Chronic otitis media middle ear treatment. Treatment of chronic otitis media. Chronic otitis media - the main symptoms
- Periodic or constant discharge of pus from the ear, sometimes mixed with blood. Discharge from the ear can be unpleasant.
- Persistent hearing loss.
- Ear congestion.
- Sensation of fluid transfusion in the ear.
- Periodic pain in the ear.
- Noise in the ear.
- Dizziness.
- Violation of the mobility of the muscles of the face (paresis facial nerve) - with a far advanced process.
- Headache - usually appears only with the development of complications (inflammation of the meninges, etc.).
Forms
- Chronic purulent otitis media
- caused by various bacteria, most often, several at a time. Conventionally, there are two types of chronic suppurative otitis media, although in fact it is often difficult to distinguish between them:
- mesotympanitis - only the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity is involved in inflammation, the bone remains intact. Perforation is usually marked (defect) eardrum various sizes in its central section;
- epitimpanit - bone is often involved in inflammation. In most cases, with epitimpanitis, cholesteatoma develops, a formation consisting of cells of the outer layer of the outer skin. auditory canalthat grow into the tympanic cavity through the perforations located in the upper part of the eardrum. Purulent inflammation accelerates the growth of cholesteatoma, which puts pressure on the surrounding tissues and destroys them.
- Chronic exudative otitis - accumulation of a viscous fluid in the tympanic cavity for more than 2 months, while the integrity of the eardrum is usually preserved. It develops as a result of prolonged dysfunction of the auditory tube (it connects the cavity of the middle ear with the nasopharynx).
- Chronic adhesive otitis - formation of scar tissue in the tympanic cavity, scarring of the eardrum. All middle ear structures ( auditory ossicles) soldered to each other and with the eardrum, which leads to a persistent hearing loss. Chronic adhesive otitis is usually the result of repeated acute otitis media or long-term untreated exudative otitis.
The reasons
Causes of chronic otitis media:
It can have complications such as: hearing loss, cholesteatoma formation. Treatment of chronic otitis media includes infection control with antibiotics, protection against water penetration, and surgery. This may be due to nasal obstruction, rhinitis, sinusitis, adenoid hypertrophy, incompetence of the auditory tube, or after acute otitis media. The treatment is initially clinical, but if this treatment fails, a kind of drain is introduced through the eardrum.
Chronic otitis media - the main symptoms
Symptoms of a child with otitis media. Fever Irritability Frequently transfers a hand to an ear. Difficulty sleeping or shaking. Secrecy flowing through an ear. Small response to low sounds. Long crying for no apparent reason. Vaccines against viruses and bacteria that cause respiratory infections. Avoid cigarette smoke situations. Avoid contact with other sick people. Breastfeeding Do not feed the bottle with the baby lying down. Treatment of rhinitis and nasal obstruction.
- untreated or undertreated acute otitis media;
- scars in the tympanic cavity due to recurring acute otitis media;
- dysfunction of the auditory tube (connects the cavity of the middle ear with the nasopharynx);
- some infectious diseases, such as scarlet fever (a disease usually caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A, is manifested by a punctate rash, fever, weakness, headache, inflammation of the tonsils).
- various chronic inflammatory diseases (for example, foci of infection in the paranasal sinuses - chronic sinusitis);
- violation of nasal breathing (curvature of the nasal septum, adenoids - pathologically enlarged pharyngeal tonsil);
- diabetes mellitus - a chronic disease, accompanied by an increase in blood glucose levels (sugar);
- immunodeficiencies - impaired immunity, leading to increased susceptibility of the body to infections. Can be congenital and acquired (for example, AIDS);
- long-term treatment with chemotherapy;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- malnutrition, life in adverse climatic or social conditions.
- hypothermia;
- water entering the ear;
- colds.
Diagnostics
- Analysis of complaints and anamnesis of the disease:
- whether the patient marks the discharge of pus from the ear, hearing loss, ear congestion, for how long these complaints are concerned;
- were there single or repeated acute otitis media ( acute inflammation middle ear), which was treated;
- are there chronic diseases, nasal breathing disorder.
