The structure and anatomy of the throat. The composition and purpose of the middle part. Location and function
The throat begins at the base of the chin and ends at the level of the trachea and esophagus. It consists of two organs: the pharynx and larynx. The pharynx provides food intake in the digestive tube, and the larynx is the beginning of the respiratory system.
Throat anatomy
The throat begins at the junction of the oral cavity in the pharynx. Between them there is a hole, which is called a pharynx. It is what doctors observe when asking patients to open their mouth, and then examine the throat.
The upper part of the throat is made up of the soft palate and uvula, on the sides are the palatine arches, and below is the root of the tongue. Palatine arches form two grooves with a triangular shape. It is there (glands), consisting of lymphoid tissue. These organs belong to the body’s immune system and prevent further penetration of pathogenic microbes, viruses, protozoa, fungi.
For the throat is a throat. Its initial division is at the level of the upper part of the neck. The pharynx passes into the esophagus. Its length in an adult is, on average, up to 15 cm, the width does not exceed 5 cm. It is located in the middle of the neck, in front spinal column, surrounded by muscle and loose connective tissue, vascular formations and nerve bundles. Before the pharynx is the larynx.
Pharynx
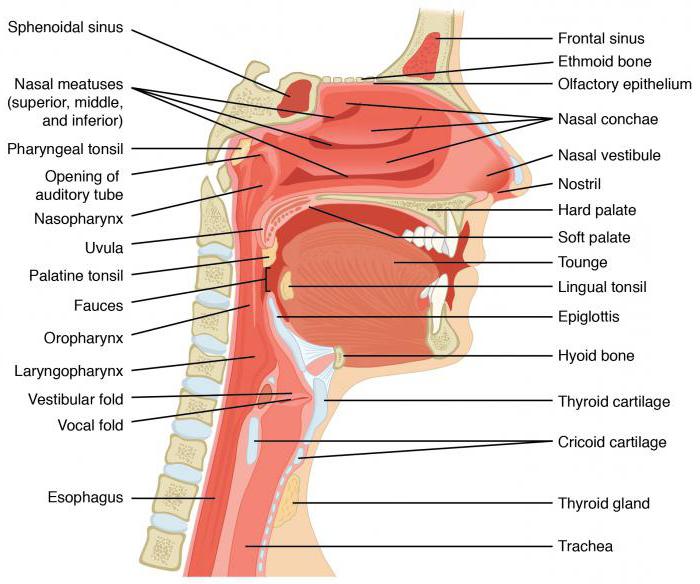
The pharynx is a cavity that has three divisions. It is formed by the top, back, two side and front walls, consisting of four layers of fabric. Features of the structure of the throat and pharyngeal walls, the functioning of the soft palate can not only swallow, but also prevent food from entering the respiratory system and nasal passages.
Allocate:
- nose section (nasopharynx);
- oral (oropharynx);
- guttural (hypopharynx).
The nasal part is involved in the promotion of air from the nasal passages, in moisturizing, neutralizing it, determines the ability of a person to distinguish odors. The oral part of the pharynx provides the natural movement of food through the digestive tract. Throat - breathing and the formation of sounds.
Below the nasopharynx, at the level of the root of the tongue, in the direction of the back begins the oropharynx. It ends with the entrance to the larynx.
The internal surface of the pharynx, facing the oral cavity, is covered with flat epithelial cells arranged in several layers. The mucosa also contains a large number of glands that secrete mucus. Under the mucous is the muscle tissue that forms the throat constrictor. Thanks to these muscles, food moves towards the esophagus, that is, the beginning of the digestive tract.
Near the walls of the pharynx (on the sides) are arteries and veins that provide blood supply to the head and neck, as well as large nerve trunks of the sympathetic section. nervous systemresponsible for the regulation of all functions internal organs and human body systems.
Larynx
The larynx refers to the upper respiratory tract. Begins at the level of the bone located directly under the tongue. Ends transition to the trachea. The structure of the organ is formed by cartilage tissue, ligament apparatus, muscle fibers, blood and lymphatic vessels, and nerves.
