regardless of the meal 4-6 times a day. Enhances the action of oral anticoagulants.
- Ampicillin trihydrate tab. 250mg №20
- Ampicillin trihydrate tab. 250mg №24
- Ampicillin sodium salt powder for solution for injection
Penicillinase Resistant
Oxacillin
Oxacillin is prescribed for the same diseases as benzylpenlin, if the bacteria produce penillillinase, an enzyme that destroys penicillins. In addition, it is acid-resistant, because it can be used inside. Quickly excreted by the kidneys, it is necessary to apply often (every 4-6 hours). 1 hour before meals or 2-3 hours after meals. The course of treatment usually lasts 7-10 days.
- Oxacillin sodium salt tab. 250mg №10
- Oxacillin sodium salt tab. 250mg №20
- Oxacillin sodium salt tab. 500mg №20
If inside penicillin there is no possibility to take (for example, if there are some diseases digestive systemor a patient has diarrhea, vomiting, or if ill small child), then prescribed in the form of injections (intramuscularly, intravenously).
- Oxacillin sodium salt powder for solution for injection 500mg
Combined drug contains oxacillin sodium salt and ampicillin trihydrate. Combines the range of action of oxacillin and ampicillin. Take 4-6 times a day. Duration of treatment is from 5-7 days. Most often prescribed, if severe infection (sepsis, postpartum infection), if the pathogen is unknown or mixed infection, for the treatment of infections in newborns.
- Ampioks caps. 250mg №20
Combined drug, contains oxacillin and ampicillin sodium salts. Injected intramuscularly or intravenously
- Ampioks sodium powder for solution for injection
Amoxicillin
similar in activity and spectrum of ampicillin, absorbed from the intestine more fully. Resistant in the acidic environment of the stomach.
- Amoxicillin granules for oral suspension
- Amoxicillin caps. 500mg №10 "Lechiva", Czech Republic
- Amoxicillin caps. 500mg №16 "Hemofarm", Yugoslavia
- Amoxicillin t / g tab. 250mg №20
- Amoksil-KMP tab.250mg №20
- Amoksil-KMP tab.500mg №20
- Bactox caps. 500mg №12 "Innotech International", France
- Gramox-A caps. 500mg №12
- Ospamox granules for the preparation of suspensions for oral administration ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Ospamox caps. 250mg # 10 ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Ospamox Tab. 1g №10 ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Ospamox Tab. 500mg # 10 ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Ospamox Tab. 500mg №12 ("Biochemie", Austria)
- Flemoxin tab. 125mg # 20 ("Yamanouchi", the Netherlands)
- Flemoxin tab. 1g №20 ("Yamanouchi", the Netherlands)
- Flemoxin tab. 250mg # 20 ("Yamanouchi", the Netherlands)
- Flemoxin tab. 500mg # 20 ("Yamanouchi", the Netherlands)
Flemoxin contains amoxicillin tetrahydrate. These tablets can be taken as convenient, for example, chewed, swallowed whole, prepare a syrup suspension in a teaspoon or tablespoon, prepare a solution in a glass. You can dissolve in water, tea, milk, breast milk, juices. You can take at any time, regardless of the meal. The composition of the tablets includes hypoallergenic apricot-vanilla additive, gives a pleasant taste and smell. The drug is well absorbed from the intestines (about 7% of the drug is not adsorbed, it is an insignificant amount for amoxicillin), due to this it has less of a harmful effect on digestion, rarely there are disorders, diarrhea, dysbiosis, allergies. The duration of the drug up to 12 hours, which allows you to take it only 2-3 times a day. Most other penicillins prescribed to children, pregnant and elderly patients. Advantages: less frequent allergies, dysbacteriosis, high bioavailability (about 93%), less stress on the body. Children are dosed as follows: first, determine the daily dose - 25-50 mg doxycycline per 1 kg of body weight. This dose is divided into 3 equal parts, given 3 times a day, one part (every 8 hours).
- Hikontsil caps. 250mg №16 ("KRKA", Slovenia)