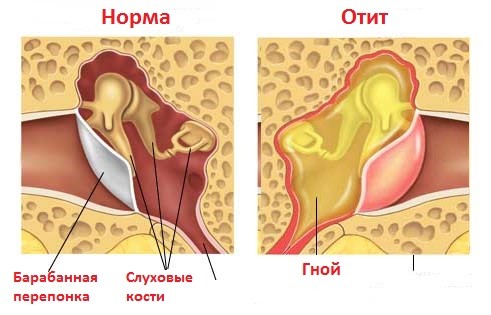
- Examination of the ear (otoscopy), including using a microscope or endoscope. If pus is present in the ear canal, it is necessary to carefully clean the ear to carefully examine the eardrum.
- In chronic purulent otitis media, out of an exacerbation, perforation (defect) of the eardrum is usually determined.
- Areas of retraction of the eardrum (so-called retraction pockets) may be noted.
- With the exacerbation of chronic purulent otitis media, there is a release of pus from perforation.
- Chronic exudative otitis the membrane is usually intact, the fluid appears through it.
- With chronic adhesive otitis on the membrane visible scars, it is deformed, retracted.
- Hearing test:
- tuning fork tests (special tests with tuning forks make it possible to find out if hearing loss is associated only with chronic inflammation in the middle ear or if the hearing nerve damage has joined);
- audiometry - the study of hearing with a special device. Allows you to more accurately determine the degree of hearing loss, as well as the involvement in the process of the auditory nerve.
- While maintaining the integrity of the tympanic membrane spend tympanometry. The method allows to estimate the mobility of the eardrum, the pressure in the tympanic cavity. In the presence of fluid or scarring in the middle ear, there is a decrease or complete absence of mobility of the eardrum, which is reflected in the shape of the tympanogram curve.
- In chronic purulent otitis media, a swab from the ear is taken to determine the causative bacteria and their sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Computed tomography (CT) of the temporal bones.
- Vestibular tests (assessment of dizziness, balance) - to detect lesions of the inner ear.
- If necessary, consult.
Treatment of chronic otitis media
Treatment depends on the form and stage of the disease.
Otitis externa occurs in the outer ear. There is inflammation and infection of the skin that covers the ear canal with bacteria or fungi. This can occur after prolonged exposure to water on beaches and pools, and injury through manipulation. Symptoms: pain in the ears, which worsens if you touch or tighten, and you feel the ears.
Treatment: antibiotics, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Care: protect your hearing while swimming, avoid new injuries. Hearing loss can be complete or partial. A hearing deficiency may be present from birth or may begin at any other stage of life. This may occur suddenly or gradually subside depending on the cause.
- In the presence of perforation (defect) of the eardrum, water is strictly contraindicated in the ear. When taking a shower or bathing, it is necessary to cover the ear with a cotton wool dipped in oil.
- With the exacerbation of chronic suppurative otitis media, conservative treatment is carried out. Most effective method is a regular earwash at an otolaryngologist and use ear drops with antibiotics. It is important to prevent the use of drops containing substances that are toxic to the ear, as well as alcohol, since this can lead to irreversible hearing loss due to toxic effects on the auditory nerve. Self-treatment in such a situation is extremely dangerous.
- Conservative treatment of chronic purulent otitis media should be considered as a preoperative preparation. The main method of treatment is surgery, the purpose of which is to restore the integrity of the eardrum to prevent infection in the middle ear and improve hearing.
- The operation is carried out more often under anesthesia, ear to ear (incision behind the ear, a more radical option) or through the external auditory canal (incision inside the ear, more gentle option). The choice of operation technique depends on the prevalence inflammatory process, the presence and size of cholesteatoma (a complication of chronic otitis media in the form of a tumor-like formation consisting of cells of the upper layer of the skin, growing into the cavity of the middle ear and the temporal bone), skills of the surgeon.
- The defect of the eardrum is covered with various materials. It is convenient to use for this the patient's own cartilage, which is usually taken from the tragus (the cartilaginous process, which closes the entrance to the external auditory canal), since there is no rejection of it. A very small piece of cartilage is taken, the trestle after that practically does not change shape.
- After surgery, the patient should be under the supervision of the attending physician, ear washing is carried out.
- In chronic exudative otitis, shunting of the tympanic cavity is shown: under local anesthesia, a small hole is made in the eardrum, into which a shunt is installed - a microscopic tube for several months. Through the shunt remove the contents from the cavity of the middle ear, injected medication. The hole in the membrane after removing the shunt usually overgrown independently.