The composition of the larynx
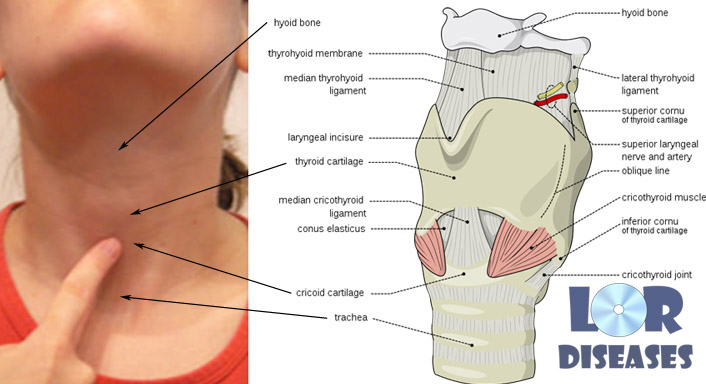
The structural basis of the larynx is cartilage. The thyroid, cricoid and scapular cartilages of the larynx together form the laryngeal cavity in which the vocal folds are located and where the main process of voice formation occurs.
Cricoid cartilage
Is the main. Its shape is somewhat reminiscent of the ring. This explains the name. The narrow part of the cricoid cartilage is turned anteriorly, wide, resembling the signet of the ring - posterior.
Thyroid cartilage
Above, above the cricoid cartilage, is the thyroid cartilage. It consists of two cartilaginous plates that form a tenderloin at the junction. The front of the thyroid cartilage is directly adjacent to the skin, so it can be felt on the front surface of the neck. In men, it comes forward, sometimes significantly. It is called "Adam's apple".
Cortical cartilages
Located on the upper surface of the cricoid cartilage.
From the base of the cartilage depart two processes:
- voice;
- muscular.
Epiglottic cartilage
The epiglottis covers the entrance to the larynx. This cartilage is attached in the region of the edge of the upper cutting of the thyroid cartilage with the help of ligaments.

Features voice device
All laryngeal cartilages are interconnected by means of a multitude of ligaments consisting of connective tissue. True lumps protrude into the lumen of the larynx vocal cords. In the thickness of these ligaments is located vocal (thyroid) muscle. The vocal cords are stretched between the inner surface of the thyroid and the voice process of the scarp-like cartilage.
During active inhalation, the vocal cords form a triangular shaped glottis, sufficient for the normal passage of air. The vocal cords move, converge and form lumens of various shapes and sizes. Thus, the formation of sounds.
Above the true vocal cords are false. They are the folds of the mucous membrane. Together they form along the lateral surfaces two slit-like spaces, which are called the morogean ventricles. They contain a large number of mucous glands, thanks to which the vocal cords are moistened, facilitating the formation of sounds.
Functions
The throat is involved in ensuring the work of the two most important systems of the body, whose activities are related to the external environment: respiratory and digestive. In addition, together with other anatomical structures (tongue, sky), the throat forms a person's ability to make sounds.
The pharynx is a unique organ of the human body, where the respiratory and digestive tracts intersect. It promotes the movement of the food bolus from the oral cavity into the esophagus and at the same time conducts air from the nasal passages or the mouth to the larynx, that is, to the external respiratory organ.
The main functions of the larynx:
- protective;
- respiratory;
- voice forming.
Thanks to the larynx, a person can hold his breath and prevent fluid from entering the respiratory tract. The structure of the throat and larynx allows you to arbitrarily and involuntarily block the flow of moving air, which provides protection for lung tissue.
A glottis is formed in the larynx, which provides sound. Also the presence of a large number nerve endings provides reflexes aimed at the removal of foreign bodies, saliva into the organ. Thanks to coughing and vomiting movements, the airways are cleared of obstacles to normal air flow.
When hit foreign body in the region of the glottis, the muscle fibers contract, the lumen of the larynx sharply decreases. This, on the one hand, does not allow closing the airway at a lower level. This complication can be a dangerous development. purulent inflammation and tissue damage. On the other hand, there may be a sharp choking attack, which requires emergency roomaimed at the release of the lumen of the larynx or air access.