- Hikontsil caps. 500mg №16 ("KRKA", Slovenia)
- Hikontsil granules for the preparation of suspensions for oral administration 125mg / 5ml 60ml ("KRKA", Slovenia)
- E-Moks powder for suspension for oral administration 250mg / 5ml 60ml ("E.I.P.I.CO" Egypt)
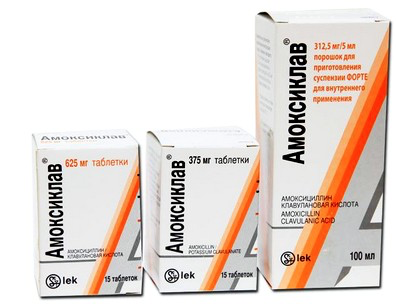
Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid
Clavulanic acid inhibits the enzyme that destroys amoxicillin, thus increasing the stability and activity of the antibiotic. Take 3 times a day. Children - in the form of a suspension.
- Amoxiclav granules for the preparation of suspensions for oral administration 156.25 mg / 5 ml ("Lek", Slovenia)
- Amoxiclav tab. 375mg №15 ("Lek", Slovenia)
- Amoxiclav tab. 625mg №15 ("Lek", Slovenia)
Benzylpenicillin sodium salt powder for injection diluted with water for injection, saline (isotonic NaCl solution) or novocaine solution. In most cases, the doctor tells you which solvent to use, if for some reason he did not do this and to consult additionally he has no way, what should he do?
For intramuscular injection (at home it is most likely not to be intravenous), you can use any of these solvents. It is necessary to ensure that the solvent is not warm, not warmer than room temperature - in warm water the salt is destroyed very quickly, if the summer and the ampoules with water for injection are warm, then put them in the refrigerator for several minutes until they cool to 18-20 degrees . C. Powder dissolves well in water.
Nevertheless, it is preferable to dissolve the powder in the saline solution, then with the injection there will be less discomfort, a slight content of NaCl (0.9%) does not significantly affect the solubility of the powder. But of greater interest are the solutions of benzylpenicillin salt in novocaine. Often with the introduction of penicillins at the injection site there is pain, burning. Novocaine has a local effect on the skin. BUT (!) When dissolving benzylpenicillin in a solution of novocaine, novocaine salt of benzylpenicillin may form, which may cause the solution to become cloudy. This is quite normal. The effectiveness of the drug does not deteriorate, you can continue the procedure.
Oxacillin sodium for intramuscular injection diluted with water for injection. If in a bottle of 250 mg - take 1.5 ml of water, if the active substance is 500 mg - dilute 3 ml of water for injection.
Ampicillin sodium and ampioks sodium for intramuscular injection is diluted with water for injection - 2 ml of water for 1 bottle.
Pregnancy planner
Antibiotics of the non-penicillin series are widely used for angina. In terms of effectiveness, they are often not inferior to penicillins, and in cases of bacterial resistance to the latter, they are the only way to really successfully and reliably cure the disease.
At the same time, all antibiotics of the non-penicillin series have some or other disadvantages, due to which they are used to treat sore throats only when penicillins are unavailable or inappropriate. For example, the need for nepenicillins arises when the same pathogen resistance, the patient has an allergy, the inaccessibility of penicillins. In most cases, if it makes sense to take any antibiotics of the penicillin series, then they are appointed. Nonenicillins are considered the means of the second line of choice.
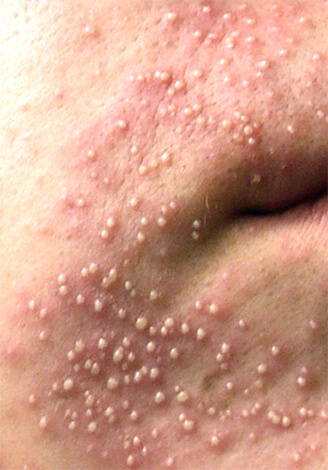
Skin rashes on the face of a person who is allergic to penicillin antibiotics
On a note
The term “non-poicillin antibiotics” is not entirely correct. There is no single "non-poicillin series" - there is, for example, a number of macrolides, a number of cephalosporins, a number of linkosamides, and others. The error arises from the fact that non-specialists - ordinary patients - believe that if there is a number of penicillins, then there must be a number of nepenicillins. This is not true. We will treat non-penicillin antibiotics as non-penicillin drugs.