- In case of chronic adhesive otitis media for hearing restoration, surgical treatment is also indicated - excision of scars from the middle ear cavity, replacement of the scar eardrum with a graft (artificial eardrum), for example, from the patient's own cartilage.
- For effective treatment chronic otitis media is extremely important to eliminate foci of chronic inflammation in the nose, nasopharynx, paranasal sinuses, restore nasal breathing.
Complications and consequences
- Mastoiditis (inflammation mastoid temporal bone) - is characterized by swelling, swelling of the ear region.
- Intracranial complications (meningitis - inflammation of the dura mater, encephalitis - inflammation of the brain substance, abscess of the brain - limited abscess in the brain) are characterized by severe general condition, severe headache, the appearance of brain symptoms (tension in the occipital muscles, vomiting, confusion, etc.).
- Sinus thrombosis (cavities in the dura mater in which venous blood is collected). At the same time there is a strong headache, exophthalmos (bulging eyes), convulsions, coma (lack of consciousness) and other severe disabilities nervous system.
- Neuritis of the facial nerve (inflammation of the facial nerve) - manifested by asymmetry of the face, impaired mobility of half of the face.
- Otogenic sepsis is a generalized infection that spreads to various organs and tissues through the bloodstream.
- Cholesteatoma - education, consisting of cells of the upper layer of the skin of the external auditory canal, which grow into the tympanic cavity through the perforation (defect) of the eardrum. Can destroy surrounding tissues, including bone.
- Irreversible hearing loss.
- Risk of death.
Prevention of otitis media chronic
- Timely and adequate treatment of acute otitis media.
- Treatment of chronic diseases of the nose, nasopharynx; nasal breathing correction.
- Correction of immunodeficiency and diabetes mellitus - chronic diseaseaccompanied by an increase in blood glucose levels (sugar).
- Timely treatment to the doctor at the first signs of ear disease. Self-treatment is unacceptable, self-use of ear drops (they may be ineffective or even dangerous), warming the ear without a doctor's prescription.
Additionally
The drum cavity of an adult has a volume of about 1 cm 3; there are auditory ossicles in it, which are responsible for the transmission of the sound signal — the malleus, the incus and the stirrup.
The tympanic cavity is connected with the nasopharynx of the auditory (Eustachian) tube, by means of which pressure is equalized externally and internally from the eardrum: during the swallowing movements, the auditory tube opens, the middle ear is connected with the external environment.
Normally, the tympanum is filled with air.
The aging process that achieves hearing is not considered a disease, and the natural loss of function due to the degeneration of the auditory organ expresses presbyokuzii. This loss is a result of environmental and genetic factors. Older people with hearing loss can be considered confused and even behave behaviorally, leading to social, intellectual and even depressive isolation.
A child may have difficulty learning and interacting with other children. Ear waxes Chronic ear infections Aging Degenerative diseases Otosclerosis Injuries Rubella Meningitis Intensive exposure to noise Ototoxic drugs Genetic diseases Tumors.
You have java script disabled in your browser, you need to enable it, or you will not be able to get all the information on the article " Chronic otitis and symptoms of manifestation. "
Chronic otitis media - the main symptoms are:
Chronic otitis is inflammatory disease middle ear, which is characterized by the formation of a hole in the eardrum with a constant or recurrent discharge of pus from the ear.
It is very important to look for an otolaryngologist for correct and rapid diagnosis in order to minimize the consequences. The solution must be individualized for each patient. In some diseases, there is treatment or surgical treatment, but other situations may be irreversible, and the use of hearing aids can overcome the disadvantage.
Treatment of chronic otitis media
The hearing begins at the 5th month of pregnancy, when the baby hears the sounds of the mother’s body and her voice. Through the rumor that the children still in the mother’s belly begin language development. Hearing loss, even if it is small, does not allow the child to properly receive the sound information necessary to acquire a language.
Etiology
Chronic otitis media develops on the basis of the acute form of the disease and with frequent episodes of inflammation of the tympanic cavity. The initial causes of the formation of such a disease are infection or mechanical damage.
The disease is formed in the human ear cavity for certain reasons:
- scars in the ear due to relapses of exacerbation;
- dysfunction of the auditory tube;
- infectious diseases, for example.
Also provoking factor can become frequent blowing of the nose at the same time two nostrils. The nasal and ear canals are interconnected, so if the nasal mucosa is affected or begins, then otitis is quite possible.