The anatomical structures that form the human throat provide a number of essential life-supporting functions. Interaction with the environment requires not only a contract and the normal movement of air and food along the appropriate paths, but also full protection from adverse factors. Voice device provides communication with other people.
Ensuring oral and throat hygiene, maintaining the tonsils, pharynx and larynx in a healthy state helps to prevent a significant number of diseases not only of the upper respiratory tract, but also of the respiratory and digestive systems.
Useful video about the structure of the throat
The structure of the human throat, the scheme of which is given below, indicates the region that begins with two cavities: the nasal and oral cavities, and the trachea and the esophagus, respectively. The lower part of the pharynx enters the esophagus and is connected to the larynx. The structure of the mouth and throat is easy to see in the mirror. Today we look at the full structure of the throat and understand how it looks.
The structure of the human throat resembles an hourglass located at the front of the pharynx at the level of 4, 5 and 6 cervical vertebrae (below the hyoid bone). The newborn's throat is wider and shorter. Then through the gate enters the larynx and trachea. Trachea (respiratory throat) - continuation of the larynx. Externally, the farinx is covered with a layer of glands that produce mucus (moisturizes the mouth and throat). Voice timbre depends on the structure and anatomy of the larynx. Also in the throat is located a large number of small, but very important vessels and nerves, which provide human activity.
What is the throat
The pharynx is a smooth transition of the human oral cavity and visually looks like a hole in its back wall. And sore throat may be overdried due to the fact that inflammatory process closes the pores of the glands, and sputum is not produced. The nasopharynx has a special passage and connects the throat with the nose, carrying air through the nose to the larynx.
We have already reviewed the first part of the throat, it remains to understand the structure of the larynx, and it has a somewhat more complex structure. Respiratory function is fundamental and ensures the movement of air from the environment into the lungs for breathing.
It is curious that the timbre of the voice and its sound depends only on how lucky you are with the anatomical structure of the larynx. A continuation of the pharynx and larynx is the trachea. The lower part, narrower, is connected to the larynx. These parts have their location and perform certain functions. The lower part of the throat performs the function of swallowing. The movements of the throat must be very clear and synchronous in order to simultaneously ensure the penetration of air into the lungs and the food into the esophagus.
How does the human throat and larynx?
In the cavity of the larynx there is a vestibule, interventricular division and sub-vocal region. The interventricular region is the narrowest part of the larynx. The narrowest part of the larynx is the glottis. It is formed by webbed tissue and interchondral tissue.
It should be noted that the height and sonority of the voice depends on the anatomical structure of the larynx. The throat is a part of our body that has a rather complex structure that corresponds to the functions performed. Through the throat pass vessels, esophagus, nerves. It provides the process of breathing and swallowing, as well as speaking.

Imagining the structure of the human throat, we first of all mean the pharynx, which is scientifically called the pharynx. The nasopharynx is the cavity that connects the inside of the nose and the upper part of the pharynx. Further, the nasopharynx, falling down, goes into the middle throat.

The larynx is surrounded by nine cartilages that are interconnected, and these joints are mobile. So, the structure of the human throat helps him to ensure the performance of all its functions.
These include, for example, the throat - an area in which there are elements of two systems - the respiratory and digestive. Therefore, one part of the throat that is related to the digestive system is called pharynx, that is, the pharynx, and the other, which is an element of the respiratory system, is called the larynx (larynx).
The larynx is an unpaired organ of the respiratory system. The larynx consists of hyaline cartilage, movably interconnected by joints. Cartilage is divided into paired and unpaired. 1 Perstnevidny cartilage - consists of a plate and arcs in front and sides. It resembles a ring shape.
2 Thyroid cartilage - consists of 2 plates that are interconnected. The angle of connection in children, women and men is different. The main part consists of hyaline cartilage, and the processes to which the vocal cords are attached are made of elastic. It is located at the root of the tongue, blocking the entrance to the larynx when swallowing. The middle cavity is between the false vocal cords and the real ones.