The very first antibiotic, which gave the name to all the group. Today it is used relatively rarely.
What non-penicillin antibiotics can be prescribed for tonsillitis?
Cephalosporins (especially cefadroxil) and macrolides are most commonly used for sore throats instead of penicillins. And those and other antibiotics have certain specific features, because of which they did not become the main means of treatment of typical angina:

It is important to understand that it is penicillins that are the most common, numerous and available antibiotics for treating sore throats. Among them there is the greatest number of relatively inexpensive drugs, which are quite affordable for almost every patient. Antibiotics of the non-Picillin groups are usually in a higher price category (with the exception of inexpensive erythromycin).
Rules for taking non-poicillins for sore throat
There is no uniform method of taking antibiotics of non-poicillin series in angina - here a lot depends on the form in which the drug is used, on the condition and age of the patient, for some drugs - on the concentration of the active substance. But some universal recommendations exist:
In any case, only a doctor should choose a non-penicillin antibiotic. Such a choice is always forced, and is made only for serious reasons, because of which the most common penicillins cannot be applied. It is impossible to decide for yourself at home, which antibiotic can be drunk, and which one should not, how long the treatment should last and how to take the medicine itself. This decision should be based on a clear understanding of the causes of the disease and the process of drug interaction with the pathogen of angina. This is the prerogative of the doctor.
It is enough for the patients themselves (or their parents) to know that, if there are relevant reasons, the antibiotics of the non-penicillin series can be used to treat angina, and if the doctor prescribes such antibiotics, this is quite normal. It is only important to clarify with the doctor what his decision is based on to prescribe a non-penicillin antibiotic, and to hear a really reasoned answer.
No medicine in modern medicine causes so many questions and doubts, so many disputes and polar judgments, like antibiotics. Preparations antimicrobial action sometimes vital, and sometimes can hurt. Parents often ask in which cases it is possible to begin treating a child with antibiotics, and in which cases it is better to refrain from taking such powerful drugs? Where is the so-called "golden mean"?
What it is?
Antibiotics - vegetable substances, semi-synthetic or synthetic; their main ability is to destroy the pathogenic cells immediately or suppress their ability to reproduce.
The first antibiotic, penicillin, was accidentally obtained in 1928 by Alexander Fleming. But the resulting substance was destroyed so quickly that the scientist could not even convince colleagues of the need for his discovery. Later, in 1938, two Oxford scientists corrected his mistake - Howard Florey and Ernst Chain, who taught penicillin in its pure form and were able to establish its industrial production.
Penicillin saved millions of lives in hospitals of the Second World War. In 1945, Chein and Florey received the Nobel Prize for penicillin.

Kinds
Antimicrobial agents are narrowly targeted (capable of destroying a certain type of bacteria) and broad-spectrum (acting against a large number of known bacteria, atypical pathogens, and even some large viruses).

All existing antibiotics can be divided into groups according to differences in chemical composition. It is advisable for parents to learn more about the most popular groups of antimicrobial drugs that can be prescribed to children.
Penicillins
Antibiotics of natural origin or semi-synthesized. They have a relatively mild, sparing action against the body, but are deadly for the cocci of all calibers, including staphylococci, streptococci, almost all gram-positive bacteria, and parts of gram-negative bacteria. Penicillin preparations destroy the cell wall of bacteria, thereby making its further activity impossible.
Doctors usually begin treatment for a child with this group of antibiotics. They are less toxic, and are well suited to children from birth. The doctor may switch attention to other groups of drugs only if the penicillin antimicrobials have not had the desired effect.

Macrolides
These antibacterial substances are considered among the most low-toxic, and therefore they are widely used in pediatrics. The “founding father” of the drug group “Erythromycin” was obtained in 1952 and retains its position in terms of relevance to this day. Representatives of the group "Macrolides" are very effective against chlamydia, mycoplasma, staphylococcus. They are prescribed to children who are allergic to penicillins, and also in case the first group of drugs could not help the little patient.

Cephalosporins
Antibiotics that affect the bacteria that are in the breeding stage. They destroy the cell membrane and release the enzymes that kill the pathogens. Cephalosporins are very effective against many bacteria, it is a strong antibiotic. Children medications belonging to this group are prescribed in case of severe illness.They irritate the mucous membranes, and the risk of occurrence of associated with them dysbiosis, thrush, and stomatitis increases.