When hearing loss is diagnosed on early stage and treatment is carried out up to 6 months, in children emotional, cognitive, social and language development improves. Ear tests or otoacoustic emissions. It consists in placing a probe in the ear of a child, which emits low-intensity sounds and collects in the computer the sound responses that the cochlea produces in the child; these responses are otoacoustic emissions.
Performed with a sleeping child in natural sleep. It is painless, does not need bites or blood of the child. If otoacoustic surges are present, the exam is normal. If they are absent, hearing loss or the immaturity of the newborn's hearing system may occur to produce a response, so we must complete additional exams within 3 months.
The reasons for the transition from acute to chronic can be:
- inflammatory diseases of ENT organs;
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- immunodeficiency;
- prolonged use of chemotherapy;
- nicotine and alcohol;
- unbalanced diet;
- unsuitable climate
In children, chronic purulent otitis media develops from an infection that affects unstable immunity. Also, a provoking factor may be the structural features of the ear and nasal septum, poor diet and lack of vitamins in the body. Contribute to the progression of the disease can:
Risk factors for deafness. The child becomes yellow due to an increase in the amount of a substance called bilirubin, and he needs to swim in the light. When the child had to be intubated, because he could not breathe alone. Signs submitted by children with healthy hearing.
From 0 to 6 months: the child is afraid, screaming or waking up with loud, sudden sounds. He recognizes the voice of the mother and looks for the origin of the sounds. From 6 to 12 months: quickly find sounds and reacts to soft sounds. He talks about some sounds and finds out his name when his name is.
- hypothermia;
- pressure drops;
- cold;
- water entering the ear.
Classification
Clinicians found that chronic otitis media can be of 3 types:
- chronic suppurative otitis media (HCG) - triggered by bacteria. It is further divided into two subtypes - mesotympanitis, in which only the tympanic cavity is damaged, and the bone does not inflame, and epitimpanitis, which is characterized by bone lesions;
- exudative otitis media - for two months or more, a viscous fluid accumulates in the tympanic cavity. At the same time, the membrane is not damaged, but the functioning of the auditory tube may be severely disturbed in a person;
- chronic adhesive otitis - scars appear in the tympanic cavity, as well as on the membrane, all the auditory ossicles grow together, which causes a significant impairment of hearing. Such a form is progressing from frequent recurrences of the disease or with prolonged exudative form.
According to the orientation of the pain syndrome, the doctors share three main types:
Injury caused by pressure. The chance of a barotrauma depends: - Frequency of change of pressure difference - Individual adaptive ability. Symptoms - Mild discomfort or pain - Pressure or blocked ear - Discrete hearing loss - Tinnitus - Dizziness.
If prolonged or intense - Severe pain - Feeling of pressure, similar to immersion. - Reduction of moderate or heavy hearing. Risk factors - cold or flu - sinusitis - rhinitis - children are more vulnerable due to the anatomy of the auditory tube - divers - mountaineers - practicing water skiing.
- external - often formed from mechanical damage to the auricle and external auditory canal;
- medium - occurrence in the tympanic cavity, auditory tube and mastoid process;
- inner - undertreated otitis of the previous form provokes damage to the vestibular apparatus.
In the moments of exacerbation, the pathology goes through several stages of development:
Diagnostics - History - Otoscopy - Examinations. Complications - Perforation of the tympanine membrane - Ear infection - Hearing loss. Look for Otorrino if: - Symptoms do not disappear after 12-24 hours. - Saving pain. - If new symptoms appear, such as fever, strong pain or falling out of the ear.
Avoid alcohol and caffeine. Chewing gum or candy during the flight. Avoid sleep during the descent. In children: Encourage fluid intake during ascent and descent. Paracetamol 30 minutes before flight. Take medicine from allergic rhinitis. Tuba opens maneuvers during takeoff and landing. Topical decongestant. Avoid traveling if you have an upper infection respiratory tract. Imported earplugs - slowly equalize pressure.
- inflammatory, also called inflammation in the auditory tube;
- catarrhal, inflammation of the middle ear begins;
- deportative, manifested in the form of purulent clots in the middle ear;
- postperfect, purulent accumulations begin to flow out of the ear;
- reparative, inflamed areas are reduced, the affected areas are healed by scars.