Anatomical features of the throat
A similar structure of the vocal apparatus have gibbons (the stomach is smaller). They easily produce sounds similar to human speech. The larynx is a tube that consists of cartilage, muscles, ligaments, fascia. The length of the vocal cords in women and children is shorter than in men. Such a structure has a direct impact on the timbre of the voice. It is located higher by 3 vertebrae, where the formation of the larynx in puberty ends.
The main functions of the larynx
At the same time the lungs and bronchi are protected from the inflammatory process. The pharynx is located behind the oral cavity. For this, specialists use various instrumental and laboratory techniques. The treatment is carried out taking into account the diagnosis and symptoms of the disease.
The throat is the most important element of two systems at once: one part of it is responsible for the food that is crushed into the stomach, and the other provides air for the lungs. Also around the throat are concentrated all the muscles of the neck, which support the head in an upright position and allow it to move. That part of the pharynx that narrower smoothly enters the larynx. A healthy throat functions normally, but during an inflammatory process, the tonsils also always become inflamed.
The larynx is located behind the pharynx and somewhat lower, approximately at the level of the 5th vertebra of the cervical spine. The vocal cords of a person that expands. And those that stress the vocal cords. The larynx also begins with its entrance, which, in turn, begins with the epiglottis.
The structure of the human throat, as well as the functions of its departments will be discussed in this article. We recommend to watch a detailed video about the structure of the throat of a person! For the promotion of food in the digestive tract and air in the lungs meets the throat.
Excessive mucus formation in the body is the cause of many diseases and inflammatory processes. When we eat boiled, processed food, mucus is formed. Over the years, it accumulates, and if the body does not cope with timely cleansing, mucus begins to fill all the cavities of our body. Primarily affected lungs, bronchi, stomach. When it is collected a lot, the mucus rises up and out through the nose.
Frequent colds and infectious diseases, chronic fatigue, drowsiness, apathy may indicate a general slagging of the body, an abundance of toxins and other harmful substances with which the body is not able to cope on its own.
ACQUISITION OF MUSIC IN AN ORGANISM
When the body tries to deduce such a secret, cough, fever, runny nose, bags under the eyes begin. When these symptoms occur, we immediately begin to respond to them according to the usual scenario:
runny nose - drops in the nose,
temperature - bring down aspirin,
and if we are also attacked by a cough, then we take antibiotics.
That is, with our own hands, we prevent a healthy body from getting rid of mucus. As a result, we switch to the detoxification process of drugs, while the secretion layer becomes even thicker.
Up to a certain point, the mucus remains clear, but if too much of it forms, it becomes more dense and may have a yellow, brown and even greenish tint.
It envelops the intestinal walls and becomes a “mediator” between the food we eat and the blood vessels.
In this state, our body becomes a haven for all sorts of microorganisms that feed on cooked food. If we change our diet and begin to give preference to raw food, all these “scavengers” immediately die and the detoxification of the body begins. Arises headache, vomiting, nausea and diarrhea, which are the result of cleansing.
Diseases from excess mucus
Doctors, hygienists, naturopaths, nutritionists agree that most diseases come from the accumulation of toxins in the body. The so-called colds - bronchitis (including asthmatic), acute respiratory infections, catarrh, colds, cough, laryngitis, pleurisy, emphysema, and also hay fever, allergies are associated with attempts of the body to get rid of toxins and mucus in the respiratory tract. American doctor naturopath Norman Walker describes all of the above in this way:
Adenoids - inflammation or increase in the almond glands as a result of the delay and accumulation in the body of various slags.
Sore throat - inflammation of the throat, caused by the presence in the body of a large number of decay products and food waste.
Asthma - the accumulation of mucus in the bronchi leads to difficulty breathing. For effective treatment it is necessary to refuse food and drinks that form mucus (pasteurized milk and dairy products, white bread, almost all concentrated and carbohydrate-rich food.) It is useless to hide from allergens, take anti-allergy medications and be tested. The disease is caused solely by the accumulation of mucus, from which you need to get rid of proper catering.
Bronchitis develops due to the accumulation of mucus in the body.
Inflammation of the lungs occurs due to excessive accumulation of mucus and other wastes.