Tetracyclines
These are broad-spectrum antibiotics. Destructive for gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, but completely useless against mold fungi. Tetracyclines inhibit protein synthesis in the cells of the pathogen. Due to its peculiarity, accumulate in the skeleton of the skeleton, tetracycline antibiotics are not recommended for the treatment of children under 8-9 years. They can stain teeth enamel in brown color. And for children older than 8 years, tetracyclines are prescribed with great care.
Aminoglycosides
Antibiotics that are active against gram-negative aerobic bacteria. These drugs do not interfere with the multiplication of pathogens, as do many other antibacterial agents. They immediately kill the bacteria. Aminoglycosides are highly toxic drugs. They are prescribed for very severe conditions. In children, the use of aminoglycosides can cause serious damage to the central nervous system.Such antibiotics are rarely prescribed and under the close supervision of doctors, in a hospital, for example.
Quinolones
Antibacterial drugs of this group are prescribed to children extremely rarely, since quinolone has a long list. side effects. Some of the drugs in this group may cause deafness or blindness in a child. However, quinolones (in particular, fluoroquinolones) are still prescribed for children, but only for health reasons, and, as a rule, only in the conditions of a hospital.
Antifungal
Antifungal antibiotics, anti-tuberculosis drugs stand out. These drugs are few, and they are prescribed to children of any age by doctors, if required by the health of the baby and his confirmed diagnosis.
Are there any children's drugs?
The concept of "children's antibiotics" as such does not exist. Children on prescription give the same drugs as adults. However there is dosage formsmost adapted for children - they available in the form of suspensions or dry matter for self-preparation at home suspensions. Antimicrobial suspensions can be given to children from birth. They are comfortable, children are eager to drink them, as the manufacturers have taken care of the pleasant smell and taste of the medicine. This is usually a fruity flavor.
For children who are already able to swallow pills, it usually becomes possible between the ages of 5-6 years, they are allowed to use solid forms of drugs. Manufacturers recommend capsules to children from 12 years. Antibiotics that are injected into the body are suitable for children of all ages.
However, parents, talking about "children's antibiotics", often involve drugs that are shown to kids. In the instructions for use to each drug indicated age restrictions. Do not ignore them.
 Antibiotics are given to children strictly on doctor's prescription.
Antibiotics are given to children strictly on doctor's prescription.
In addition, antibacterial drugs with a large list of side effects and a list of contraindications are practically not suitable for children.
Many drops (in the ears, nasal, eye), solutions for inhalation, part of ointments and gels containing antibiotics, as well as in candles can be referred to the “children's” forms of medicines. Antibiotic sprays are very popular with moms and dads. They are easy to splash into the throat.
Local antibiotics have an important advantage - they penetrate into the zone of inflammation, without affecting the mucous membranes of the digestive system and intestines. The likelihood of developing dysbiosis is reduced.
They are very widespread in the treatment of certain infectious inflammations of the eyes in children (conjunctivitis, blepharitis, barley), and in skin diseases caused by microorganisms, for example, in streptoderma.

What diseases are prescribed for?
Antibiotics are not prescribed for children. viral diseases, as antimicrobial substances cannot cope with viruses. However, they can cause serious harm to children's health if, in the event of a viral infection that “undermines” the child’s immunity, enters the body.
Antibiotics exacerbate the situation by destroying the beneficial microflora. Therefore, antibiotic therapy is not necessary for:
- Influenza (all strains).
- ARVI (with adenoviral and rotavirus infections inclusive).
- ARI caused by a virus.
- Other diseases that have become the causative agents of viruses (rubella, herpes, chickenpox, mononucleosis, etc.)
 With viral infections antibiotics are not prescribed
With viral infections antibiotics are not prescribed
Antibiotics are needed when bacteria, fungi, or atypical pathogens (chlamydia and mycoplasma) have become the cause of the baby’s illness. In addition, antimicrobial agents may be needed for a secondary infection. If a child has bacterial inflammation due to flu or ova, complication.
The doctor will prescribe antibacterial drugs if he finds signs of a bacterial infection. Analyzes can reliably confirm it, but bacteriological laboratories are not in every clinic, and the time for conducting such studies is long - from 10 to 14 days. Usually, the doctor and parents do not have so much waiting time, and the child is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics.
I have to say right away that a thinking and competent doctor will hasten to prescribe antibiotics to the baby not at every bacterial infection. If the doctor is sure that the immunity of the crumbs is able to cope with the infection on their own, he will prescribe only symptomatic treatment. After all, antibiotics are not sweet vitamins, and the balance of benefits and harms from taking them is in delicate balance, and sometimes outweighs one side or the other.
 Antibiotics are not prescribed if the child’s immunity fights the infection on its own, according to the doctor’s
Antibiotics are not prescribed if the child’s immunity fights the infection on its own, according to the doctor’s
Most often, antibiotics for children are prescribed:
- With high temperature, above 39 degrees, and in children under 1 year old - above 38 degrees. A prerequisite - the heat does not subside for about three days.
- With bronchitis (bacterial forms).
- When sinusitis (especially with purulent, as well as with sinusitis heavy current diseases).
- With adenoids (antibiotics will be needed for bacterial adenoids).
- With otitis (especially often with internal otitis and abundant purulent discharge).
- With tonsillitis.
- With whooping cough.
- With pneumonia (if proven its bacterial nature).
- With meningitis.
- In case of severe intestinal infection caused by rods and bacteria.
- With angina (in its bacterial form, with purulent quinsy. Antibiotics are mandatory for scarlet fever), as well as for other ENT diseases (pharyngitis, tracheitis, rhinopharyngitis, etc.)
- With urinary tract infections and kidney diseases (with bacterial cystitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.)
- With intestinal infections (not associated with viruses or food poisoning).
- In the postoperative period.