Symptomatology

The balance of the body allows the body to stand still or move harmoniously and precisely. Our balance depends on the proper functioning and interaction of the maze, proprioceptive nervous system and vision. Imbalances, dizziness, dizziness and instability are popularly called labyrinthitis, but labyrinthitis is rare and serious. infection. The most appropriate term is labyrinth or maze diseases. There are several causes of labyrinth disorders.
Sometimes dizziness and vertigo can signal the first sign of some other important disease. Symptoms of labyrinth diseases: - Dizziness - Imbalance - Nausea - Weakness - Concentration of difficulty - Visual disturbance, especially after rapid head movements. - Tinnitus - Impact ear sensation.
Chronic otitis is manifested by a variety of symptoms, which differ depending on the acute stage and the location of the inflammatory focus. Doctors note the main morphological signs of otitis progression - non-healing damage in the eardrum, temporary purulent accumulations and discharge from the ear and hearing impairment.
Diseases of the ear and the labyrinth. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: short episodes of vertigo associated with a change in the position of the head. This occurs when calcium carbonate crystals pass through the labyrinth channels, stimulating the labyrinth sensors to simulate the sensation of movement and producing vertigo.
Meniere's disease: - Increased endolymph pressure can also cause tinnitus and blockage of the ear. Tumors. Systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, rheumatism, etc. The use of drugs that we call ototoxic, for example, some antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs that alter ear function.
Depending on the location of the focus of inflammation, the patient may experience different symptoms. The clinical picture of the progression of otitis externa is a strong pain syndrome in auriclewhich increases with pressure drops. Also feel discomfort when opening oral cavity and with the introduction of a special apparatus for examining the affected area. The outer shell swells and reddens noticeably.
Barotrauma: sudden changes in barometric pressure, as in diving and on airplanes. Habits: excess sweets, caffeine, smoking, alcohol or drugs. Problems of the cervical spine and jaw joint. Osteoarthritis, joint and muscle changes.
Stress and psychological problems. Pre-syncope, such as orthostatic hypotension and heart failure. Sensory disturbances. Infection maze. Diagnosis and treatment of labyrinth disorders. Diagnosing the cause of a labyrinth disease includes several tests, such as blood tests, audiometry, neurology, tomography, magnetic resonance, etc.
The clinical manifestations of chronic otitis media vary depending on the stage of development:
- Stage 1 - lays the ears, the temperature does not rise, noise and tinnitus;
- Stage 2 - increased congestion of the affected ear, the pain is intense, piercing in nature and an unpleasant noise appears, the body temperature may rise;
- Stage 3 - appear purulent education in the middle ear, the pain syndrome progresses and passes to the teeth, eyes and neck, the body temperature is very high, there is a hemorrhage in the eardrum, hearing can disappear;
- Stage 4 - pain and noise are reduced, however purulent inflammation increases, pus begins to flow from the ear;
- Stage 5 - the intensity of the symptoms decreases, there may be a decrease in hearing.
Development can be recognized by dizziness, nausea, vomiting, unbalanced walking, strong tinnitus and impaired hearing. Also, with the appearance of this form of the disease, symptoms of acute middle ear exacerbation will manifest.
The treatment can be divided into three stages: the treatment of symptoms, the treatment of the cause and the rehabilitation of the labyrinth. How to prevent and control maze disturbances. During a crisis: do not drive a car or drive it. When you feel dizzy, sit down or lie down immediately. Do not leave all lamps at night to avoid accidents.
Avoid cigarettes, alcohol and excess caffeine. It has been scientifically proven that well-designed exercises improve cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, reduce the risk of heart disease, prevent obesity, and strengthen muscles. You avoid problems with metabolism and, therefore, dizziness.
Diagnostics
During the diagnosis of chronic purulent otitis It is important for the doctor to clarify the complaints, to collect the history of the disease and the life of the patient. For this, the medic needs to know:
- were there purulent discharge the patient has an auricle;
- whether hearing has declined;
- how long the symptoms worsened;
- were there relapses of inflammation, and how was the disease;
- are there any chronic ailments and disturbances in nasal breathing?
Then the ear cavity is examined - otoscopy. If the patient has pus in the ear canal or sulfur plugsthen it must be removed so that the doctor can carefully examine and analyze the condition of the eardrum and the auditory canal.