Influenza is caused by excessive accumulation in the body of food waste and metabolic products, which are a favorable nutrient medium for reproduction of pathogenic bacteria acting on the respiratory organs.
Qatar - heavy discharge mucus from the mucous membrane. Similar phenomena develop due to the fact that the body refuses to absorb dairy products and concentrated starches.
Cough is most often associated with body attempts to get rid of mucus in the respiratory tract.
Laryngitis - inflammation of the respiratory throat caused by the presence of toxins in the body.
A cold is the same as Qatar, only in a weaker form. Best treatment - detoxification. However, it is better to prevent colds by cleansing the body of mucus and other slags, after which you should switch to food consisting of raw fruits, vegetables, as well as fresh juices, which do not contribute to the formation of mucus. Medicines, vaccinations and injections, as a rule, do not bring the desired results.
Rhinitis is an inflammation of the nasal membrane caused by a large amount of mucus in sinusoidal cavities. (Norman Walker Juice Treatment, St. Petersburg, 2007)
DEDICATE
The most effective method, which helps to bring this secret, is the use of fresh ginger. To do this, you need to clean a small piece of ginger root, cut it into thin ringlets, so that you get about a teaspoon, and pour boiling water over it. After the drink is infused and slightly cooled, you can add 1 teaspoon of honey and squeeze out some lemon juice. Drink a drink should be warm throughout the day, preferably half an hour before meals.
To remove the accumulation of this plaque in the stomach and intestines, you can perform a cleansing procedure. You will need a teaspoon of black pepper peas, it is necessary, without chewing, swallow and drink a glass of clean water. For a better body cleansing, this procedure should be performed in the evening, until 18 o'clock, and only between meals. The general course of procedures is seven days, with a frequency of execution in two days on the third.
No less effective means of clearing unnecessary mucus is lemon and horseradish. You need to squeeze the juice of five lemons and add 150 grams of pre-ground horseradish to it, and then mix well. The resulting mixture should be taken in a teaspoon on an empty stomach and before bedtime.
The main advantage of such a drug mixture is that it, without damaging the membrane, contributes to the complete dissolution of the secret and at the same time does not irritate the digestive tract or the gall bladder at all.
Among the medicinal plants that allow you to clear the body of mucus, are the following:
chamomile flowers;
pine and cedar buds;
leaves of eucalyptus, black currant and mint;
hop cones.
They make tinctures and teas.
You can try this collection: a tablespoon of lime blossom and two teaspoons of licorice root brew boiling water, leave for half an hour to infuse, strain and drink hot 150 ml before breakfast, lunch and dinner. The course of full treatment is 30 days.
For 70 years of life, 100 tons of food and 40 thousand liters of fluid pass through the intestines. The result: more than 15 kg of fecal stones, toxic waste, which poison the blood and cause irreparable harm to our body, accumulate in the intestines.
The fact that the intestine is contaminated, indicate:
frequent constipation
metabolic disease,
diabetes,
allergies
overweight or underweight
diseases of the filtering organs of the kidneys and liver,
diseases of hearing and sight
skin hair nails
systemic diseases ranging from arthritis and ending with cancer.
Using enemas cleans only a small area of the colon (40-50 cm). Washing the intestines with the help of equipment is quite expensive, time consuming and violates the intestinal microflora.
Indications for use:
inflammatory processes of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract,
gastrointestinal tract, gastritis, colitis,
peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer,
diseases of the urinary tract - pyelitis, cystitis,
overweight,
lipid metabolism disorder.
Effective for prophylactic daily use.
Bowel Cleansing:
1 week: 1 dessert spoon of coarse flax flour + 100 g of fermented milk product (kefir, sour cream, yogurt).
2 week: 2 dessert spoons of coarse flax flour + 100 g of fermented milk product (kefir, sour cream, yogurt). Take this mixture instead of breakfast.
During the cleaning period it is necessary to observe the water regime: drink water up to 2 liters per day.
There is another way - removes 15 kg of toxins from the intestines and blood vessels! Here is one of the most natural and effective means alternative medicine, which consists of only 4 simple ingredients.
buckwheat flour
Kefir is considered the elixir of youth and health, and buckwheat flour has excellent healing properties.