Antibiotics are not used for the prevention of diseases, complications, so there is no point in taking them simultaneously with antiviral drugs. The risk of complications from this will only be higher.
The most popular drugs prescribed for children
|
Antibiotic name |
Affiliation group |
Release form |
Age restrictions for children |
|
"Amoxicillin" |
Penicillins |
Granules for suspension |
Since birth |
|
"Amoxiclav" |
Penicillins |
Pills Dry matter for suspension Powder for preparation of injection solution |
From 0 over |
|
"Flemoksin Solutab" |
Penicillins |
Dissolving pills |
From 0 and up |
|
"Flemoklav Solyutab" |
Penicillins |
Pills |
Since birth |
|
Augmentin |
Penicillins |
Pills Powders for suspension. |
Children from 3 months |
|
"Ecoclav" |
Penicillins |
Pills Suspension dry matter |
From 0 and up |
|
"Cefuroxime" |
Cephalosporins |
Pills Dry matter for solution for injection |
From 0 and up |
|
"Supraks" |
Cephalosporins |
Suspension granules |
Children from 6 months |
|
"Sumamed" |
Macrolides |
Pills Dry matter for injection Suspension Powder |
Children from 6 months |
|
Cephalosporins |
Children from 3 months |
||
|
Hemomitsin |
Macrolides |
Powder for suspension Pills Powder for injection |
Children from 6 months |
|
Azithromycin |
Macrolides |
Pills |
Children over 12 years old |
|
"Clarithromycin" |
Macrolides |
Pills |
Since birth |
|
"Macropen" |
Macrolides |
Pills Suspension granules |
Since birth |
|
"Unidox Solutab" |
Tetracyclines |
Dissolving pills |
Children over 8 years old |
|
Ceftriaxone |
Cephalosporins |
Dry matter for injection |
Children from 1 year |
|
“Fluimucil-IT” |
Combined drug |
Dry matter for injection Substance for preparation of solution for inhalation |
Children from 2 years |
Treatment rules
Taking antibiotics requires strict adherence to certain rules. Uncontrolled use of antimicrobial agents can cause serious harm to the health of the child.
- Antibiotics must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-prescription and treatment are unacceptable. Since January 2017, they have not been released in Russian pharmacies without prescriptions. This decision was not without reason: over the past few years, the widespread and uncontrolled intake of antibiotics has increased the number of microbial strains that are resistant to drugs. And the pharmaceutical industry does not have time to create new drugs against them.
- It is very important to comply with the prescribed dosage of the drug. Excess dose or reduction can cause an overdose, or vice versa - the lack of the desired therapeutic effect.
- All antibiotics should be taken multiple, i.e. while respecting the time interval between taking the next dose. This is due to the duration of action of a drug. To achieve the effect, the effect on bacteria must be continuous, therefore, as soon as the effect of the previous portion of the drug ends, the following should be taken.
- Effectiveness is assessed within 72 hours from the time of the first dose.If during this time there is no improvement in the child’s condition, you should inform the doctor. Perhaps the drug is not suitable for the child, then the doctor will prescribe a new drug.
 Antibiotics are strictly prescription.
Antibiotics are strictly prescription.
- If during the day after taking the first dose of antibiotic, the baby has an allergy- rash, itching, appeared allergic cough, runny nose, problems with stool have begun, should be discontinued, inform the doctor. He will change the drug.
- With the improvement of the child's well-being, it is impossible to cancel the antibiotics.Positive changes were made possible due to the fact that the drug was able to destroy most of the pathogenic bacteria. But living pathogens will continue to remain in the body. If you cancel the remedy, they will form addiction and resistance to antibacterial drug. The next time the doctor will have to prescribe a child more strong remedy with more side effects and more expensive for the price. The appointed course, and usually it is from 7 to 14 days, should be carried out to the end.
- The instructions for use of each drug indicate exactly how it should be taken. Some people drink before meals, others - on time, and others - a couple of hours after meals. This is due to the characteristics of the absorption of the substance. Do not be lazy and read the instructions to the end. It is important.
- It is impossible to combine febrifuge with antibiotics.Even at high temperatures. The fact is that fever is another indicator of the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy. If everything is done and chosen correctly, the temperature itself will begin to fall within a day after the start of reception. Antipyretic drugs can distort the treatment pattern.
- While taking antibiotics in the body, the balance of friendly bacteria is disturbed, which also die during antibiotic therapy. This can cause dysbiosis, thrush. At the same time with antimicrobial agents for the prevention of unpleasant consequences, it is desirable to take prebiotics and probiotics that will support the intestinal microflora. The most well-known drugs that conquer dysbacteriosis are Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Bifiform, and others. It is also necessary to take Linex and other similar drugs, following the dosage and recommendations of the doctor, rather than relying on experienced users from the Internet. .
- If there is thrush or stomatitis in the mouthrecommended local treatment with antiseptics with antifungal agents.
- If vomiting or diarrhea has opened after taking the drug, or vice versa, constipation has begun, the child complains of abdominal pain, he has increased gas formation, all this will require additional treatment. Be sure to report the consequences to the doctor. He will take tests to rule out other causes. unpleasant symptoms, and prescribe therapy, which will include vitamins, the use of which after antibiotics is very welcome, anti-diarrhea (or laxatives), drugs for the normalization of water-salt balance and medications that restore the microflora, such as "Atsipol".