Split your diet and watch for a long fast: try to feed yourself every three hours, avoiding large amounts of food. Abuse of fruits, vegetables and vegetables. Two liters of water is recommended per day. Greater kidney filtration eliminates toxins accumulated by the body.
Stress worsens any organic condition, including dizziness. Tinnitus or tinnitus is the perception of sound that is not generated in the environment. Many ailments can cause tinnitus, and more than one reason may be present in the same person. Therefore, it is crucial to find out the cause of tinnitus for each patient.

It is also important to determine the patient's hearing by conducting dial-tuning and audiometry.
With the whole eardrum, tympanometry is performed to the patient, thanks to which the mobility of the membrane can be determined. If there is fluid in the cavity or scarring has formed, then the mobility of the membrane can be reduced or completely absent. This can be seen in the crooked form of the tympanogram.
The diagnosis is not always simple, and sometimes you may need several tests, such as blood tests, hearing and neurological tests, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. There are several treatment options, and the selection must be personalized.
It is normal to think that the symptom worsens at night, because in a quiet environment there are no other noises masking tinnitus, and perception towards it increases. Factors related to tinnitus. Anxiety, Depression, and Stress - Some Medications. - Cardiovascular diseases - Metabolic changes in cholesterol, triglycerides, thyroid hormones, glucose and blood zinc - Spinal problems - Infections in the ears or sinuses and changes in the auditory tube. - Otosclerosis, - Meniere's disease - Tinted wax - Exposure to intense noise - Hearing loss - Problems with tendon tendons in the joints and improper teeth bite - Head and neck injury - Auditory nerve tumor - Neurological diseases.
To identify the bacteria that caused the development of pathology, the doctor makes a smear from the ear.
Tomography of the temporal bones and vestibular samples can also be performed.
If necessary, the patient may be referred to a neurologist for consultation.
Treatment
In moments of exacerbation of symptoms, a person is worried about issues related to how to treat chronic otitis media. To cure this form of pathology, the patient needs a significant period of time, and sometimes surgical care. Drug therapy quite often assigned along with the means traditional medicinehowever, unconventional drugs do not need to be taken independently without consulting a doctor. A patient can only aggravate his condition and provoke the development of complications.
Treatment of chronic otitis media is to follow these doctor's recommendations:
- reduce the ingress of bacteria in the ear - do not dive, do not visit beaches and pools, wash your hair with closed ears in the shower;
- use a drop with antibacterial effect.
If conservative therapy did not help the patient, he will be given more effective remedy for the treatment of inflammation of the ears - surgical care. As part of this therapy, the patient is undergoing surgery to restore the structure of the eardrum and prevent the infection from getting inside.
Surgery can be carried out in several ways:
- through the ear canal;
- by cut behind the ear.
Thanks to radical treatment, the doctor manages not only to significantly improve the condition of the patient, but also to remove polyps, tumor-like formations that could form from the inflammatory process.
Chronic toubimpimpanal purulent otitis media is also cured by surgery. Drug treatment It is used only as a preparation for the operation. With such therapy, the patient can be relieved of all possible foci of infection - inflammation in the nose, nasopharynx, and paranasal sinuses the nose.
After the operation, the patient begins a period of rehabilitation, which lasts 2 weeks and consists of undergoing a course of physiotherapy.
Complications
If the exacerbation of otitis was not eliminated in time, then a person can develop serious complications:
- and / or;
- venous sinuses;
- otogenic;
- cholesteatoma;
- complete hearing loss.
Prevention
In order not to provoke the development of chronic suppurative otitis media, doctors recommend timely treatment of diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Also, the disease can be prevented by correct elimination and correction of the immunodeficiency state.
Doctors prohibit self-treatment with drops or heating, as serious complications can begin.
If you think your symptoms are characteristic of this disease, a doctor can help you.
Popular
- How do antibiotics affect and act on viruses and inflammation?
- Structure, functions and age characteristics of the human skeleton
- What is the prevention of tick-borne borreliosis after a bite?
- External and internal structure of crustaceans on the example of crayfish
- Third degree breast cancer: prognosis and treatment
- Remantadin tablets, instructions for use
- The structure, composition and connection of the bones of the human skeleton
- Remantadin tablets, instructions for use
- Influenza in children: how to treat, what can and cannot be done to parents, what medicines will help?
- Longevity breast cancer