As for ginger, I can say that this is a true miracle of nature, especially when it comes to detoxification. It also regulates intestinal activity and promotes fat burning.
Buckwheat flour lowers blood pressure, reduces the symptoms of atherosclerosis and prevents constipation. In combination with kefir and ginger, it lowers blood sugar levels, cleanses the intestines and blood vessels, regulates metabolism and pancreatic function.
To prepare the mixture, you will need:
1 tbsp. l buckwheat flour;
1/4 tsp ginger powder (fresh ginger can also be used);
200 ml of kefir;
1 tsp. natural honey.
Preparation: mix the buckwheat flour, ginger, honey and kefir in a bowl, leave the mixture in the refrigerator overnight, the next morning, mix the mixture again and your medicine is ready for use.
The drug should be used instead of breakfast! It is advisable not to use other products within 3 hours after consumption. Continue to use the drug this way for 14 days. If you have high sugar, you can use the mixture without adding honey.
Because of what a throat accumulates in the throat and how to get rid of it
because of various factors external environment and diseases of internal systems and organs in the throat accumulates mucus. An increased amount of this viscous substance is produced when bronchial asthma. The mucus-producing goblet cells thus protect the human body and help remove allergens from it.
Most common cause accumulations of cell secretion products are diseases of the upper respiratory tract of bacterial, fungal, allergic, post-infectious origin.
Also, persistent mucus in the throat can occur due to abnormal development of the nasopharyngeal area ( anatomical features buildings).
Chronic persistent occurrence of a viscous substance may occur during different diseases nose and sinuses, as well as in case of curvature of its septum or the presence of polyps.
Pharynx - it is a canal with muscular walls connecting the mouth and nasal sinuses to the larynx and esophagus; the pharynx is also an organ digestive system. Larynx - a cartilaginous canal connecting the pharynx with the trachea; the air passes through the larynx into the lungs and out of them; this organ also performs the function of a voice resonator.
It is a funnel-shaped canal from 12 to 14 cm long and 35 mm wide at the top edge and 15 mm at the bottom. The pharynx is located behind the nasal sinuses and the oral cavity, it goes deep into the neck, and then passes into the larynx and esophagus. It is an integral part of both the respiratory system and the digestive system: through the throat passes the air we breathe, as well as food.
In the pharynx there are three segments: the upper pharynx, or the nasopharynx, connected by its front wall with the nasal sinuses, on the upper wall of which there is a formation of lymphatic tissue, called the tonsil pharynx; the middle pharynx, or oropharynx, which communicates with the upper part of the oral cavity and on the side walls has a formation of lymphatic tissue, called the palatine tonsils; and the lower part of the pharynx, or laryngopharyngeal space, which is connected in front with the larynx, and behind with the esophagus.

The implementation of the dual function that the pharynx performs is possible due to the epiglottis - the formation in the form of a tennis racket located on the upper wall of the larynx; Usually, the epiglottis remains open, allowing air to pass from the larynx to the nose and vice versa, however, during swallowing, the epiglottis closes and blocks the entrance to the larynx - this causes the food to go to the esophagus.
It is a truncated cone-shaped canal consisting of a variety of articular cartilage connected by various muscles, membranes and ligaments. The larynx is located between the pharynx and trachea, its size varies with age: in an adult, the larynx reaches 3.5-4.5 cm in length, 4 cm in the transverse and 2.5-3.5 cm in anterior-posterior section.
In the upper part of the larynx there is an epiglottis, a cartilage, the movements of which direct air into the trachea during breathing and restrict its entry during swallowing. In addition to supplying air to the lungs and its excretion, the larynx performs another equally important function: it forms the sounds of the human voice. On the inner surface of the larynx there are two folds on each side: fibrous - false vocal cords and fibrous-muscular - true vocal cords separated from each other by a V-shaped slit, called the glottis, which is responsible for the formation of sounds (for more details about larynx can be found in the following articles: laryngeal muscles, cartilage and laryngeal joints, laryngeal cavity, vocal folds of the larynx, and functions of the larynx).