The most common questions and complaints related to treatment:
- "A lump remains after the injection." This is due either to the improper administration of the antibiotic intramuscularly to the child, or to the antibiotic itself. There are drugs that you need to prick the child only once a week or even once a month. They have a long and powerful effect, but at the initial stage they really accumulate under the skin, this can explain the very effect of the “bump” after the injection. As a rule, you do not need to do anything with it, it will resolve itself. But if the problem is bothering, you can make an iodine mesh.
- "There are many antibiotics, which one is the best?" Most best drug for your child - the one that is right for him in a particular disease. Neither the price nor the reviews of other patients can not navigate. What helped one may not help another. What to drink and whether it is worth to use antibiotics at all, only your doctor knows.
- "There are no children's antibiotics in the syrup in pharmacies." Indeed not. Because in this form they are not issued. Parents often call syrups solutions that can be ingested. For example, they can be obtained if diluted dispersible tablets (“Flemoxin”) in a small amount of water. Do not confuse them with suspensions!
- "The child spits out the pills!" They are usually not tasty, so there is nothing surprising in this behavior. In order not to miss the next intake of the drug, not to persuade the capricious to drink the pill, it is better to immediately start giving him the prescribed antibiotic in suspension. The form is allowed for newborns and infants.

- "A child has a brown tongue after taking antibiotics." This effect happens after taking antibiotics, and after drugs for the treatment of liver and stomach. The strange color of the child's tongue will pass on its own, immediately after the course of treatment is completed.
- "Should I give antibiotics for flux?". Flux - a sure sign of the beginning of purulent inflammatory process in the mouth. Of course, antibiotics can stop it. But to eliminate the cause of this inflammation is unlikely. It is better to send the child to the dentist.
- "How to prepare a suspension?". Granules for the preparation of suspensions or powder for suspensions are most often sold in bottles with a special mark. It is up to it that it is necessary to add chilled boiled water, shake well, and give it to the destination. Shake suspension should be each time before taking, so that at the bottom of the bottle there was no sediment. Store the finished suspension should be in the refrigerator for no more than 15-25 days (for each drug its shelf life).
- "Are there alternative treatments without injections and tablets?"There is. For diseases of the upper respiratory tract, for example, you can get by inhalation with fluimutsilom. And with otitis on early stage help drops with antibiotics. However, the doctor often recommends such methods of treatment not as basic ones, but in the form of additional ones to the main course. The safest option is to consult a doctor.
- "Is it advisable to prescribe antibiotics for the child?" Not always. Evgeny Komarovsky, a pediatrician respected by mothers, often talks a lot about this. More than 90% of all illnesses in children, according to the doctor, are caused by viruses. And antibiotics use impractical. They can be harmful and dangerous for the baby. But if your doctor recommends starting antibiotic treatment, listen to it. After all, the remaining 10% of diseases can result in rather sad complications if you do not give the child such a drug in time.