From the ligamentous apparatus of the larynx, the following should be remembered: the larynx is attached to the hyoid bone on the thyroid membrane, and between the arc of the cricoid and the lower edge of the thyroid cartilage is stretched a strong elastic cricoid.
The small ligaments strengthen both joints of the larynx and fix the epiglottis to the hyoid bone and the angle of the thyroid cartilage. The most famous is the vocal cords, it is located between the thyroid cartilage and the vocal process of the scyphoid cartilage of the corresponding side. In parallel to her and just above, there is a not pronounced front door fold. Both are paired.
The vocal cords form the glottis. From its width and the degree of tension of the ligaments themselves depends on how the voice changes. Both that, and another is defined by reduction of this or that striated muscle. Therefore, having considered the cartilaginous, articular and ligamentous apparatus, it is logical to pay attention to the muscles of the larynx. To understand the principle behind the movement of the larynx.
The sounds that a person makes are caused by the vibration of the vocal cords as the air passes from the lungs back to oral cavity; from sounds man makes words. During inhalation, as in exhalation, when a person does not speak, his vocal cords are relaxed and leaning against the walls of the larynx so that the air passes without any resistance. Conversely, when a person is talking, during exhalation, thanks to the muscles that contract the laryngeal cartilage, the vocal cords tighten, move closer to the midline of the larynx, and vibrate before the air from the lungs comes out. So, according to the degree of tension and the form that the vocal cords take at a certain moment, sounds of different pitch are formed.
Throat diseases - this is the result acute infections respiratory tract (cold). In children, they develop 3 times more often than in adults. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the risks of complications increase, which is the higher, the younger the child. How to protect a vulnerable children's body? We share modern achievements of medicine.
Why is the throat at risk?
According to the latest data, pathogens catarrhal diseases are about 300 different microorganisms. Colds are most often caused by viruses, which is why they are called ARVI - acute respiratory viral infections. Barrier mechanism, a kind of first line of protection in the path of inhaled alien microorganisms, serve tonsils - small organs, representing clusters of lymphoid tissue and located in the region of the nasopharynx and oral cavity. Due to the complex porous structure of the tonsils, with a large number of depressions - lacunae, viruses and bacteria trapped in the mouth with inhaled air, are deposited on the lymphoid tissue, being trapped.In response to the introduction of alien microorganisms, the formation of lymphocytes- The main cells of the immune system. Lymphocytes promote the production of antibodies (protective immunoglobulins), and in addition, they are able to directly kill microorganisms. However, in the fall and winter, that is, during the season of epidemics of colds, when more viruses circulate in the air, it is not able to completely protect the tonsil from them. Then there is an inflammatory process in the throat, which is manifested by bright redness, pain and discomfort when swallowing. A clinical picture of acute tonsillitis develops, characterized by:
- sore throat, worse when swallowing;
- fever;
- disturbed general condition of the child due to severe intoxication.

What's next?
If a proper treatment starts on time then which is also known as angina- inflammation of the tonsils, passes without consequences. If the treatment is not sufficiently effective, then the infection from the tonsils may drop lower - down the throat, larynx, trachea, bronchi, or even the lungs.Often, in angina, the infection in the tonsils subsides, but does not go away completely, therefore acute tonsillitis becomes chronic. Each aggravation disrupts the immune system, which leads to the repetition of colds. And if the infectious process caused by streptococcus, it threatens the development of autoimmune, rheumatic diseases: kidney damage - glomerulonephritis, heart muscle disease - myocarditis, joint damage - arthritis. In this case, only antibiotics can help.
However, it is possible to protect a child from colds and increase the effectiveness of treatment; it is only necessary to take care of his throat in a timely manner.
How to help throat?