The other extreme - the appointment of such drugs "just in case." Doctors, reinsuring, immediately attributed to antibiotics. This is done to legally protect themselves from possible legal claims on the part of parents. Unfortunately, this practice is ubiquitous, and it leads to the fact that the immunity of children weakens.
Caring and attentive parents do not have to memorize the complex and numerous names of medications, it’s enough to learn one thing - antibiotics should not be a first aid tool. They have many contraindications. Cheap means are not always bad, and expensive ones will not always serve your child in good stead. Experimenting with your own children is a crime against the future. Save for your crumbs the main value, such as health.

In the following video, a popular children's doctor Komarovsky tells in detail about antibiotics, what they are for and when they are used.
Look and transfer to "Live healthy", in which everything is described in detail.
Mushrooms are the realm of living organisms. Mushrooms are different: some of them fall into our diet, some cause skin diseases, some are so poisonous that they can lead to death. But Penicillium fungi save millions of human lives from pathogenic bacteria.
Penicillin-based antibiotics based on this mold (mold is also a mushroom) still find use in medicine.
Discovery of penicillin and its properties
In the 30s of the last century, Alexander Fleming conducted experiments with staphylococci. He studied bacterial infections. Having grown up a group of these pathogens in a nutrient medium, the scientist noticed that there are areas in the cup that have no live bacteria around. The investigation revealed that the usual green mold that likes to settle on stale bread is to blame for these spots. Mold was called Penicillium and, as it turned out, produced a substance that kills staphylococcus.
Fleming explored the matter further and soon isolated pure penicillin, which became the world's first antibiotic. The principle of action of the drug is as follows: when the cell of a bacterium divides, each half restores its cell membrane with the help of a special chemical element, peptidoglycan. Penicillin blocks the formation of this element, and the bacterial cell simply “resolves” in the environment.
But soon difficulties arose. Bacteria cells have learned to resist the drug - they began to produce an enzyme called “beta-lactamase,” which breaks down beta-lactams (the base of penicillin).
The next 10 years there was an invisible war between the pathogens that destroy penicillin, and the scientists who modify this penicillin. Thus, many modifications of penicillin were born, which now form the entire penicillin series of antibiotics.
Pharmacokinetics and principle of action
 The drug for any form of use spreads quickly through the body, penetrating almost all its parts. Exceptions: cerebrospinal fluid, prostate gland and visual system. In these places, the concentration is very low, under normal conditions it does not exceed 1 percent. When inflammation may rise to 5%.
The drug for any form of use spreads quickly through the body, penetrating almost all its parts. Exceptions: cerebrospinal fluid, prostate gland and visual system. In these places, the concentration is very low, under normal conditions it does not exceed 1 percent. When inflammation may rise to 5%.
Antibiotics do not touch the cells of the human body, as the latter do not contain peptidoglycan.
The drug is rapidly excreted from the body, after 1-3 hours, most of it comes out through the kidneys.
Watch a video on this topic.
Antibiotic classification
All drugs are divided into: natural (short and prolonged action) and semi-synthetic (antistaphylococcal, broad-spectrum drugs, antisexaginal).
Natural
 These drugs produced directly from mold. At the moment, most of them are outdated, as pathogens have been immune to them. In medicine, benzylpenicillin and bicillin are most often used, which are effective against gram-positive bacteria and cocci, some anaerobic and spirochaetes. All these antibiotics are used only in the form of injections into the muscles, since the acidic environment of the stomach quickly destroys them.
These drugs produced directly from mold. At the moment, most of them are outdated, as pathogens have been immune to them. In medicine, benzylpenicillin and bicillin are most often used, which are effective against gram-positive bacteria and cocci, some anaerobic and spirochaetes. All these antibiotics are used only in the form of injections into the muscles, since the acidic environment of the stomach quickly destroys them.
Benzylpenicillin in the form of sodium and potassium salts belongs to natural antibiotics. short acting. Its action stops after 3-4 hours, so you need to often do repeated injections.
Trying to eliminate this disadvantage, pharmacists have created natural antibiotics with prolonged action: Bicillin and Novocain benzylpenicillin. These drugs are called “depot forms”, since after they are introduced into the muscle, they form a “depot” in it, from which the drug is slowly absorbed into the body.
Examples of drugs: salt of benzylpenicillin (sodium, potassium or procaine), Bicillin-1, Bicillin-3, Bicillin-5.
Semisynthetic antibiotics of the penicillin group
 A few decades after receiving penicillin pharmacists were able to highlight its main active substance, and the modification process began. After improvement, most drugs acquired resistance to the acidic environment of the stomach, and semi-synthetic penicillins began to be produced in tablets.
A few decades after receiving penicillin pharmacists were able to highlight its main active substance, and the modification process began. After improvement, most drugs acquired resistance to the acidic environment of the stomach, and semi-synthetic penicillins began to be produced in tablets.
Isoxazolpenicillins are medicines that are effective against staphylococci. The latter have learned to produce an enzyme that destroys benzylpenicillin, and preparations from this group prevent the production of an enzyme. But for the improvement you have to pay - drugs of this type are worse absorbed into the body and have a smaller spectrum of action compared to natural penicillins. Examples of drugs: Oxacillin, Nafcillin.
Aminopenicillins are broad-spectrum drugs. Lose benzylpenicillin in strength in the fight against gram-positive bacteria, but capture a wide range of infections. Compared to other drugs, they stay longer in the body and better penetrate certain body barriers. Examples of drugs: Ampicillin, Amoxicillin. You can often find Ampioks - Ampicillin + Oxacillin.
Carboxypenicillins and ureidopenicillins - antibiotics, effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. At the moment, they are practically not used, as infections quickly become resistant to them. Occasionally you can meet them as part of a comprehensive treatment.
Examples of drugs: Ticarcillin, Piperacillin
Note!
For the treatment and prevention of spinal diseases and joints, many have begun to use the increasingly popular method of natural, rapid and non-surgical treatment, recommended by leading Russian specialists in diseases of the musculoskeletal system. According to the doctors ... "
Drug List
Pills