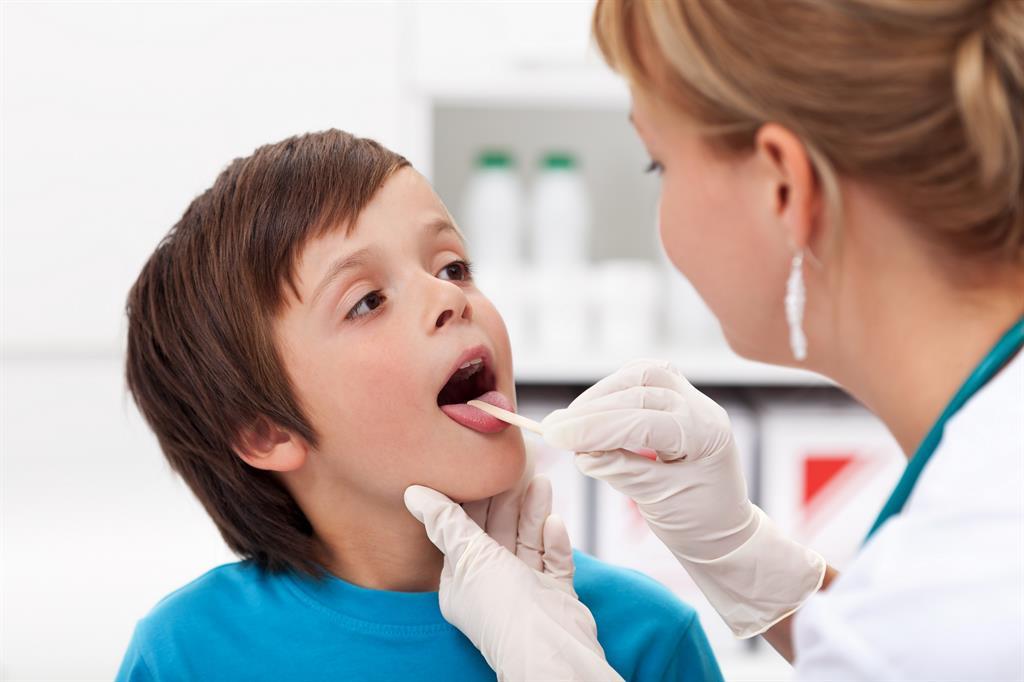
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia with a preventive purpose during ARVI epidemics and with medical treatment at the first signs of throat diseases recommends taking tonsilgon® drug N. This, which has not only local but also systemic effects on the body.
The composition of the drug Tonsilgon® N are included only vegetable ingredients: Althea root, chamomile flowers, oak bark, horsetail grass, yarrow and dandelion grass. Natural ingredients have an antiseptic, complex anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating effect, due to which, after 3 days of administration, manifestations of the disease are reduced and the intensity of pain in the throat is reduced.
Drug action Tonsilgon® N helps to prevent the transition to chronic inflammation and prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Important!
In the treatment acute inflammations throat should always be remembered that if or sore throat is caused by a particular type of bacteria: β - hemolytic streptococcus group A (GABHS-tonsillitis), then only antibiotics will be able to effectively help the child from this banal, seemingly infection, and save it from terrible complications, such as glomerulonephritis, myocarditis and arthritis. For any types of tonsillitis or tonsillitis, it is always necessary first of all to exclude infection with this type of bacteria, and only a doctor can prescribe a proper treatment and make an accurate diagnosis.
Available in droplets that can be taken by adults and children. from 1st yearas well as jelly beans that are approved for use in adults and children from 6 years.
Advantages of the preparation Tonsilgon® N:
- vegetable drug from Germany for the treatment and prevention of SARS and diseases of the oropharynx
- reduces the number of relapses chronic diseases oropharynx
- has an immunomodulatory effect
- proven efficacy of therapeutic and prophylactic action
- the drug is well tolerated
- increases the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy
- used for the treatment and prevention of SARS in adults and children from the age of 2 years.
Popular
- Breast cancer is curable at any stage.
- The remedy for the cold Sinupret
- Azitrox - official instructions for use
- Chicken-bjaka: allowed antibiotics were found in Russian chicken
- Oral Cancer: Symptoms and Treatment
- Dark and thick blood during menstruation.
- Modern analogues of doxycycline tablets
- Is it possible to die from pneumonia
- What earwax will tell all about your health
- Tussin: instructions for use