Sumamed
Active ingredient: azithromycin.
Indications: respiratory tract infections.
Contraindications: intolerance, severe renal failure, children under 6 months.
Price: 300-500 rubles.

Oxacillin
Active ingredient: oxacillin.
Indications: infections sensitive to the drug.
Contraindications: hypersensitivity.
Price: 30-60 rubles.
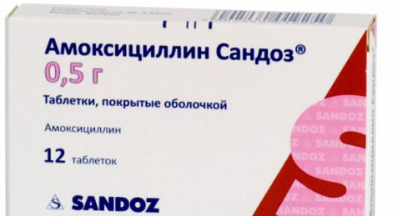
Amoxicillin Sandoz
Active ingredient: amoxicillin.
Indications: respiratory tract infections (including sore throat, bronchitis), infections of the urogenital system, skin infections, other infections.
Contraindications: intolerance, children up to 3 years.
Price: 150 rubles.

Ampicillin Trihydrate
Active ingredient: ampicillin.
Indications: pneumonia, bronchitis, sore throat, other infections.
Contraindications: hypersensitivity, liver failure.
Price: 24 rubles.

Phenoxymethylpenicillin
Active ingredient: phenoxymethylpenicillin.
Indications: streptococcal diseases, infections of mild and moderate severity.
Contraindications: intolerance.
Price: 7 rubles.
Popular
- What is oral cancer, its profilatika, symptoms and treatment
- How to treat herpes on the lips and body of folk remedies
- Details about fluoroquinolone antibiotics and drug names
- First aid for sprains and fractures
- White cheesy discharge from women - a sign of thrush
- Variants of white discharge before menstruation and all the reasons for their appearance
- Life expectancy for breast cancer
- Consequences of the introduction of poliomyelitis vaccine
- Penicillin antibiotics, penicillin use
- Why does brown daub appear instead of regul